Inborn errors of metabolism Flashcards
(11 cards)
What is inborn errors of metabolism?
= single gene defects resulting in disruption to metabolic pathways
Due to:
- Toxic accumulation of substrates
- Toxic accumulation of intermediates from alternative metabolic pathways
- Defects in energy production
How are inborn errors of metabolism caused?
By mutations in genes which then produce abnormal proteins whose functional activities are altered
What is alkaptonuria?
- Autosomal recessive disease
- Congenital
- Homogentisic acid oxidase deficiency
- Urine turns black on standing
- Black ochronotic pigmentation of cartilage and collagenous tissue
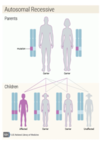
What is autosomal recessive mechanism of inheritance?
- Both parents carry a mutation affecting the same gene
- Consanguinity increases risk of autosomal recessive conditions
- Eg. PKU, alkaptonuria
What is autosomal dominant mechanism of inheritance?
- Rare in IEMs
- Eg. Marfan’s, acute intermittent porphyria

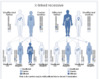
What is X-linked mechanism of inheritance?
- Recessive X linked conditions passed through the maternal line
- Condition appears in males
- Condition carried in females
What is mitochondrial mechanism of inheritance?
- Mitochondrial gene mutation - fail to produce enough energy for the body
- Maternally inherited as only the egg contributes mitochondria to the developing embryo
- Affects both male and female but affected male cannot pass on the disorder

What is heteroplasmy?
= each cell contains varying amounts of normal mtDNA and mutated mtDNA (people with mitochondrial disease)
- Distribution of affected mitochondria determines presentation
- Mitochondrial disease can vary in symptoms
- High energy-requiring organs are more frequently affected
How can you classify to inborn errors of metabolism?
- Toxic accumulation
- Deficiency in energy production/Utilization
- Disorders of complex molecules involving organelles
What is the presentation of inborn error of metabolism?
Neonatal to adult onset depending on severity of metabolic defect
Late- onset due to accumulation of toxic molecules - organ failure, seizures
What is the symptoms of inborn errors of metabolism in neonates?
Can be born with normal birth weight and no abnormal features
Symptoms present frequently in the first week of life when starting milk feeding
Neonates presentation
- Poor feeding, vomiting
- Profound hypotonia
- Organomegaly
- Dysmorphic features
- Sudden death
- Hypoglycaemia
- Unexplained ketoacidosis
- Lactic acidosis
Confirmatory investigations:
- Enzymology
- Biopsy
- Fibroblast studies
- Whole genome sequencing


