Lab 7 Flashcards
Mastering the concepts and anatomy of lab seven. (25 cards)
What do tendons connect?
Tendons connect muscles to bones.

What do ligaments connect?
Ligaments connect bone to bone.

Name the three layers of skeletal muscle and where they can be found.
1. Epimysium - directly underneath the fascia
2. Perimysium - surround each fascicle
3. Endomysium - surrounds individual muscle fibres

What are muscle fibres called?
Myofibers.

What are the thick filaments made of?
Myosin.

What are the thin filaments made of?
Actin.

What is a neuromuscular junction?
A neuromuscular junction is a connection between a motor neuron and a muscle cell.

What is a sarcolemma?
The plasma membrane for the muscle.

Name the A band, I band, and Z line.
A band - the thickest and darkest parts
I band - the lightest part composed uniquely of actin
Z line - a line composed of protein that bisects the I band

What is a sarcomere?
Found from Z line to Z line.

What is the axial skeleton made of?
- Skull
- Vertebral column
- Thoracic cage

The appendicular skeleton is made up of what?
Upper and lower limbs.

Name three types with examples of fibrous joints.
1. Sutures - cranial
2. Syndesmosis - interosseous membrane
3. Gomphosis - teeth

Name the two types of cartilaginous joints with examples.
1. Synchondrosis - epiphyseal plate and the costal cartilages
2. Symphysis - pubic symphysis

Name the six types of synovial joints with examples.
1. Pivot - atlas and axis
2. Ball and socket - hip joint
3. Hinge - elbow
4. Gliding - between the carpals
5. Saddle - thumb
6. Condyloid - between the metacarpals and proximal phalanges

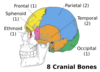
What are the eight cranial bones?
- Frontal
- Parietal (x2)
- Temporal (x2)
- Occipital
- Sphenoid
- Ethmoid
What are the four main features of the ethmoid bone?
- Crista galli
- Perpendicular plate
- Cribiform plate
- Olfactory foramina

What are the three main features of the sphenoid bone?
- Sella turcica is the depression in the middle of the sphenoid bone containing the pituitary gland
- Greater wings
- Lesser wings

Describe the features of the mandible.
- Body
- Rami
- Mental formen
- Coranoid process
- Condylar process
- Mandibular notch

Name the paired facial bones.
- Zygomatic
- Nasal bones
- Maxillae
- Inferior nasal conchae

Name the four main sutures and their locations.
- Coronal
- Sagittal
- Lambdoidal
- Squamous

What does the temporomandibular joint involve?
The mandibular fossa of the temporal bone articulates with the condylar process of the mandible.

What are the five muscles of facial expression and what do they do?
1. Frontalis
Origin: Frontal bone
Insertion: Skin of the eyebrows and the superior portion of the nose
2. Orbicularis oculi
Origin: Medial portion of the eye
Insertion: Medial portion of the eye
3. Orbicularis Oris
Origin: Midline of mandible and maxilla
Insertion: Tissue of the upper and lower lips
4. Zygomaticus
Origin: Zygomatic bone
Insertion: Corners of the mouth
5. Platysma
Origin: Deltoid and pectoralis major muscle
Insertion: Lower portion of the mandible

Name the two muscles of mastication, along with their origin and insertion.
1. Masseter
Origin: Zygomatic arch
Insertion: Lateral surface of the ramus
2. Temporalis
Origin: Medial wall of the temporal fossa
Insertion: Coronoid process and the border of the mandibular ramus




