L8 - MSK - Upper Extremity Arthrology Flashcards
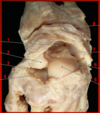
A. What joint is this?
Ligaments 1-3?

A. Sternoclavicular Joint
- Anterior Sternoclavicular L.
- Interclavicular L.
- Costoclavicular L.
What M. is this?

Subclavius M.
What Joint?
Ligaments 1-2?

Acromioclavicular Joint
- Acromioclavicular L.
- Superior Transverse Scapular L.
1-6?

- Acromioclavicular L.
- Trapezoid L.
- Conoid L.
- Coracoclavicular L.
- Acromioclavicular L.
- Articular Disc

- Trapezoid Line
- Conoid Tubercle
What joint injury is often referred to as a “Shoulder Separation”?
Does a ligament rupture?
If so, what ligament?
CN: The Acromioclavicular Joint is susceptible to injury and separation, often referred to as “Shoulder separation,” and is capable of separating with or without rupture of the Coracoclavicular L.

What Joint?
1-9?

Glenohumeral Joint
- Deltoid M.
- Subacromial Bursa
- Supraspinatus M.
- Articular Cartilage
- Glenoid Labrum
- Synovial Membrane
- Fibrous Capsule
- Articular Capsule (6&7)
- Long Head Biceps Brachii T.
What joint?
Label 1-7

Glenohumeral Joint
- Acromion
- Coracoacromial L.
- CoraCoid Process
- Coracoacromial Arch
- Coracohumeral L. (probably won’t see)
- Glenohumeral L.
- Transverse Humeral L.

What injury is the Glenohumeral Joint susceptible to?
Why?
What most commonly occurs due to the presence of the Coracoacromial Arch?
Dislocation
due to mobility and relative instability (shalow Glenoid Cavity)
Dislocation most commonly occurs anteriorly and inferiorly
CN: The Glenohumeral Joint is susceptible to dislocation due to its mobility and relative instability. Due to the presence of the Coracoacromial Arch dislocation of the Glenohumeral Joint most commonly occurs anteriorly or inferiorly.


Glenohumeral Joint
- Transverse Humeral L.
- Long Head Biceps Brachii T.
1-7

- Humerus
- Ulna
- Radius
- Radial Collateral L.
- Articular Capsule
- Ulnar Collateral L.
- Annular L.

Joint?
Aspect?
1-3?

Elbow Joint
Lateral Aspect
- Annular L.
- Articular Capsule
- Radial Collateral L.

Joint?
Aspect?
1-6?

Elbow Joint
Medial Aspect
- Articular Capsule
- Anterior Band
- Posterior Band
- Oblique Band
- Ulnar Collateral L.
- Annular

Which way does the elbow dislocate?
What type of force does this?
Involves a tear of what L.?
CN: The Elbow is capable of being dislocated posteriorly in response to force transmitted along the long axis of the Forearm, this usually involves a tear in the Ulnar Collateral L.

What is the point of Bursa?
3 types?
Bursa is extra synovial fluid to decrease friction
Sub = inside skin
intra = inside tendon
sub = deep tendon

What has the nicknames Students Elbow, Dart Throwers Elbow, and Miners Elbow?
Inflammation of Subcutaneous Olecranon Bursa
CN: Two of the more common Bursae to become inflamed are the Subcutaneous Olecranon Bursa and the Bicipitoradial Bursa. Subcutaneous Olecranon Bursitis, sometimes called “Student’s Elbow,” “Dart thrower’s Elbow” and “Miner’s Elbow” results from excessive friction between the Skin and the Olecranon.

What are these called?
What is purpose?
1-8

Bursa
Reduce Friction
- Subcutaneous Bursa of Medial Epicondyle
- Subcutaneous Bursa of Lateral Epicondyle
- Bursa of Anconeus
- Bursa at Origin of Extensor Carpi Radialis Brevis
- Subtendinous
- Intratendinous
- Subcutaneous
- Olecranon Bursae
Joint?
What end?
1-2?

Radioulnar Joint
Proximal
- Radial Notch of Ulna
- Radial Head
Joint?
End?
1-2?

Distal Radioulnar Joint
- Ulnar Notch of Radius
- Ulnar Head
Bones?
Joint?
1-4?

Radius and Ulna
Radioulnar Joint
- Annular L.
- Oblique Cord
- Interosseous Membrane
- Articular Capsule for Distal Radioulnar Joint

What has the nicknames “Nursemaid’s Elbow” or “Pulled Elbow”?
What happens?
CN: The Radial Head is capable of being dislocated out of the Annular L. to varying degrees, this injury typically occurs from pulling on the arm of a child, sometimes called “Nursemaid’s Elbow” or “Pulled Elbow.”

Joint?
1-7?

Radiocarpel Joint
- Articular Surface for Scaphoid (on Radius)
- Articular Surface for Lunate (on Radius)
- Articular Disc of Radiocarpal Joint
- Ulna
- Triquetrum
- Lunate
- Scaphoid

Joint?
Aspect?
Ligaments 1-4?

Radiocarpal Joint
Anterior Aspect
- Ulnar Collateral L. of the Wrist
- Radial Collateral L. of the Wrist
- Palmar Radiocarpal L.
- Palmar Ulnocarpal L.

Joint?
Aspect?
Ligaments 1-4?

Radiocarpal Joint
Posterior Aspect
- Ulnar Collateral L. of the Wrist
- Radial Collateral L. of the Wrist
- Dorsal Radiocarpal L.
- Dorsal Ulnocarpal L.

Joints?
Aspect?
Joints 1-6?

Intercarpal Joints
Anterior / Palm
- Pisiform Joint
- Lunotriquetral Joint
- Scapholunate Joint
- Capitohamate Joint
- Trapeziocapitate Joint
- Trapezoitrapezoid Joint

Joint?
Aspect?
Ligaments 1-2?
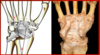
Intercarpal Joints
Anterior Aspect (palm)
- Pisohamate L.
- Anterior Intercarpal L.
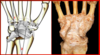
Joint(s)?
Aspect?
Ligament 1?
Intercarpal Joints
Posterior Aspect (back of hand)
- Posterior Intercarpal L.

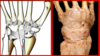
Joint?
1-8?

A. Midcarpal Joint
- Lunate
- Scaphoid
- Trapezium
- Trapezoid
- Capitate
- Hamate
- Triquetrum
- Radiocarpal Joint