L23: Wrist & Hand Anatomy, Examination & Management Principles Flashcards
(59 cards)
What are the 5 arthrology features of Wrist & Hand?
- 1st CMC joint is mobile for opposition
- Mobile joints are more likely to wear out (arthritis) - 1st CMC joint
- 2nd & 3rd CMC joints are stable
- 4th & 5th CMC joints are mobile for grips
- Wrist used to be ball & socket joints. Evolution broke it up to 8 carpals for dexterity.
- Brachiation: Forearm pronation supination
What are the 4 nomenclature features of Wrist & Hand?
- Digit: Thumb (Th), index finger (IF), middle finger (MF), ring finger (RF), little finger (LF)
- Joints: CMC, MP, PIP, DIP
- Total active motion (TAM)
- Total passive motion (TPM)
What are the muscles of the wrist and hand?

What are the 3 tendons of the wrist and hand?
- Central slip
- Lateral slip joined with intrinsics
- Terminal slip

What are the 4 flexor tendon anatomy for the hand and wrist?
- FDS
- FDP
- Retinacular sheath
- Vincula brevis & longus

What are the 3 tendon excursion?
- FDP 32mm, FDS 24mm
- At DIP 1 mm excursion = 10° ROM
- At PIP 1.3 mm excursion = 10° ROM
What are the nerves of the wrist and hand?

What are 3 subjective examinations of the wrist and hand?
Majority of hand patients are traumatic/post-surgical. Some are overuse.
- Know the structures involved
- Know the healing timeframe
- Know how to assist healing
What are the 3 history of current injury in the subjective examination of the wrist and hand?
- Mechanism, force & duration of injury
- Time interval between injury and treatment
- Early treatment is easier to manage
- Late treatment has secondary issues
- Medical/surgical management
- Structures damaged, repaired and technique
- Good communication between surgeon and therapist
What are the 4 history of primary complaint in the subjective examination of the wrist and hand? What are the 3 outcome measures?
- Location, intensity & type of symptoms
- Behaviour of symptoms
- Hand dominance
- Occupation, social issues
- General health questions
Outcome measures: DASH, PRWE, VAS
What are 5 observations in the objective examination of the wrist and hand?
- UL & general posture screen
- Wounds, scars, lacerations
- Skin condition & colour: Red, shiny, dry
- Oedema
- Deformity, wasting
Reassure them if they are anxious to let you see the hand
What are 6 wound assessments in the objective examination of the wrist and hand?
- Location & size of wound
- Wound classification
- Types of wound
- Type of closure
- Inflammatory response
- Exudate
What are 4 wound classification in the objective examination of the wrist and hand?
- Black = Necrotic tissue
- Yellow = sloughy tissue
- Red = Granulation tissue
- Pink = Epithelial tissue
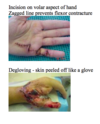
What are 2 types of wounds in the objective examination of the wrist and hand?
- Tidy: e.g. Clean surgical incision
- Untidy: e.g. Tissue loss +/- soft tissue coverage

What are 4 types of closure in the objective examination of the wrist and hand?
- Primary
- Delayed primary
- Secondary intention
- Closure: Sutures, staples, steri-strips etc.

What is the inflammatory response in the objective examination of the wrist and hand?
Normal or abnormal
What is the exudate in the objective examination of the wrist and hand?
Colour, amount, odour
What are 3 oedema assessments in the objective examination of the wrist and hand?
- No normal standards
- Location & type of oedema
- Pitting or hard brawny oedema
- Signs of infection
- Measurements
- Circumferential measure around MCP, PIP etc.
- Volumetric measure: Put hand in a jar of water, measure volume of water displaced (volume of hand) - uncommon
What are 5 palpation assessments in the objective examination of the wrist and hand?
- Skin temperature, sweating
- Hand hot, sweating, shiny - SNS overdrive
- Scar tethering
- Hypersensitivity: Presence & location
- Muscle spasm
- Tenderness over tendons, tendon sheaths, joints
What are 5 ROM assessments in the objective examination of the wrist and hand?
- Measure AROM then PROM
-
Hand goniometer dorsal placement
- 5° inter-tester error
- American Society for Hand Therapists uses E/F
- Plus (+) to indicate hyperE
- Minus (-) to indicate loss of full E
- e.g. +15/110 means 15° hyperE. -15/110 means 15° loss of E
- If hand is stiff and cannot make a fist, then measure tip to distal palmar crease.
-
Tenodesis effect: Wrist position affects finger tendons contraction
- Wrist F + finger E
- Wrist E + finger F

What are 3 tightness assessments in the objective examination of the wrist and hand?
- Intrinsic muscle tightness
- Extrinsic flexor tightness (FDP, FDS, FPL)
- Extrinsic extensor tightness (EDC, EI, EPL)
What are 2 intrinsic muscle tightness assessments in the objective examination of the wrist and hand?
- With MCP joint F, PIP and DIP can passively full F
- With MCP joint E, PIP and DIP cannot fully F
What are 3 extrinsic flexor tightness (FDP, FDS, FPL) assessments in the objective examination of the wrist and hand?
- With MCP joint F, PIP and DIP can passively E
- With MCP joint E, PIP and DIP cannot fully E
- With fingers E, then passive wrist E, the fingers will be pulled into F.
What are 3 extrinsic extensor tightness (EDC, EI, EPL) assessments in the objective examination of the wrist and hand?
- With MCP joint E, PIP and DIP can passively F
- With MCP joint F, PIP and DIP cannot fully F
- With fingers F, then passively wrist F flex the wrist, the fingers will be pulled into E.








