L3 - Non-stationary Processes Flashcards
(25 cards)
What do we can an AR(1) process where θ = 1?
- random walk = unit root
- Variance should be constant and not vary over time but in this case, it does!!!
- it is the sum of all the variances of the error terms in the series (more errors through time will then increase the variance!)

Examples of how differencing can make a process stationary?
- Why does differencing make a series stationary?
- As it gives us white noise which is stationary by definition
- Example 1
- As we can see that one of the roots of L is 1, we know it is unit root and therefore I(1), so differencing it once will give us a stationary process, I(0)
- Example 2
- We now have two unit-roots from the factorised characteristic equation so we need to difference the process twice
In both cases, the coefficient on the differenced term is the other root of the characteristic equation

What is the definition we a relying on when converting a non-stationary process into a stationary one?

What are the four common cases of nonstationary processes?
- Determinist trend processes
- Simple random walk
- Random walk with drift
- Random walk with drift and deterministic trend
What does a determinist trend process look like and how can we make it stationary?
- Its the time variable that makes the expected value non-stationary?

What does a simple random walk process look like and how can we make it stationary?

What does a random walk with a drift process look like and how can we make it stationary?

What does a random walk with drift and deterministic trend process look like and how can we make it stationary?
- Random walk as the coefficient on the lag of x is 1
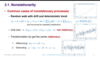
How can we determine the order of integration from any general autoregressive process?

How do we know if a transformed non-stationary process is now stationary?
- Look at its correlogram

How do we perform a Dickey-Fuller unit root test?
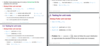
What statistical table do we use for the Dickey-Fuller unit root test?
- Reject the Null of unit root if the DF critical value is greater than the test statistic (the one you work out)

What is the Augumented Dickey-Fuller unit root test?

In finance, what variables tend to be stationary?
Most financial variables are I(1)
- Therefore most series are stationary are:
- first differenced
- growth rates
- a ratio of two variables
how do you perform an ADF test with a drift and deterministic trend?
- P-value is between 1 and 5% so it may be hard to decide whether we reject or accept depending on what level we use

What is one problem with the ADF test?
- One problem of this test is its lack of power, i.e. the inability to reject a false null hypothesis
- Can be even more of a problem when the number of observations or time period is small
- Caused by the fact that the alternative hypothesis includes a wide range of values (some very close to the null)
- Alternative tests: KPSS; Phillips-Perron; Modified ADF test
What is the KPSS test?
- Only unit root test where the null hypothesis is Stationary

What is the Phillips-Perron test?

What is the Modified ADF test?

How do we test a time series for more than one unit root?
- Second derivative –> accelerator in the underlying macroeconomic variable

How does forcasting change with nonstationary processes with a trending variable?
- forcasted value now rely’s on kα and variance also is multipled by k
- varaince increases the further in the future we wish to forecast

How does forcasting change with nonstationary processes when it is trend stationary?

example of a series correlogram exhibiting seasonality?
- Also can appear when the time series in graphed
- in some quarters sales may be consistently high whereas in others than may be consistently lower

What are the ways in which we can deal with seasonality?




