Lab 1 & 2 (Q1) Flashcards
What is the Inverse Square Law?
X-ray intensity DECREASES w/ distance from the tube
How exactly is X-ray intensity related to distance from the tube?
- Decrease in intensity is proportional to the square of the distance from the source
- Is an expression of energy conservation
- Small differencess in FFD may alter the image substantially

Distance from the X-ray tube affects film _________.
Blackness
When focal-film distance (FFD) _________, film blackening decreases due to _________ intensity of the X-ray beam and vice versa.
- Increases
- Decreasing
(FFD and film blackening are INVERSELY related)
What happens to the image if you take rads at 32 inches (80 cm) instead of 40 inches (1 m)?
- Increase the beam intensity by 56% & overexpose the image.
_I1 _ = (d2)2
I2 (d1)2
Why type of radiation is X-ray?
(2)
- Electromagnetic radiation
- Ionizing radiation
ID the parts of an X-ray tube


Increasing the ___1___ increases the potential difference btwn the filament and the ___2___
and electrons are accelerated to higher __3__ and have more __4__ when striking the target.
- kVp
- target
- velocities
- energy
Which type of radiative interaction at the target/anode
creates the majority of the X-ray spectrum used?
Bremsstrahlung radiation
(braking radiation)
What 2 things effect scatter?
- Patient’s size
- Size of exposed area
How can you prevent scatter?
- Expose only as much as necessary (collimation)
- Utilize a grid
- Air gap technique
At what point should you always use a grid to prevent scatter?
for any structure > 10 cm
Why is it NOT practical to reduce scatter by lowering the kVp?
Low energy x-rays are readily absorbed by the pateint & radiation exposure is increased
How is image contrast affected by the energy of the X-ray beam?
due to the Photoelectric effect (PE)
Describe the Photoelectric Effect.
- form of interaction of an X-ray w/ matter
- low energy photon interacts w/ the e- in the atom & removes it from its shell → removed e- = photoelectron
- It is related to the atomic number of the attenuating medium (Z)
- PE =Z³
- Inversely proportional to the third power of the photon energy
When will the PE be greater, at lower beam energy or higher beam energy?
Lower beam energy
How can you control Image Contrast?
High mAs/Low kVp settings increase tissue contrast
Which tissues would you use Low mAs/High kVp setting?
Why?
- Tissues w/ inherent tissue contrast (i.e. thorax)
- To avoid too high a contrast and achieve a wide lattitude
What is Ultrasound?
Sound waves w/ a frequency higher than the upper range of human hearing .
(Human hearing = 20 kHz vs. Diagnostic U/S = 2 to 10 MHz)
What is the unit of measurement for U/S?
HERTZ!!!
- 1 Hz = 1 cycle per second
- 1 kHz = 1,000 cycles per second
- 1 MHz = 1,000,000 cycles per secong
What is the audible range of human hearing?
20 Hz to 20kHz
What is the range of Infrasound?
< 20 Hz
What is the range of U/S?
> 20 kHz
List & define the 4 properities of U/S waves!
- Frequency (f) ⇒ # of sound waves per second
- Wavelength (w) ⇒ distance that a sound wave travels during one cycle
- Speed ⇒ f x w
- Amplitude ⇒ intensity of the wave
What is the relationship btwn Wavelength, Resolution and Penetration?
- Short wavelength ⇒ High resolution, Low penetration
- Long wavelength ⇒ Low resolution, High penetration
What happens to the penetration if you try to improve resolution by increasing the frequency?
Decrease penetration
How should you select a transducer?
Always choose the highest frequency (resolution) that will penetrate
to the depth needed for the particular shot.
How should you set the Power (Intensity, Output) setting on the U/S?
Why?
- Should be set as low as possible
- Will allow the best resolution & prevent artifacts
What does the Gain setting on the U/S control?
Amplification of the returning echoes
What is echogenicity?
What are the 4 different terms used to describe echogenicity?
- the extent to which a structure gives rise to reflections of ultrasonic waves.
- Anechoic, Hyperechoic, Hypochoic, Medium Echogenicity
Which anatomical structures are Anechoic (produce no echo/are black) ?
- Veins
- Arteries
- Gallbladder
- Bone (with a hyperechoic rim)
- Lymph nodes
Which anatomic structures are Hyperechoic (creates a strong reflection back/appears bright)?
- Bladder stones
- Gas in the stomach
- Spleen
- Fascia
- Ligaments
- Tendons
- Pleura of the lungs
Which anatomical structures are Hypoechoic?
- Liver
- Cartilage
- Muscles
- Lymph nodes
Which anatomical structure has medium echogenicity?
Spleen
What is acoustic enhancement?
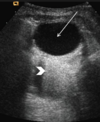
- Characteristic interaction of sound w/ fluid.
- An area of increased brightness underneath fluid resulting from the lack of impedance when sound waves pass through fluid and increased echoes from underlying structures.
What is acoustic shadowing?
- Characteristic interaction of sound w/ mineralized material
- Causes a signal void behind structures that strongly absorb or reflect ultrasonic waves
- Happens most frequently with solid structures, as sound conducts most rapidly in areas where molecules are closely packed, such as in bone or stones.

