Integumentary System and Dermatopathology Flashcards
What are some of the many functions of the skin?
6
- Prevents fluid loss
- Protection barrier
- Area for heat exchange
- Harbors immune cells that protect against invading microorganisms
- Neurological receptor relay system:
- Touch, pressure, temp, pain - Vitamin D synthesis
- What does the epidermis cover?
- Composed of four different cell types. What are they?
- Covers the entire body
- Composed of four different cell types
- Keratinocytes (further categorized into the “stratum” layers)
- Melanocytes
- Merkel’s Cells (basal layer of epidermis)
- Langerhans’ cells
- What is the predominant cell of the epidermis?
- Change size and shape as they move superficially, replacing what?
- Produces fibrous protein called keratin which is what?
- Structural protein of what?
- Keratinocytes
- cells lost during normal cell shedding
- which is essential to the protective function of the skin and is the
- structural protein of hair and nails
What are the five separate layer of the epidermis?
Five separate layers:
- Stratum germinativum or stratum basale
- Stratum spinosum
- Stratum granulosum
- Stratum lucidum
- Stratum corneum
Describe the following skin layers:
- Stratum germinativum or stratum basale?
- Stratum spinosum?
- Stratum granulosum?
- Stratum lucidum?
- Stratum corneum?
- Single layer of columnar cells, undergo mitosis, no migration
- Two to four layers, cells differentiate
- Only a few layers, most differentiated (some losing cytoplasm, others continue to synthesize keratin)
- Thin, transparent layer mostly confined to the palms of the hands and soles of feet, transitional cells
- Many layers (15-100 layers depending on location), dead squamous-type keratinized cells
- Melanocytes are where?
- What do they do?
- Each melanocyte supplies several keratinocytes with melanin through what?
- Located at or in the basal layer
- Pigment-synthesizing cells (produce melanin)
- cytoplasm-filled extensions
- Ability to synthesize melanin depends on the ability of the melanocytes to produce the enzyme ________.
- What if you had a genetic defect where you lacked this enzyme?
- tyrosinase (converts amino acid tyrosine to precursor of melanin)
- Albinism
Melanocytes:
- What increases production of melanin?
- Primary function is to do what?
- What about melanocytes makes people light skin or darker skinned?
- All people, regardless of skin color, have relatively few or no melanocytes where?
- ***Exposure to UV rays increases production of melanin
- Primary function is to protect from UV rays (melanin absorbs and scatters radiation)
- Dark-skinned and light-skinned people have same amount of melanocytes (efficiency of production and shipping differs however)
- in palms of hands or soles of feet
- What are the least densely populated cells of the epidermis?
- These function as what?
- Where would you suspect these cells to be most prominent?
- Least densely populated cells of the epidermis
- Function as mechanoreceptors (touch receptors)
- Finger tips
- What are Langerhan’s Cells? Where are they?
- Describe the amount to kerotinocytes?
- What are do they do?
1.
- ***Immunologic cells responsible for recognizing foreign antigens harmful to the body
- Scattered in the suprabasal layer of the epidermis
2. Few in number compared to keratinocytes
3. Bind antigen to their surface, process it, send it on to regional lymph nodes
- What is the dermis?
- Mostly composed of what?
- Also composed of what? 3
- Connective tissue layer separating the epidermis from the subcutaneous fat layer
- Mostly composed of collagen (major stress-resistant material of the skin)
- Also composed of:
- Variety of immune cells
- Nerves (wide distribution of receptors for touch, pressure, heat, cold, and pain)
- Blood vessels (dermis is richly supplied by arteriovenous anastomoses.
- Subcutaneous tissue consists primariliy of what?
- What two structures extend to this layer?
- Consists primarily of fat and connective tissues that lend support to the vascular and neural structures supplying the dermis and epidermis
- Eccrine glands and deep hair follicles extend to this layer
What are skin appendages? 4
- Sweat Glands
- Sebaceous Glands
- Hair
- Nails
What are the two types of sweat glands?
- Eccrine (merocrine) sweat galnds
- Apocrine sweat glands
Eccrine (merocrine glands)
- Located where?
- Originate where?
- Open directly to where?
- Primary function?
Apocrine sweat glands
- Located where and what do they look like?
- OPen through where?
- Secrete what kind of substance?
- Sterile until what?
- Function and location? 3
Eccrine (Merocrine) sweat glands
- Located over entire body surface,
- originate in dermis and
- open directly to the skin surface
- Primary function is to transport sweat to body surface to regulate body temperature (through what process- evaporation from the skins surface causes cooling)
Apocrine sweat glands
- Less numerous, larger, located in deep dermal layer
- Open through a hair follicle (so where would they primarily be found- where there is hair :P)
- Secrete more of an oily substance
- ***Sterile until mixed with bacteria
- -Axilla, areola, genetalia, (sweat glands, earwax, breast milk)
Apocrine or Mericrine?

