Intro to the Glomerulus and Review of Microscopic Urinalysis Flashcards
(28 cards)
What type of stain is this?
Where are the capillary spaces?
what type of epithelia cell is lining the bowman capsule?
is the glomerulus normal?

This is an H and E stain of a normal glomerulus
the capillary spaces are obvious (the clear spaces in the middle of the glomerulus)
the bowman capsule is lined by parietal epithelia cells
The glomerulus is normal
What type of stain is this?
What does it have an affinity for?
what structures are highlighted?

This is a PAS stain
it has an affinity for type IV collagen
the stain highlights the basement membrane of the bowman capsule, the mesangial matrix, and the tubules that are rich in this type of collagen
What type of stain is this?
what does it highlight
How does it work?

This is a silver stain- it is used routinesly in kidney biopsies.
The silver stain highlights the basement membrane of the bowman capsule and the capillary loops
the periodic acid oxidizes the carbohydrate components of teh baseent membrane which produce aldehydes. The aldehydes reduce the silver to a visable metalic silver.
Trichrome stain
what is its affinity?
what does it show?
trichrome stain and is helpful in evaluating fibrous connective tissue in a renal biopsy.
What type of stain is this?

Trichrome stain
what type of stain is this?
What does it stain for?
How else might it appear?

This is congo red stain. It highlights amyloid deposits red and will have an apple green birefringence when under a polarizing microscope
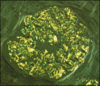
What is represented by the blue line?
what is highlighted by the pink line?
What are the FP?
GBM?

The blue line is the sub-epithelial space
the pink line is highlighting sub-endothelial space
the FP are the foot proceses (podocytes)
and the GBM is the glomerular basement membrane.
the arrow represents a slit diaphragm
What type of lesion is this?
what are its characteristics?
what part of the glomerulous is affected?

This is a sclerotic lesion.
deposition of extracellular collagenous matrix, may be confined to mesangial areas or capillary loops or both
What type of lesion is this?
what part of the glomerulus can be affected?

This is a proliferative lesion- hypercellularity
it can be endocapillary mesangial cells increase in number >2-3 in one area
Extracapillary incease in parietal epithelial cells
What type of lesion is this?
what part of the glomerulus is affected?
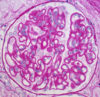
membranous lesion
affects the basement membrane
-thickening and expansion of capillary basement membrane
What type of lesion is this?

Endocapillary proliferation
this is a proliferation of the cells in the glomerular tuft.
the cells can be:
mesangial, leukocytes, or endothelial
What type of lesion is this?

Combination of proliferative and membranous lesions
What type of lesion is this?

Extraapillary proliferation (crescent formation)
parietal epithelial cells that line the bowman capsule
What is the extent of this lesion?

This is a segmental lesion it affects a portion of the glomerular tuft
What is the exten of this lesion?

Global lesion
the lesion affects the ENTIRETY of the glomerular tuft
What is the difference between an focal and a diffuse lesion?
A focal lesion: less than 50% of the glomeruli are affected
Diffuse lesion: more tha 50% of glomeruli are affected
What type of lesion is this?

Sub-endothelial
Where is the location of this lesion?
What type of imaging is being used?

This is a sub-epithelial lesion (between the basement membrane and the podocyte)
It is an Electron Microscopy image
what is happening here?

the image shows effacement of foot processes or fusion of the podocites
What is happening here?

splicing and duplication of the basement membrane
What is this?
Is this normal?

Squamous cells in the urine-
squamous cells are flat cells with an angular border. They are anuclear or have a small central nucleus. The presence of squamous epithelial cells is most likely a contamination (from skin, genital tract) in voided urine
what type of cell is this?
is it normally found in urine?

Transitional (urothelial) cell
they are larger than WBC’s with round central nucleus cell. Finding these cells in a urine sample is not unusual because they are derived from the lining of the GI system, however, if there are lots of them it is hard to differentiate fro a well differentiated neoplastic process and requires more info from urine cytology
what type of cell is this?
is it normally found in urine?

These are white blood cells. they tend to be neutrophiles which are easier to identify because of granules and multilobed nuclei.
women normally have <5 WBC/HPF
men normally have <2 WBC/HPF
what type of cell is this?
is it normally found in urine?

Red blood cells
the presents of 3+ RBCs per HPF in two of three samples is the accepted definition of hematuria