What is Reverberation?
- An artefact of the interaction of sound w/ gas
- Occurs when ultrasound bounces between two highly reflective surfaces. The waves will move backwards and forwards btwn these interfaces. The machine recognizes these waves as parallel lines with equal distances between them

What happens when sound waves interact w/ soft tissue?
Why?
What effects this?
- Become ATTENUATED
- Loss strength b/c some waves are transmitted & some are reflected back to the transducer
- Distance traveled, type of tissue & frequency of the sound waves
List the possible ultrasound artifacts that can be encountered.
- Acoustic shadowing
- Acoustic enhancement
- Edge shadowing
- Mirror image
- Reverberation (comet tail, ring-down)
What type of areas does acoustic shadowing cause?
How does it appear?
- Hypoechoic or Anechoic areas
- As a dark band deep to the gas containing, bone mineral or metal structures
How much of the incoming sound beam is reflected by gas?
99%
How much of the sound waves are reflected by bone?
20-30%
How can acoustic enhancement be useful to the U/S user?
May help differentiate cysts from solid hypoechoic nodular lesions
How does edge shadowing (A.K.A refraction) occur?
- Occurs deep to the edge of curved surfaces of round or oval structures which refract the beam
How do mirror image artifacts occur?
- occur on rounded, strongly reflective interfaces (ex. btwn lungs & diaphragm)
- Causes “duplication” structures

What causes a “Comet tail”?
How is it formed?
- A narrow band of reverberation
- Caused by small echos (metallic structures & gas bubbles separated by fluid)
What is a “Ring-down”?
What causes it?
- Type of reverberation
- Occurs when a sequence of repetitive hyperechoic lines are displayed on the screen
List Non-Ferrous metals.
- Alloys: brass
List Ferrous metals.
(Will be attracted by the magnet)
- Aluminum
- Copper
- Zinc
- Lead
- Nickel
- Tin
- Titanium
What is a Faraday cage?
- An enclosure formed by Copper mesh that blocks external static & non-static electric fields
- Provides constant voltage on all sides of the enclosure

What is the effect of external electric fields on the inside of a Faraday cage?
External electric fields are cancelled out on the inside of the cage
(electric charge inside = 0)
Which alignment, aligned w/ the magnetic field or opposite to the magnetic field, has more energy?
protons aligned OPPOSITE to the magnetic field have slightly more energy
Which protons create the net magnetization vector and generate the MR signal?
the small excess of protons aligned with the magnetic field

What happens to protons in T1 MRI mode?
protons regain order and return to their original vertical orientation
(pointing up)
What happens in T2 MRI mode?
protons lose their order and are oriented horizontally (→)
When does Resonance occur?
when the net magnetization vector rotates toward the X-Y plane
& protons spin in phase
What pulse applied at larmor frequency of H+ protons and perpendicular to the main magnetic field causes the magnetization vector to ROTATE out of alignment & towards the X-Y plane?
Radiofrequency (RF) pulse
Does the Radiofrequency pulse cause a gain or a loss of energy?
Why?
- A gain of energy
- b/c more H+s align against the main magnetic field
What does the flip angle depend on?
on the strength & duration of the applied RF pulse
What flip angle is refered to as a transverse plane?
90°
What is the component of the net magnetization vector
perpendicular to the main magnetic field call?
Transverse magnetization
What is the component of the net magnetization vector
parallel to the main magnetic field call?
Longitudinal magnetization
What 3 things occur simultaneoulsy once the RF pulse is turned off?
- Absorbed energy is re-transmitted at the resonance frequency
- Spins begin to return to orginal longitudinal orientation → T1 relaxation
- Protons that were in in-phase begin to de-phase → T2 relaxation
What are other names for T1 relaxation?
- Longitudinal relazation
- Spin-lattice relaxation
- T1 recovery
T1 referes to the time it take 63% of _________ magnetization to recover.
Longitudinal
Photons ________ their engery during T1 relaxation.
give up
Photons ______ their energy during T2 relaxation.
share
T2 is the time it takes 63% of _________ magnetization to be lost.
transverse
What determines the overall magnetization of the nuclei during T1 & T2 relaxation?
the sum of the vectors from all individual nuclei
How quickly is longitudinal magnetization (T1)
regained in fat? In H2O?
- Fat = quickly
- H2O = slowly
How quickly is transverse magnetization (T2) lost in fat? H2O?
- Fat = quickly
- H2O = slowly
What are T1 Weighted MRI’s good for?
What do they demonstrate?
- Visualizing anatomical detail & differentiation btwn different tissue types
- Demonstrates differences in the T1 relaxation times of different tissues
How does fat and fluid appear on a T1 Weighted MRI?
- Fat = bright
- Fluid = dark
How does fat & fluid appear in T2 weighted images?
- Fat = intermediate to bright
- Fluid = Bright
How do the different tissues appear in
Proton Density Images?
- Fat = very bright
- Grey matter = brighter than white matter
- CSF = intermediate signal strength (grey)
What are Proton Density MRIs useful for?
Evaluating tissues w/ low signal intensities
(bone & connective tissue)
Which type of relaxation is used to generate
FLAIR & STIR images?
Inversion Recovery
What does FLAIR stand for?
Fluid Attenuated Inversion Recovery
What does STIR stand for?
Short Tau Inversed Recovery
How will the different tissues appear on FLAIR?
- Fat = bright
- White matter = grey scale
- Grey matter = grey scale
- CSF (free fluid)= black
What is FLAIR best used for?
- FLAIR →nulls fluid→ spine
- To detect hyperintense lesions (i.e. brain edema) that are directly adjacent to fluid filled structures (i.e ventricles of the brain) & is especially useful when those changes are subtle
How will the different tissues appear on STIR?
- Fat = black
- CSF, Grey matter & White matter = grey
- CSF > GM > WM (brightness)
Why are STIR images useful?
- Nulls out the fat signal & allows fluid due to pathology to be visualized in regions w/ high fat content (ex. orbits of the eye)
- Can see bone bruises or bone edema
What is the effect of slice thickness on reconstructed CT images?
Thin slices = better image & better resolution


