Lab #3.1 Flashcards
Striatum
- Putamen + Caudate Nucleus
- Contain MSNs that synthesize, release GABA (inhibitory)
- D1: project to GPi
- D2: project to GPe
Corpus striatum
Putamen + caudate nucleus (because they have the anterior internal capsule in between them)
Lentiform Nucleus
- Putamen + globus pallidus
- Encapsulated by:
- External capsule laterally
- Internal capsule medially
- Resides medial to the insular cortex
Caudate nucleus
- Runs in lateral wall of the lateral ventricle
- Part of the striatum (with the putamen)
- Input area of the BG
- Motor function
Basal Ganglia Components
- Caudate Nucleus
- Putamen
- Globus Pallidus
- Nucleus Accumbens
- Olfactory Tubercle
Thalamus is lateral to
IIIrd ventricle
Internal Capsule parts, functions
- Carries fibers to/from cerebral cortex
- Anterior limb: descending fronto-pontine fibers
- Major input to cerebellum
- Genu: descending corticobulbar fibers
- Brainstem motor nuclei muscles
- Posterior limb: descending corticospinal fibers
- Motor in SC
- And all other corticopontine fibers other than fronto
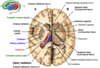
Corpus Callosum Parts
- Genu (anterior)
- Spleium (posterior)
External Capsule
- Contains cortico-cortical associatoin fibers (Axons connecting different parts of the cortex on the same side)
- Located lateral to the putamen, medial to the claustrum

Extreme Capsule
- Another cortico-cortical association bundle
- Lateral to the claustrum, medial to the insular cortex

Claustrum
- Gray matter sandwiched between medial external and lateral extreme capsule
- Neurons here play a role in multisensory integration
Optic Radiation
- White matter bundle running posteriorly away from the posterior limb of the internal capsule
- Connects the lateral geniculate nucleus of the thalamus to the primary viual cortex in the occipital lobe
Lenticulostriate arteries of M1 (MCA) supply…
- Putamen, globus pallidus (lentiform nucleus)
- Body of caudate nucleus
- Basically all of internal capsule high up (dorsal)
Recurrent artery of Heubner (ACA deep branch) supplies…
- Head of caudate nucleus
- Anterior limb of internal capsule
Anterior choroidal arteries supply…
- Genu and posterior limb of internal capsule
- Innermost part of globus pallidus
- Hippocampus
- Tail of caudate nucleus

Thalamus blood supply
PCA
Crus Cerebri
Cerebral peduncle edge
Septum pellucidum
Membrane separating the lateral ventricles
Ventral pallidum
- Extension of GPe
- Indirect = no-go pathway using STN
- Portion of globus pallidus that’s below the anterior commissure in coronal view

Ventral striatum
- Components:
- nucleus accumbens
- olfactory tubercle
- Function: reward system
- Portion of the striatum below the anterior commissure in the coronal view
Corona Radiata
Descending corticobulbospinal fibers from the cortex
Cortex > IC > crus cerebri > basis pontis > pyramids

Computed tomography
- Combines multiple x-rays from different angles
- Looks at bone, constrast-enhanced soft tissue, acute bleeding
- Good for imaing basic shape of brain, ventricles
- Bright = bone, blood
- Dark = edema, air, CSF
- Pros: easily available, fast
- Con: high radiation
Magnetic Resonance (MR)
- Hydrogen nuclei absorb, release engergy after being aligned with an external magnetic field
- Images are based on photon energy, based on water concentration (weights)
- T1: fat/myeling appears bright, tissue appears dark. Lesions often do not show up
- T2: water/tissue is bright, fat appears dark. Lesions & CSF appear bright.
- FLAIR: T2 image where CSF is rendered dark, lesions are therefore distinct.
- Hours for new lesion to show up
- Stroke stays visible forever

What kind of scan is this?

- MRI, T1
- CSF = dark
- White matter = light
- Gray matter - gray
What kind of scan is this?

- MRI T2
- CSF = bright
- White matter = dark gray
- Gray matter = light gray
What kind of scan is this?

- MRI FLAIR (T2)
- CSF = dark
- White matter = dark gray
- Gray matter = light gray
- Best for seeing lesions
- But can’t tell if they’re old or new
- For new, use DWI
- But can’t tell if they’re old or new
Diffusion Weighted Imaging
- Type of MRI
- Low resolution
- But acute strokes show up brighter than chronic
- Includes DTI which shows white matter tractography
Corpus Callosum Components
- Rostrum (anterior edge)
- Genu (anterior bend)
- Splenium (posterior edge)



