Diabetes and Hypoglycaemia Flashcards
What happens during the fed state?

What happens in the fasting state?

How is plasma glucose level regulated?
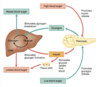
What is the role of insulin?

What are the functions and metabolic paths of the hormones in plasma glucose level regulation?

What is diabetes mellitus?
= metabolic disorder characterised by chronic hyperglycaemia and associated abnormalities of lipid and protein metabolism
What is type 1 diabetes?
- Deficiency in insulin secretion
- childen and young adults - sudden onset
- cause = autoimune destruction of B-cells
- starts with autoantigen formation presented to T-lymphocytes to imitate autoimmune response –> produces islet cell antibodies
- causes hyperglycaemia due to absolute deficiency of both insluin and amylin which lowers blood glucose by supressing glucagon output from pancreatic cells
What are the genetic predisposition and enviromental factors of type 1 diabetes?

What are the metabolic complications of type 1 diabetes?

What is type 2 diabetes?
- Insulin secretion is retained but there is target organ resistance to its actions
- Slow onset, middle-aged - linked with exercise and obesity

What are genetic predisposition and lifestye factors of type 2 diabetes?

How can you test for type 2 diabetes?
As well as symptoms you will be diagnosis by oral glucose tolerance test or testing the random plasma glucose levels
- Impaired glucose tolerance
- Imparied fasting glycaemia
Without symptoms, diagnosis will follow test blood samples on 2 separate days
Oral glucose tolerance test:
- checks body’s ability of metabolizing glucose

What are the different types of diabetes?
- Type 1
- Type 2
- Secondary - chronic pancreatitis, pancreatic surgery
- Gestational - occurs for the first time in pregnnacy
How do you monitor glycaemic control?
- to prevent complications or avoid hypoglycaemia
- Self-monitor capillary blood measurement and urine anaylsis
- Every 3-4 months check of blood HbA1c
- Urinary albumin
What are the long-term complications of diabetes?
Micro-vascular disease - retinopathy, nephropathy
Macro-vascular disease - atherosclerosis heart attack/stroke
What is hypogluycaemia?
can occur in patients with and without diabetes
Plasma glucose less than 2.5mmol/L
Without having diabetes:
- Caused by drugs like alcohol
- Endocrine diseases can cause it
- Inherited metabolic disorders
- Insulinoma
What is reactive hypoglycaemia?
= hypos after eating
Drop in blood sugar usually recurrent and occur within 4 hours after eating
Cause is unclear:
- Benign tumour in pancreas could cause overproduction of insulin
- Too much glucose may be used up by the tumour
- Deficiencies in counter-regulatory hormones
What is the counter-regulatory response of hypoglycaemia?

What are the signs and symptoms of hypoglycaemia?
Neurogenic
- Triggered by falling glucose levels
- Activated by ANS and mediated by sympathoadrenal release of carecholamines and Ach
- Mood changes, paleness, sweating, hunger, tiredness, headaches
Neuroglycopenia
- Due to neuronal glucose deprivation
- Confusion, difficulty speaking, paraesthesia, seizures, coma and death


