Clinical cancer genetics Flashcards
(9 cards)
What is the difference between constitutional (germline) mutations and somatic mutations?
Germline
- hereditary
- informs future cancer risk
- informs treatment decisions
- provides information for other family members
- born with
Somatic
- aquired
- informs treatment decisions
- provides reassurance for family and future childen
- tumour only mutations
What is the effect size compared to allele frequency?
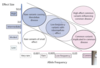
What is multifactorial/polygenic familial risk?
Larger proportion of predisposition genes
No single high risk gene identified
Risk conferred through multiple lower risk genetic factors +/- environmental factors
- Usually SNPs found in GWAS
No current testing
Increased screening is available for some cancer types in at risk individuals
Why identify patients with increased genetic predisposition to cancer?

How can we identify cancer genetics?
- Family history
- Age of onset
- Multiple reoccurrence in same person (both breasts)
- Multiple cancer diagnoses of same type in related individuals
- Cancer related together - ovarian and breast eg.
- Syndromic features of cancer and genes
- Pathology of cancer
- Tumour testing
- Cancer patient are now being offered cancer screening of their tumour
- If we find a disease causing change in a cancer predisposition gene on testing, it is possible it might also be in the germline and use a blood test to check this
What is stratified prevention?
= categorisation of the population into risk groups, each of whom would be offered a different intervention

Using the idea of familial risk who whom they would be on right hand side as increased risk so will have increased screening programme so more cost effective
What is the genetic testing for cancer?
Single gene
NGS panel
WES - whole exome sequencing
WGS - whole genome sequencing
What are the outcomes of doing a diagnostic genetic testing?
- No disease causing variant identified
- Variant of uncertain significance identified
- Disease causing variant identified
What are the significance of genes BRCA1 and 2?
Both increase the of having hereditary breast and ovarian cancer
- Chemoprevention for BRCA2 carriers
- Screening
- Risk-reducing surgery
- Male BRCA2 carriers recommended to have annual PSA test


