Immune Cells and Organs Flashcards
Where are lymphocytes produced?
Bone Marrow
Generation of lymphocytes is also known as ….?
Lymphopoiesis
Name the primary lymphoid organs?
Thymus and bone marrow
Where do lymphoid stem cells differentiate into mature and functional lymphocytes?
Primary lymphoid organs
Name some secondary lymphoid organs?
-spleen -lymph nodes -mucosal associated lymphoid tissues (MALT)
In which part of the body can lymphocytes interact with antigen and with other lymphocytes
Secondary Lymphiod organs

Name the components that make up the structure of the human Thymic lobe?
Capsule Cortex Medulla Interlobular Septum Lobule Corpuscle
The thymus is bi lobed in mammals. True or false?
True
What happens to the thymus as you get older?
atrophies
What organ produces white blood cells in a fetus?
Liver/spleen
Where are the active sites for lymphopoiesis?
Spongey regions at the end of long bones vertebral bones Sternum ribs flat bones cranium pelvis
label the structure of the lymph node?

Add picture

In the lymph node, what cell is found in the cortex area?
B cell
In the In the lymph node, what cell is found in the paracortex area?
T cell

What are the two main types of tissue in the spleen?
Red pulp and white pulp

What does the red pulp do in the spleen?
Generel filter for blood
What does white pulp do in the spleen?
White pulp is the lymphoid tissue and constitutes the major initiator of responses to blood-borne antigens.

Which part of the spleen surrounds the the central arteriole and and has a high concentration of lymphiod tissue?
the periarterial lymphatic sheath (PALS)

what is a mucosa?
a mucous membrane
What does MALT stand for?
Mucosa-Associated Lymphoid Tissue (malt)
What is MALT?
aggregates of lymphiod tissue which do not have a tougher outer capsule
What is the name of the structure that enables naive lymphocytes to enter the secondary lymphoid organs from the blood?
High endothelial venue
Describe the mechanisms in which naive lymphocytes enter the lymph nodes?
Step 1-Rolling Step 2-activation Step 3-Arrest/adhesion Step 4- Transendothelial migration
What do lymphocytes look like under a microscope?
Agranular white blood cells have few or no granules in the cytoplasm Small cells with agranular cytoplasm and a large nucleus
What is the cluster of differentiation system?
It is a way of identifying cell surface molecules present on leukocytes.
What receptor do all T cells express?
CD3
What are CD markes used for?
used to discriminate between cells of the haematopoietic system (and other cells
Name some of the CD markers that B lymphocytes express?
CD19 and CD20
Name the three main structures of the lymph node?
Cortex Paracortex Medulla

In which part of the lymph node is the B cell located?
The cortex
In which part of the lymph node is the T cell located?
The paracortex
Lable the diagram of the spleen?
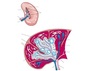
add pic
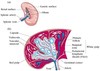
Name the two types of tissues located in the spleen?
Red pulp and white Pulp
What is the function of red pulp?
acts as a general filter for blood
What is the function of white pulp?
White pulp is lymphiod tissue and constitutes the major initiator of responses to blood-borne antigens
Which part of the spleen is B cells located?
Germinal Centre
Which part of the spleen are T cells located?
Periarterial lymphatic sheath (PALS)
What does MALT stand for?
mucosa associated lymphoid tissue
Name some examples of MALT?
The tonsils, the Peyer patches within the small intestine, and the vermiform appendix are examples of MALT.
Summarise the recirculation of lymphocytes?
Naive lymphocytes circulate constantly from the blood into the secondary lymphiod tissue They leave the vasculature through specialised sections of the post capillary venule known as the High Endothelial Venule (HEV) They move from the lymph node to the lymphiod vessels and eventually return to the blood via the thoracic duct In the prescence of an infection cells which recognise infectious angents are held in the lymphiod tissue where they proliferate and differentiate
Name the features of lymphocytes?
Small cells with agranular cytoplasm and a large nucleus
Explain the use of CD (clusters of differentiation) markers for discrimination between lymphocytes?
the CD system is a way of identifying cell surface molecules present on leukocytes using monoclonal antibodies. each set of antibodies that recognise a particular molecule forms a cluster
What are Surface molecules on cells of the immune system (and other cells) are named by?
Cluster of Differentiation (CD) nomenclature system
Name the differnces between t and b lymphocytes?
T lymphocytes express CD3 and only recognise processed antigen presented on cell surfaces by specialised molecules: B lymphocytes express CD19 and CD20 and can recognise intact, free antigen.
What are germinal centres and where are they located?
Germinal centers or germinal centres (GCs) are sites within secondary lymphoid organs – lymph nodes and the spleen[1] where mature B cells proliferate, differentiate, and mutate their antibody genes (through somatic hypermutationaimed at achieving higher affinity), and switch the class of their antibodies (for example from IgM to IgG) during a normal immune response to an infection. They develop dynamically after the activation of follicular B cells by T-dependent antigen.


