Immunology Introduction: Immune System, Cells and Molecules Flashcards
Primary (central or regenerative) immune system tissue: contents and examples
Contain developing lymphocytes
Examples: Bone marrow and Thymus
Secondary (peripheral) immune system tissue: contents and examples
Contain mature cells, active in host defense
Examples: Spleen, lymph nodes, MALT (mucosal-associated lymphoid tissue; includes tonsils, adenoids, appendix, Peyer’s Patches in GI tract, other mucosal lymphoid tissues)
Bone marrow activity (what happens here)
Site of hematopoiesis and B-cell maturation
Hematopoiesis and age
As a person ages, most hematopoiesis in flat bones (sternum, vertebrae, ileac, and ribs)
Thymus location and function
Bi-lobed organ in upper anterior thorax
Function: maturation and selection of T-cells
Thymus structure
Two lobes - each surrounded by capsule
Lobes divided into lobules by fibrous septa
Each lobule has outer cortex and inner medulla
Thymus vascular supply
Rich vascular supply
Cells enter thymus via blood, exit via lymphatic vessels or blood
Chest Radiograph

Classic “sail sign” of thymus
Spleen location and function
Large, vascular organ in left upper quadrant of the abdomen under the diaphragm
Major site of immune responses to pathogens and other foreign substances in the blood
Spleen structure
Blood supply from a single artery, divides into smaller arterioles
Two sections:
- White pulp: contains lymphocytes; T cells near arterioles in the periarteriolar sheath; B cells are more peripheral
- Red pulp: involved with RBC breakdown
Lymph nodes location and function
Small nodular aggregates of lymphoid tissue; 500-600 in human body located along lymphatic channels/vessels
Generally the first lymphoid structure to encounter foreign antigens; fluid draining from lymph enriched with antibodies and lymphocytes
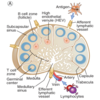
Lymph nodes structure
Outer fibrous capsule
Multiple afferent lymphatic vessels, one efferent
Three concentric regions: cortex, paracortex, medulla
Lymph node cortex contents
Contain follicles (cell aggregates) which may contain germinal centers
Lymph Node diagram
Lymph node groups (9)
- Cervical
- Supraclavicular
- Axillary
- Mediastinal
- Supratrochlear
- Mesenteric
- Inguinal
- Femoral
- Popliteal
Can someone ask my silly mother if ferrets poop?
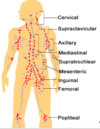
Most palpable lymph node groups?
Cervical, axillary, and femoral
Cervical LNG: location and site of drainage
Location: head and neck
Drainage: scalp, face, nasal cavity, pharynx
Axiallary LNG: location and site of drainage
Location: axilla
Drainage: arm, chest wall, breast
Inguinal LNG: location and site of drainage
Location: groin
Drainage: genitalia, buttock, anus, abdominal wall, leg
Mediastinal LNG: location and site of drainage
Location: In/near mediastinum/central posterier thorax
Drainage: Mid chest, upper abdomen, lungs
Mesenteric LNG: location and site of drainage
Location: lower abdomen, near intestine
Drainage: small/large intestine, upper rectum
MALT
Mucosal-Associated Lymphoid Tissue
Aggregates of lymphocytes found throughout mucosal surfaces in body (GI, resp, GU tracts)
Large number of Ab-producing cells; crucial pathogen defense
MALT divisions
- GALT: Gut-Associated Lymphoid Tissue
- Tonsils, adenoids, appendix, Peyer’s patches
- BALT: Bronchial/Tracheal-Associated Lymphoid Tissue
- NALT: Nose-Associated Lymphoid Tissue
- VALT: Vulvovaginal-Associated Lymphoid Tissue
Mucosal Immune System

Lymphatic System and Function
Separate vascular system through which the lymph moves
Functions: Collect/drain excess fluid, absorb fat, conduit for immune cells
Lymphatic System/Lymph Structure
Branching vessels (not circular)
Lymph fluid: WBC and plasma, no RBCs
Lymphatic drainage: Initiation
Initiated by interstitial fluid uptake in lymphatic capillaries
Lymphatic drainage: flow
By skeletal muscle contraction, arterial pulsation, unidirectional valves; smooth muscle in walls of larger vessels; NO PUMP
Flow through multiple lymph nodes before entering circulation in blood
Lymphatic drainage system
2 separate, asymmetric systems
Upper right areas (right side of head, heart, lungs): right lymphatic duct –> right subclavian vein
Rest of body: thoracic duct –> left subclavian vein
Contents of lymph fluid and changes throughout flow
- Phagocytic cells & antigens may be in lymph entering lymph node
- Initiation of an immune response, processing of foreign antigens
- Fluid exiting nodes with higher number of immune cells and antibodies
Virchow’s node
left supraclavicular node
enlargement implies inflammation or infection in left chest/abdomen—could be malignant
Lymphedema Definition
Interstitial collection of lymph due to disruption of lymphatic flow
Usually progressive, can lead to tissue hypertrophy & fibrosis