Apocrine
Which is apocrine and which is eccrine?

Eccrine 1
Apocrine 2
Sebaceous Glands
- Located where? Except (3)?
- Secrete a mixture called sebum which is composed of what? 3
- Function?
- Realtively inactive until when?
- Amount of sebum produced directly associated with what?
- What sex gland influences gland size?
- Located over the entire skin surface except for the palms, soles, and sides of feet
2.
- lipids,
- cholesterol, and
- other substances
3. Function is to lubricate hair and skin
4. Relatively inactive until adolescence
5. gland size
6. Androgens/testosterone
- Most hair follicles are associated with what?
- Entire hair structure consists of what? 4
- Most hair follicles associated with sebaceous glands (the pilosebaceous unit)
- Entire hair structure consists of
- Hair follicle and hair shaft
- Sebaceous gland
- Hair muscle (arrector pili muscle)
- And sometimes an apocrine gland
- The hair shaft is mostly composed of the fibrous protein…?
- Undergoes cyclic______?
- Hair follicles work_________?
- Human beings shed hair__________?
- What determines if a hair is shed? 3
- What determines the length of hair?
- Kerotin
- shedding
- independently
- asynchronously
- stress, drugs or if it reaches a certain length
- Genetic
- Vascular network at the site of the ___________nourishes and maintains the hair follicle.
- Melanocytes located in the bulb determine what?
- Arrector pili muscle is located under the___________?
- This causes_________?
- follicular bulb
- hair color
- sebaceous gland
- goose bumps
Nails
- What are they made of?
- Function?
- Grows how?
- Floor of the groove is the ________, which is the germinal region of the_________?
- Nail plate lies in the_______?
- Medical term for cuticle is_________?
- Hardened keratinized plates
2.
- Protects fingers and toes
- Enhances dexterity
3. Grows from curved transverse groove called nail groove
4. nail matrix, nail plate
5. nail bed
6. eponychium
Rash
- Defined how?
- What kind of patterns? 2
- Evaluate? 3
- Change of the skin affecting color, appearance or texture.
- Localized or affects all the skin.
- Evaluate:
- Appearance
- Distribution
- Symmetry
Manifestations of Skin Disorders
- Primary lesions arise from where?
- Secondary lesions arise from where?
Primary Lesions
- Arise from previously normal skin
Secondary Lesions
- Created by another process such as scratching or infection
Types of Primary Lesions?
10
- Macule,
- Patch
- Papule,
- Plaque,
- Nodule,
- Tumor,
- Wheal
- Vesicle,
- Bulla,
- Pustule
Describe each of the following?
- Macule,
- Patch
- Papule,
- Plaque,
- Nodule,
- Tumor,
- Wheal
- Vesicle,
- Bulla,
- Pustule

