Lab 5 Flashcards
Mastering the concepts and anatomy of lab five.
Name the four regions of spinal nerves and how many are found in each region.
1. Cervical - 8
2. Brachial - 12
3. Lumbar - 5
4. Sacral - 5
5. Coccygeal - 1

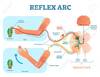
Describe the four steps of the reflex arc and the parts of the spinal cord it travels through.
- Receptor travels through the dorsal root
- Taking the dorsal ramus it travels through the dorsal root ganglia
- Passes through an interneuron and hops onto a ventral ramus
- Passes through the ventral root out to the corresponding motor neuron
What is the name of cranial nerve I, where does it come from, and where does it go?
Olfactory
Origin: Cribiform plate of the ethmoid bone
Innervation: Innervation of the olfactory sensation.

What is the name of cranial nerve II, where does it come from, and where does it go?
Optic
Origin: Optic chiasma
Innervation: Carries impulses from the retina to the brain

What is the name of cranial nerve III, where does it come from, and where does it go?
Oculomotor
Origin: Wrapped around the inside of the cerebral peduncles Innervation: Innervates the medial rectus, inferior oblique, inferior rectus, and superior rectus. Also, it innervates the superior palpebrae superioris

What is the name of cranial nerve IV, where does it come from, and where does it go?
Trochlea
Origin: Wrapped around the outside of the cerebral peduncles Innervation: Innervates the superior oblique muscle.

What is the name of cranial nerve V, where does it come from, and where does it go?
Trigeminal
Origin: On the lateral portions of the pons
Innervation: Innervates the muscles of mastication, tensor tympani, and sensation in the face. It is composed of three branches: ophthalmic nerve, maxillary nerve, and the mandibular nerve.

What is the name of cranial nerve VI where does it come from, and where does it go?
Abducens
Origin: Directly anterior to the inferior portion of the pons Innervation: Innervates the lateral rectus muscle.

What is the name of cranial nerve VII, where does it come from, and where does it go?
Facial
Origin: Lateral to the abducens nerve.
Innervation: Innervates the muscles of facial expression, and is responsible for gustatory sensation for the anterior 2/3 of the tongue.

What is the name of cranial nerve VIII, where does it come from, and where does it go?
Vestibulocochlear
Origin: Inferior to the facial nerve.
Innervation: Innervates the vestibules of the ear, as well as the cochlea.

What is the name of cranial nerve IX, where does it come from, and where does it go?
Glossopharyngeal
Origin: Inferior to the vestibulocochlear nerve.
Innervation: Sensory portion innervates the posterior 1/3 portion of the tongue and the motor portion controls the stylopharyngeus muscle.

What is the name of cranial nerve X, where does it come from, and where does it go?
Vagus
Origin: Directly inferior to the glossopharyngeal nerve. Innervates: Contributes to the sympathetic and parasympathetic portion of the autonomic nervous system.

What is the name of cranial nerve XI, where does it come from, and where does it go?
Spinal Accessory
Origin: Found along the outside (lateral) border of the medulla Innervation: Innervates the sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles.

What is the name of cranial nerve XII, where does it come from, and where does it go?
Hypoglossal
Origin: Anterior to the vagus nerve.
Innervation: Motor control of the extrinsic muscles of the tongue.

Name the seven main characteristics of the eye and where you can find them.
- Palpebrae (eyelids)
- Palpebral fissure
- Medial and lateral canthus
- Caruncle
- Orbicularis oculi
- Levator palpebrae superioris
- Lacrimal apparatus which consists of the lacrimal gland nasolacrimal duct

What are the six eye muscles, what do they do, and where can you find them?
1. Superior rectus - move the eye upwards
2. Inferior rectus - move the eye downwards
3. Medial rectus - move the eye to the middle
4. Lateral rectus - move the eye away from the middle
5. Superior oblique - push the eye downwards and medially
6. Inferior oblique - push the eye upwards and laterally

Name the three tunics of the eye and their corresponding names.
1. Fibrous tunic - sclera (whites of the eyes) and cornea
2. Vascular tunic - choroid, ciliary body, and iris
3. Nervous tunic - retina made of the pigmented layer and neural layer

What does relaxation/contraction of the ciliary muscles result in?
- Contraction of the ciliary muscle results in relaxation of the suspensory ligaments and therefore a more rounded lens
- Relaxation of the ciliary muscle results in taut suspensory ligaments and therefore a more flattened lens.

The anterior and posterior cavities of the eye contain what kind of humour?
- The anterior cavity contains aqueous humour and is divided into the anterior and posterior chamber by the lens
- The posterior cavity contains vitreous humour

What are the three kinds of neurons found in the retina?
- Rods and cones
- Bipolar cells
- Ganglion cells

What is the optic disc?
The optic disc is the point of entry of the optic nerve, lacking visual receptors and thus creating our blind spot.

Describe the three main features of the external ear and where you can find them.
- Auricle (pinna)
- External auditory canal
- Tympanic membrane

Describe the five main features of the middle ear and where you can find them.
- Tympanic cavity
- The three auditory ossicles (malleus, incus, and stapes)
- Tensor tympani
- Stapedius
- Eustachian tube

Describe the seven main features of the inner ear and where you can find them.
- Bony labyrinth (vestibule, semicircular canals, and cochlea)
- Membranous labyrinth (fluid-filled chambers and tubes)
- Cochlea
- Semicircular canals
- Vestibule
- Round window
- Oval window

Name the nine main characteristics of the cochlea and where they are.
- Organ of Corti
- Basilar membrane
- Vestibular membrane
- Scala media
- Scala tympani
- Scala vestibuli
- Hair cells
- Spiral ganglion
- Modiolus



