Lab #1 Flashcards
What view of the brain is this?

Lateral
What view of the brain is this?

Sagittal
What view of the brain is this?

Coronal
Telencephalon
Cerebrum
(cerebral cortex, cerebral hemispheres, hippocampus, amygdala, basal ganglia)

A) Lateral Ventricle
B) Fornix
C) Thalamus
D) 3rd ventricle
E) Massa intermedia
F) Pineal gland
G) Posterior Commissure
H) Hypothalamic sulcus
I) Hypothalamus
J) Anterior Commissure
K) Cerebral Aqueduct
L) 4th Ventricle
M) Foramen of Luschka
N) Choroid Plexus
O) Superior Colliculi
P) Inferior Colliculi
Q) Mamillary body
R) Interventricular foramen of Monro
Occipital Lobe Function, Location
- Function: Visual info processing
- Location:
- Posterior/caudal to imaginary line from parieto-occipital sulcus to pre-occipital notch
Calcarine Sulcus
- Divides the occpital lobe into two
Primary Visual Cortex (V1)
- Occipital lobe
- Superior and inferior to calcarine fissure
Association Visual Cortex (V2)
- NOT actually part of occipital lobe
- Two major pathways:
- WHERE pathway: parietal lobe
- WHAT pathway: temporal lobe
Parietal Lobe Functions
- Sensory integration
- Spatial orientation
- Language
- “Where” visual processing
Postcentral Gyrus
- Parietal Lobe
- AKA Primary Somatosensory cortex
- Uses somatotopic organization for sensory (skin) touch
Supramarginal Gyrus
- Parietal Lobe
- Basically the gyrus around the edge of the lateral fissure
- Language processing

Angular Gyrus
- Parietal Lobe
- Language processing

Temporal Lobe Functions
- Hearing
- Language
- Visual “What” processing
- Memory
- Recognition
- Reaction system
Temporal Lobe Key Features
- Transverse temporal gyrus (Heschl’s)
- Superior temporal gyrus
- Wernicke’s Area
- Limbic Lobe
- Parahippocampal gyrus
- Hippocampus
- Amygdala
Transverse Temporal Gyrus
- AKA Heschl’s Gyrus
- Located in roof of superior temporal gyrus (must be pulled away from the insula to see)
- Primary auditory cortex

Wernicke’s Area Location, Function
- Temporal Lobe
- In superior temporal gyrus
- ONLY ON SPEECH DOMINANT (LEFT) SIDE
- Anteriolateral to the supramarginal and angular gyri
- Function: deconde verbal info into sound (comprehension)
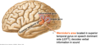
Medial Temporal Components
Some of Limbic Lobe
- Parahippocalmpal Gyrus
- Hippocampus (memory)
- Amygdala (emotional responses)

Frontal Lobe Functions, Key Features
- Intelligence, personality, motivation, executive control, motor command
- Anterior to central sulcus, superior to lateral fissure
- Contains:
- Precentral gyrus/primary motor cortex
- Inferior frontal gyrus (Broca’s area) on speech dominant side

Precentral Gyrus
- Frontal lobe
- Primary motor cortex
Broca’s Area
- Inferior frontal gyrus
- ONLY ON SPEECH DOMINANT SIDE
- Motor speech (speech production)
Limbic Lobe Function, Components
Function: emotions, basic drives, memory, smell
Includes frontal, parietal, and temporal lobes
Components:
- Cingulate gyrus
- Emotion formation
- Processing, learning, memory
- Uncus
- Smell
- Parahippocampal gyrus
- Memory coding and retrieval
- Hippocampus
- Memory formation and recall
- Amygdala
- Emotion, emotional association learning
- Insula
- Taste, visceral sensation, emotional pain
- Interoception

Cingulate Gyrus Location, Function
- Limbic Lobe component
- Superior to corpus callosum (frontal)
- Functions:
- Emotion formation and processing
- Learning
- Memory
Uncus Location, Function
- Limbic lobe component
- Located at medial, anterior edge of the temporal lobe
- Function: smell
Parahippocampal Gyrus Location, Function
- Limbic lobe component
- Surrounds, connects to hippocampus in MTL
- United with cingulate gyrus at the isthmus
- Function: memory encoding and retrieval
Hippocampal Formation Location, Function
- Limbic lobe component
- Most medial edge of telencephalon (MTL)
- Fornix is a major output
- 3-layered structure
- Function: memory formation, recall

Isthmus
Connects the cingulate gyrus with the parahippocampal gyrus in the temporal lobe
Fornix
- Major output of the hippocampus
- ARches over the thalamus

Amygdala Location, Function
- Limbic lobe component
- Comple of nuclei in antero-medial temporal. lobe, anterior to hippocampus
- Functions:
- Recognizing, reacting to challenges in environ
- Associative learning (non-emotional stim can acquire emotional salience)
- Emotion

Insula Location, Function
- Limbic lobe component
- Can only be seen by opening the opercula of lateral fissure
- Functions:
- Taste
- Visceral sensation
- Emotional aspects of pain
- Connects to amygdala for interoception (awareness of how our bodily states change in response to stim)
Basal Ganglia
- Subcortical gray matter in the telencephalon, deep to the insula
- Functions:
- Activates, coordinates internally generated movements (action selection! Not stimulus bound)
- Consolidates procedural memory

