B lymphocytes Flashcards
Name some features of Adaptive Immunity?

Where are B cells derived from?
Derived from stem cells in the bone marrow
Mature B cells are ………….. for a particular antigen
Specific
What part of a B cell determines its specificity?
B cell receptor (BCR)
What generates antigen receptor diversity?
Immunglobin gene rearrangement
How many chromosomes are involved in the conding of immunoglobulin chains?
3
Name the responsibilities of the chromosomes responsible for the coding of immunoglobulin chains?
One of the chromosomes is responsible for Kappa light chains, one for lambda light chains and one for all the heavy chains.
Each BCR receptor chain (kappa, lambda and heavy chain genes) is encoded by separate multigene families on different chromosomes
Explain how a immunoglobulin light chain is made ?
One of the V segements comes together with one of the J segements. Unwanted Dna is looped out by a special mechanism. It is then possible to produce a primary RNA transcript consisting of VJ linked to the constant region (C). Unwanted RNA between between J and C is spliced out to give mRNA for VJC. This can then be translated into a light chain. The process is similar for lambda light chains and the heavy chains, but for the heavy chains there is a series of D segments between the V and J segements and the mrna thus representing VDJC.
V–J—-C then it goes VJ—-C Then VJC for heavy chain: V—D—J—C V–DJ–C VDJ—C VDJC add pic

How is heavy chain rearrangement different to light chain rearrangement ?
Has a D region.
Constant achieved by alternative splicing add pic

Draw a diagram showing immunoglobulin gene rearrangement
add pic

What are the conditions for B cells to become mature from an immature b cell?

Selection for self tolerance + productive gene rearrangement: if the cells survive, they will become mature (or naïve) B cells (IgM and IgD)

What are the two accessory signals required by naive B cells to produce Antibodies?
General rule: naïve antigen-specific lymphocytes (B or T) cannot be activated by antigens alone.
naïve B cells require accessory signal:
1) Directly from microbial constituents
2) from a T helper cell
B cells activated by TI(T cell independant) antigens need additional signals to complete activation, but instead of receiving them from T cells, they are provided either by recognition and binding of a common microbial constituent to toll-like receptors (TLRs) or by extensive crosslinking of BCRs to repeated epitopes on a bacterial cell.[1]

What is the general rule about the activation of naive antigen-specific lymphocytes (B or T) ?
naïve antigen-specific lymphocytes (B or T) cannot be activated by antigen alone
Name the 2 pathways which dictates how antibody production by B cells is achieved?
Thymus dependant activation- T helper cell, all Ig-classes and memory.
Thymus independant activation- microbial constituents, only IgM and No memory. Antigens that activate B cells without T cell help are known as T cell-independent (TI) antigens
Antigens that activate B cells without T cell help are known as T cell-independent (TI) antigens[1] and include foreign polysaccharides and unmethylated CpG DNA.[12]They are named as such because they are able to induce a humoral response in organisms that lack T cells.[1] B cell response to these antigens is rapid, though antibodies generated tend to have lower affinity and are less functionally versatile than those generated from T cell-dependent activation.[1]
As with TD antigens, B cells activated by TI antigens need additional signals to complete activation, but instead of receiving them from T cells, they are provided either by recognition and binding of a common microbial constituent to toll-like receptors (TLRs) or by extensive crosslinking of BCRs to repeated epitopes on a bacterial cell.[1] B cells activated by TI antigens go on to proliferate outside lymphoid follicles but still in SLOs (GCs do not form), possibly undergo immunoglobulin class switching, and differentiate into short-lived plasmablasts that produce early, weak antibodies mostly of class IgM, but also some populations of long-lived plasma cells.[19]

List the steps for T dependant activation?
The membrane bound BCR recognises the antigen.
The receptor-bound antigen is internalised and degraded into peptides.
Peptides associate with “self” molecules (MHC class II) and is expressed at the cell surface.
This complex is recognised by matched CD4 T helper cell B cell activated.
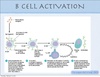
Breifly describe clonal expansion?
• T helper cells secrete lymphokines after recognition of the antigenic/self complex on the surface of the B cell • B cell enters into the cell cycle, divides and develops into a clone of cells with identical BCRs => B cells differentiate into plasma cells secreting these soluble BCRs = antibodies => B cells differentiate into memory cells

How do Ig switch classes?
There is a class switch under T cell influence (cytokines) Under the influence of T helper cells, a process of class switching can occur in which the already re-arranged VDJ can switch its attachment from Cu to Cy, Ca or Ce (these letters should be in greek letters)

What are the 3 outcomes of B cell activation?
1) Production of antibody as plasma cells 2) Differentiation into memory cells 3) Enters the somatic hypermutation and affinity maturation (improves quality of antibody)
In immunology, affinity maturation is the process by which Tfh cell-activated B cells produce antibodies with increased affinity for antigen during the course of an immune response. With repeated exposures to the same antigen, a host will produce antibodies of successively greater affinities. A secondary response can elicit antibodies with several fold greater affinity than in a primary response. Affinity maturation primarily occurs on surface immunoglobulin of germinal center B cells and as a direct result of somatic hypermutation (SHM) and selection by Tfh cells.[1]

What is affinty maturation?
In immunology, affinity maturation is the process by which Tfh cell-activated B cells produce antibodies with increased affinity for antigen during the course of an immune response. With repeated exposures to the same antigen, a host will produce antibodies of successively greater affinities. A secondary response can elicit antibodies with several fold greater affinity than in a primary response.

What is Somatic Hypermutation?
Somatic hypermutation is a process that allows B cells to mutate the genes that they use to produce antibodies. This enables the B cells to produce antibodies that are better able to bind to bacteria, viruses and other infections.
A major component of the process of affinity maturation, SHM diversifies B cell receptors used to recognize foreign elements (antigens) and allows the immune system to adapt its response to new threats during the lifetime of an organism.[1] Somatic hypermutation involves a programmed process of mutation affecting the variable regions of immunoglobulin genes.

Why are memory responses better?
Memory responses are characterised by a more rapid and heightened immune reaction that serves to eliminate pathogens fast and prevent diseases. It can confer life-long immunity to many infections.
Basis for Vaccines- Initial antigen contact induces a PRIMARY RESPONSE. Subsequent encounter with the same antigen will induce a SECONDARY RESPONSE which is more rapid.


