Introduction to Immunology Flashcards
(22 cards)
How is the immune system involved in homoeostasis?
Tissue repair
What is the immune system?
Complex cellular and protein network that has evolved to protect the host from pathogenic microbes
What does failure of the immune system lead to?
Immunodeficiency (Severe Combined ImmunoDeficiency SCID) leads to increased susceptibilty to infection- sometimes cancer
what is immunology ?
Immunology- is the study of how the physiological mechanisms that we use to defend our bodies against invasion by other organisms
Why is immunology important for human health?
Knowledge of how the immune system works allows its manipulation to improve human health e.g. vaccination to prevent infectious disease
What is the normal function of the immune system?
To identify and eliminate harmful microorganisms and harmful substances such as toxins. -by distinguishing ‘self’ from ‘non-self’ (sometimes ‘normal self’ from ‘abnormal self’ in cancer) and by identifying ‘danger’ signals
What are our most polymorphiv(Variable) genes?
Our most polymorphic (variable) genes are those that control the immune response: this variation has been selected for by exposure of populations to infectious diseases
There are two basic strategies the immune system uses to recognise non-self material.
What are these two stratergies?
- a limited number of germ-line encoded receptors ( Pattern Recognition Receptors and Toll Like Receptors) in each individual that recognises molecular patterns (PAMPS and DAMPS) not found in healthy self tissue
- a very large number of antigen specific receptors in each individual generated during lymphocyte development by recombination of gene segments. (TCR receptor - binds to processed antigen fragments presented at cell surfaces)
the first stratergy of pattern recognition is used by the immune system
the second stratergy is used by the adaptive immune system
Name a strategy used to identify non-self material that is used by adaptive immunity?
-Antigen specific receptors -Generated by random recombination of gene segments.
Because of the nature of this recombination process, these receptors have the potential to recognise self tissue, and so lymphocytes must be tightly regulated to avoid immune responses against self tissue (auto immunity)
What type of immunity is associated with Molecular patterns and Germ-line encoded receptors?
Innate immunity
What is the time scale for innate immunity?
The system works rapidly (withn minutes to hours) and has broad specificity
What type of immunity is assciated with antigen specific receptors generated by random recombination of gene segments?
adaptive(aquired) immunity
What is the time scale for adaptive immunity?
Days to weeks and has exquisite specificity
What type of receptors are used for recognition of molecular patterns (PAMPs and DAMPs)?
Pattern Recognition Receptors (PRRs)
Toll like receptor is a type of PRRs
PRRs are germline-encoded host sensors, which detect molecules typical for the pathogens[2]. They are proteins expressed, mainly, by cells of the innate immune system, such as dendritic cells, macrophages, monocytes, neutrophils and epithelial cells[3][4], to identify two classes of molecules: pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs), which are associated with microbial pathogens, and damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs), which are associated with components of host’s cells that are released during cell damage or death.
What are the two types of triggers that are associate with pattern recognition receptors?
PAMPs – Pathogen-Associated Molecular Patterns DAMPs – Damage-Associated Molecular Patterns
What is a primary immune response?
a response made by naive lymphocytes when they first encounter their specific antigen
What is a secondary immune response?
Is a response made by memory lymphocytes when thwy re-encounter their specific antigen
What cause diversity of clones in lymphocytes
Recombination of gene segments that produce antigen receptors
During B and T cell development, random genetic recombinations occur within each cell among multiple copies of immunoglobulin gene segments (B cells) or TCR gene segments (T cells).
These processes generate the diversity of clones of lymphocytes: each clone is specific to a different antigen
What is an immunogen?
antigens that can initiate an immune response.
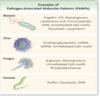
What are DAMPs?

What are PAMPs?
What are toll like receptors?
Toll-like receptors(TLRs) are a class of proteins that play a key role in the innate immune system. They are single, membrane-spanning, non-catalytic receptor susually expressed on sentinel cells such as macrophages and dendritic cells, that recognize structurally conserved molecules derived from microbes.


