Immuno Histology Flashcards
1
Q
Granulocytes (3)
A
Neutrophils Eosinophils Basophils
2
Q
Agranulocytes (2)
A
Monocytes Lymphocytes
3
Q
Size ranking of blood elements
A
Monocytes > Eosinophils/Neutrophils > Lymphocytes/Basophils > Erythrocytes > Platelets
4
Q
Leukocyte % ranking
A
Neutrophils > Lymphocytes > Monocytes > Eosiniphils > Basophils
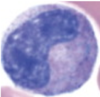
5
Q

A
Neutrophil
6
Q
A
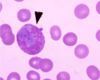
Eosinophil
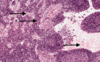
7
Q
A
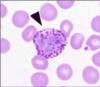
Basophil
8
Q

A
Lymphocyte
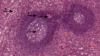
9
Q
A
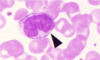
Monocyte
10
Q

A
Platelets
11
Q
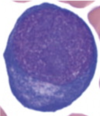
A
Proerythroblast
12
Q
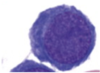
A
Basophilic erythroblast
13
Q
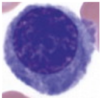
A
Polychomatophilic erythroblast
14
Q

A
Orthochomatophilic erythroblast
15
Q

A
Reticulocyte