What is a macule?
Circumscribed flat lesion less than 1cm

What is a patch?
Same description as macule but >1cm

- What is a papule?
- May become confluent and become a what?
- Elevated solid lesion with variable color less than 0.5cm
- plaque

What is a plaque?
Raised flat-topped superficial lesion where diameter is greater than the thickness (>0.5cm)(often formed by coalescence of papules)

- What is a nodule?
- Compare it to a papule
- Elevated lesion with a rounded surface
- (generally deeper and firmer than a papule)(0.5 – 1-2cm)

What is a tumor?
Large nodule (>1-2cm)

What is a wheal?
Somewhat irregular, transient swelling due to localized skin edema (what other terms are used to describe these?)

What is a vesicle?

What is a Bulla?

What is a pustule?

What are the types of secondary lesions?
7
- Scales
- Crust
- Erosion
- Ulcer
- Fissures
- Atrophy
- Scar
What are scales?

What are crusts?

What is an erosion?

What is an Ulcer?

What is a fissure?

What is atrophy?

What is a scar?

What is an excoriation?

What are comedones?

What are milia?

What is a cyst?

What is an abscess?

What is a burrow?
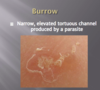
What is lichenification?

What does umbilicated mean?

What is telangiectasia?

What is petechia?

What is ecchymosis?

What is a keratin horn?

Describe Warty/paillomatous?

What is a furuncle?

What is a carbuncle?

Name examples of each of the following distribution terms:
- Symmetrical? 2
- Asymmentrical?
- Sun exposed areas? 2
- Intertriginous?
- Contact areas?
- Extensor surfaces?
- Flexural surfaces?
- Symmetrical- Involves both sides of body to a similar extent (often endogenous cause like acne, psoriasis)
- Asymmetrical- Involves predominantly one side (often external cause)
- Sun exposed areas (sunburns and photosensitivity)
- Intertriginous (often candidal rash)
- Contact areas (contact dermatitis)
- Extensor surfaces (often psoriasis)
- Flexural surfaces (often atopic dermatitis)
What is the following picture?

Contact dermatitis
What is the following a picture of?

Intertriginous Candidiasis
What is the following a picture of?

Flexural surface
What kind of distribution is the following a picture of?

extensor surface
What are the different kinds of margination you an have?
2
- Sharp, well defined, or circumscribed
- Able to draw a line around it
- Transition quickly within 1mm - Poorly defined
- Borders that merge into normal skin
- Transition over 1mm
Describe the following:
- Annular?
- Arcuate?
- Iris?
- Discoid?
- Nummular?
- Serpiginous?
- Guttae?
- Morbilliform?
- Annular: ring-shaped with active margin and clear center
- Arcuate : arched, bow-shaped
- Iris: target lesion
- Discoid: disk-shaped
- Nummular: coin-shaped
- Serpiginous: snakelike
- Guttate: drop-sized
- Morbilliform: small confluent macules, forming irregular shapes
What is the following shape?

Annular
What is the following shape?

Nummular
What shape is this?

Morbilliform
Describe what the following arrangements are:
- Confluent?
- Discrete?
- Generalized or diffuse?
- Disseminated?
- Grouped?
- Reticulated?
- Confluent: blending into adjacent lesions
- Discrete: separated by normal skin from other similar lesions
- Generalized or diffuse: covering most of the designated surface body surface
- Disseminated: widespread discrete lesions
- Grouped: multiple lesions clustered in one area (but not necessarily blending with each other)
- Reticulated: in the form of a network
What kind of arrangement is this?

Confluent
What arrangement is this?

Reticular
Describe the following Palpation types:
- Smooth?
- Uneven?
- Rough?
- Smooth: normal epidermis
- Uneven: scaly, warty, etc.
- Rough: sandpaper like (keratin horn, scarlatiniform rash, crust)
Blackheads are 1.______ comedones, yes, you heard right, blackheads are 2. _____ , whiteheads are 3.______.
- open
- open
- closed