Diencephalon Components
- Thalamus
- Hypothalamus
- Epithalamus
- Subthalamus
Thalamus Location, Function
- Diencephalon
- In the walls of the 3rd ventricle
- Processes sensory, motor info to/from cerebral cortex
Hypothalamus Location, Function
- Diencephalon
- Separated from (superior) thalamus by the hypothalamic sulcus
- Functions:
- Integrates autonomic, endocrine, and limbic functions
- Maintenance of homeostasis

Epithalamus Location, Function
- Diencephalon
- AKA Pineal Body
- Unpaired (only one!)
- Produces melatonin, releases into circulation when prompted by hypothalamus
- Circadian rhythms

Brainstem Components
- Medulla
- Olives
- Pyramids
- Pons
- Midbrain
- Cerebral peduncles

Brainstem Functions
- CNs: sensory, motor nuclei
- Regulation of:
- Cardiac and respiratory function
- CNS
- Consciousness
- Sleep cycle
Craninal Nerve Origins
- Brain or Brainstem
- EXCEPT for CN XI
Cranial Nerves innervate head and neck except for…
CN X which also innervates below the neck
Somatic Efferent Neurons
- Motor
- Originate in brainstem
- Project to muscles in periphery

Somatic Afferent Neurons
- Sensory
- Originate in periphery
- Central process enters CNS
- Cell body lives in peripheral (like DRG)

Visceral Efferent
- Autonomic motor
- Preganglionic neuron originates in brainstem CNS
- Projects to postganglionic glangia in periphery

Visceral Afferent Neuron
- Sensory
- Originates in periphery
- Central process enters CNS
- Cell body lives in periphery

Cerebellum
- Motor control:
- Synergizing, correcting movements
- Maintaining upright posture
- Maintaining muscle tone
Endosteal layer of dura mater
- Lines surface of bone fossae
- Tough, fibrous tissue
- Receives sensory innervation from CN V branches
Meningeal Layers
- Dura (outermost)
- Outer endosteal layer
- Inner meningeal layers
- Arachnoid
- Pia
Dural Inner meningeal layers
- Split to close the dural venous sinuses
- Provide sheath for exiting CN
- Note: dural sinuses are NOT located between meningeal and endosteal layers but rather between meningeal layers.
Extradural/Epidural Space
Potential space between endosteal (outermost) dura and skull
Subdural Space
Potential space between the meningeal dura and arachnoid
Arachnoid
- Meningal layer between dura and pia
- Loosely connected to pia by arachnoid trabeculae
- Subarachnoid space: CSF-filled space between arachnoid and pia with arteries, veins
Subarachnoid Space
CSF-filled space between arachnoid and pia with arteries, veins
Falx Cerebri
Dural fold between two hemispheres (in longitudinal fissure)
Tentorium Cerebelli
- Dural fold between cerebrum and cerebellum
- Compartment above: supratentorial
- Compartment below: subtentoral
- Tentorial incisure: free end of tentorium that allows brainstem to pass through
Tentorial incisure
Free end of tentorium cerebelli that allows brainstem to pass through

Location of Dural Venous Sinuses
Between layers of meningeal dura
Spinal Cord Meningal Layers
- Dura
- NO true endosteal layer; just meningeal
- Instead, true epidural space filled with CSF
- Arachnoid
- Pia
Conus Medullaris
- End of spinal cord
- At level L1/L2 of vertberal disc
- Dural sac continues to scrum at level S2
Lumbar Cistern
- Enlargement of subarachnoid space
- Below L1/L2 and above S2
- Safe for lumbar punctures
Cingulate Sulcus Location

Collateral Sulcus Location
Lateral border of the parahippocampal gyrus

Meningeal Layers and Spaces (outer to inner)
- Skull
- Epidural/extradural space (potential)
- Endosteal layer
- Dura mater
- Subdural space (potential)
- Arachnoid mater
- Subarachnoid space (CSF filled)
- Pia mater

Middle meningeal artery
- Vessel that is a branch of the external carotid system
- Primarily supplies cranial bones
- Is located in the dura
- Damage:
- Extradural bleeding, forming an extradural hematoma (space-occupying)
- Present like a “lens” on CT/MRI
Extradural Hematoma
- Caused by damage to a middle mengineal artery
- Creates a “lens” shaped hematoma in epidural space
- Is a space-occupying lesion
Medial Temporal Lobe Components
- Parahippocampal gyrus
- Hippocampus
- Amygdala
Arachnoid Granulations, Lacunae
- Along lateral edge of superior saggital sinus
- Actively return CSF to the blood
Superior Anastomotic Vein of Trolard
Runs in/close to central sulcus
Subdural Hematoma
- Results from rupture of a bridging vein
- Blood spreads widely throughout subdural space
Subarachnid Hemorrhage
- Results from damage to a cerebral artery (stroke or aneurysm)
- Blood fills the subaracnoid spaces (cisterns)
Trabeculae
- Connections betweenarachoid and pia in the subarachnoid space
Communicating Hydrocephalus
- Extraventricular obstructions where CSF is able to evacuate the ventricular system and enter the subarachnoid space
Non-communicating Hydrocephalus
- Interventricular obstruction that prevents CSF from “communicating” with subarachnoid space
Diencephalon
Thalamus, hypothalamus, epithalamus
Mesencephalon
Midbrain
Metencephalon
Pons and cerebellum
Rhombencephalon
Medulla, pons, cerebellum
Parieto-occipital sulcus
Separates parietal from occipital lobe

Preoccipital notch
Separates the occipital lobe from the temporal lobe

Calcarine sulcus
Separates the occipital lobe into two



