Immuno: Transplantation Pt.1 Flashcards
Which organ is most commonly transplanted?
- Kidneys
- Followed by Liver
What is the average half-life of a transplanted kidney?
- 12 years
- Deceased donors slightly lower ~ 10 years
What are the three phases of an immune response to a graft?
- Phase 1: recognition of foreign antigens
- Phase 2: activation of antigen-specific lymphocytes
- Phase 3: effector phase of graft rejection
What are the most relevant cellular proteins that can determine compatibility?
- ABO blood group
- HLA
Which chromosome is HLA encoded on?
Chromosome 6
What are the two major types of rejection?
- T cell-mediated rejection
- Antibody-mediated rejection
What are the alleles of HLA class I and class II?
- Class I - A, B, C
- Class II - DR, DQ, DP
Describe the basic structure of HLA Class I and Class II.
Class I
- 3 alpha domains
- 1 beta-2 microglobulin domain
- 1 transmembrane domain
Class II
- 2 alpha domains
- 2 beta domains
- 2 transmembrane domains
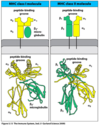
Where are HLA class I and class II expressed?
- Class I: all cells
- Class II: antigen-presenting cells (can be upregulated at times of stress)
Which HLA alleles are most immunogenic?
A, B and DR
What is 1:1:0 in terms of mismatches
For A, B and DR

Others e.g. DQ are still antigenic
Where do the antigen-presenting cells that interact with host T cells come from?
From the recipient and the donor (the donor organ will contain many APCs)
NOTE: a lot of these interactions will happen in lymph nodes
Which test is used to give a definitive diagnosis of graft rejection?
Biopsy
Describe the phases of T-cell mediated rejection.

Describe the effector phase of T-cell mediated graft rejection.
Activated CD8+ T-cells
- Release toxins to kill target cells - granzyme B
- Punch holes in target cells - perforin
- Induce apoptosis - Fas ligand
CD4+ T-cells recruit and activate macrophages which:
- Phagocytose cells
- Release proteolytic enzymes
- Produce inflammatory cytokines
- Release oxygen and nitrogen free radicals

What are the typical histological features of T-cell mediated rejection?
- Lymphocytic interstitial infiltration
- Tubulitis - WBCs within the tubular epithelium
- Arteritis - WBCs within vascular wall

What are the 3 signals of T-cell activation?
- Antigen/MHC interaction with TCR
- Co-stimulatory molecular expression - CD80/86 interaction with CD28
- IL-2
What other explanation might there be for graft failure other than rejection?
Immunosuppressive drugs may be nephrotoxic
Where are AB antigens expressed?
On erythrocytes AND endothelial cells
What are the three phases of antibody-mediated rejection?
- Phase 1: B-cells recognise to foreign HLA
- Phase 2: proliferation and maturation of B cells with anti-HLA antibody production
- Phase 3: effector phase - antibodies bind to graft endothelium = intravascular disease
What is a key difference between the production of anti-AB and anti-HLA antibodies?
- Anti-AB antibodies are naturally occuring (pre-formed)
- Anti-HLA antibodies are not naturally occuring but can be pre-formed due to previous exposure to epitopes (e.g. previous transplant, pregnancy) or post-formed (after transplantation)
Outline the pathophysiology of antibody-mediated transplant rejection.
- Antibodies bind to HLA on the endothelium of blood vessels within the transplanted organ
- The antibodies fix complement which leads to formation of MAC and endothelial cell lysis
- Binding of complement also recruits inflammatory cells
- This leads to inflammation of the microcirculation (capillaritis)
- This leads to procoagulant tendencies and occlusion of the microcirculation leading to graft fibrosis and necrosis

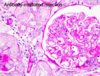
What are the main histological features of antibody-mediated transplant rejection?
- Presence of inflammatory cells within the capillaries of the graft (HALLMARK)
- Immunohistochemistry can show fixation of complement fragments on the endothelial cell surface
What are the three main approaches to preventing graft rejection?
- AB/HLA typing
- Screening for antibodies
- Overcoming organ mismatch issues


