Clinical Aspects of Glomerular Diseases Flashcards
Nephritic Syndrome:
what does the pt present with clinically?
what do labs show?
Nephritic syndrome is typically an inflammatory process that causes immune-mediated damage
Pt. presents with hematuria, oliguria, HTN
Labs: UA (+) blood, RBC casts, urine protein <3g/ day
Nephrotic Syndrome:
damage to the basement membrane causes:
proteinuria level:
____plasma albumin
___ capillary oncotic pressure
and ____ in Antithrombin III, Proteins S and C
Clinical findings:
Nephrotic Syndrome:
damage to the basement membrane causes:
proteinuria level: >3g/d
decreased plasma albumin- hypoalbuminemia
decreased capillary oncotic pressure- edema
and loss in Antithrombin III, Proteins S and C= hypercoaguability
what is the urine protein/creatinine ratio in nephrotic syndrome?
what type of casts would we expect to see in UA? why?
protein/creatinine ratio >3.5
we would expect to see fatty casts on UA due to high cholesterol burden in plasma (300-400 mg/dL) which can leak through the damaged epithelium
Clinical presentation: edema (periphral, periorbital) massive proteinuria
- onset
- etiology:
- most common cause of nephrotic syndrome in ____
- associated with:
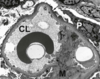
Minimal Change Disease
- onset- sudden
- etiology: idiopathic
- most common cause of nephrotic syndrome in kids (<10 yo)
- associated with:
- medications: lithium, NSAIDS
- Lymphomas
An African American adult presents with hematuria and high nitrogen blood levels. You look back at his charts and see that his proteinuria levels have gradually increased.
what is the diagnosis?
would this patient respond to steroids?
Nephrotic Syndrome- Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis
this patient would not respond to steroid treatment (this is one way you can distinguish it from Minimal Change)
FSGS is also associated with what secondary causes?
HIV
sickle cell
heroin use
A 50 yo caucasian male presents with proteinuria >3g/day
on biopsy you see the attached image.
What is the antibody associated with this type of lesion?
where is the lesion located?
what should your work up include?
what is your prognosis?

Nephrotic Syndrome: Membranous glomerulonephrpathy
antibodies against the Phopholipase A2 receptor
immune complex deposition in situ on the subepithelial aspect of the BM
work up should include tests for SLE, RA and hepatitis serologies (looking for auto antibodies?) and
**age appropriate cancer screenings**
prognosis: “rule of thirds” 1/3 remission, 1/3 persistent proteinuria with stable renal function, 1/3 progress to ESRD
Nephrotic Syndrome- Diabetic Glomerulosclerosis
What would we expect to see on a biopsy?
How do we treat?
Nephrotic Syndrome- Diabetic Glomerulosclerosis
Nodular sclerosis (kimmelsteil-Wilson nodules)
treat by:
glycemic control
BP with ACEI/ARB
intensive cholesterol control
Clinical Presentation:
Hematuria
Oliguria
HTN
Labs:
UA: (+) blood, RBC casts
Urine Protein <3g/day
Nephritic Disease
A patient comes in complaining of episodes of hematuria. He has a history of URI.
He has normal C3 and C4 blood levels and microscopic hematuria
what is the diagnosis?
A patient comes in complaining of episodes of hematuria. He has a history of URI (viral infection)
He has normal C3 and C4 blood levels and microscopic hematuria
what is the diagnosis?
Nephritic Syndrome IgA Nephropathy
an 8 yo male comes into the office with lower extremitiy bruising (palpable purpura), bloody diarrhea andd painful joints.
Dx:
what other clinical findings might we have?
Treatment:
an 8 yo male comes into the office with lower extremitiy bruising (palpable purpura), bloody diarrhea and painful joints.
Dx: Henoch-Scholein Purpura
what other clinical findings might we have? vomitin, abdominal pain, hematuria and hypertension
Treatment: supportive
A 12 yo female presents with hematuria. Hx is significant for strep throat.
Dx:
What lab findings distinguish this from IgA Nephropathy?
Prognosis:
A 12 yo female presents with hematuria. Hx is significant for strep throat. (Group A streptococcal infection)
Dx: Post-infectious GN
What lab findings distinguish this from IgA Nephropathy?
LOW C3 and LOW C4
Prognosis: complete recovery
Pt labs report low C3 and normal C4
and the image below
Dx:
Hallmarks of this pathology:

Membranoproliferative Glomerulonephritis
- 2 types:
- dense deposit disease (excessive activation of the complement pathway)
- immune complex localization
membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis has a characteristic double contour formation
A patient presents with Hx of sinus infections, (+) hematuria, (+) RBC casts, and sudden onset of HTN.
Dx based on:
prognosis:
What might kill this patient if we miss it?
A patient presents with , (+) hematuria, , and sudden onset of HTN.
Anti-GBM/Goodpasture’s Syndrome
Dx based on: Anti-GBM antibodies and biopsy
prognosis: promptness of dx and treatment and degree of kidney involvement (Cr>5 dialysis is required and progosis is poor)
If there is lung involvement its Goodpasture’s Syndrome
70% of patients with goodpasture’s syndrome will have pulmonary hemorrhage. This is an emergncy and must be treated with plasmapheresis
Pt. presents with non specific symptoms of nephritic syndrome but mentions that he has a history of sinus infections:
Dx:
What type of antibody is present?
Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis
(Wegener’s)
ANCA-C is present
Pt. presents with non specific symptoms of nephritic syndrome but you notice some skin issues as well.
Dx:
What type of antibody is present?
Microscopic Polyangiitis
(dermato-pulmonary-renal syndrome)
P-ANCA


