Immune System Flashcards
What are the types of lymphocytes?
1) T cells 2) B cells 3) NK cells
What are the types of T cells?
1) cytotoxic T cells 2) helper T cells 3) regulatory T cells
What are the surface molecules on T cells?
- T cell receptor complex: alpha and beta dimer
- CD3
- Accessory molecules: CD 4 or CD 8
What is the ligand for the T cell receptor?
- Major Histocopatibility Complexes (MHC)
- Consists of :
- MHC proteins
- digested peptide “sample” from target cells
What are the T cell surface protein & ligand pairings by cell type?
- cytotoxic killer T cell (TCTL)
- CD8+
- MHC Class I
- helper T cell (TH)
- CD4+
- MHC Class II
- regulatory T cell (TREG)
- CD25+
- controls TCTL and TH
What kind of cells express MHC I? What kinds of peptides can be found with MHC I?
- all cells
- normal peptides (cell derived) or pathogenic peptides (microbe derived)
What kind of cells express MHC II? What kinds of peptides can be found with MHC II?
- Antigen Presenting Cells (APC)
- Class II peptides are derived from phagocytosed molecules (microbe derived)
What are the B cell surface protein?
B Cell Receptor (BCR): antibody that is surface bound
What are the 5 types of antibodies?
- IgM: prelimiary isoform, usualy BRC
- IgD: early isoform
- IgG: late isoform, found in blood
- IgA: late isoform, found in GI
- IgE: late isoform, found in allergic responses
Describe the structure & function of an antibody.
- antibodies bind to specific molecular configurations on antigen
- each B cell only makes one type

What are APCs (antigen presenting cells)?
- work with lymphocytes to present antigen via MHC II
- include:
- macs
- langerans’ cells (epidermis)
- reticular dendritic cells (spleen, LNs)
- B cells
What are the ways APCs play into cell mediated immunity & humoral response?
- (cell mediated) present to TCTL –> CD8+ T killer cells
- (cell mediated) present to TH1 –> macrophage activation
- (humoral) present to TH2 –> B cell antibody secretion

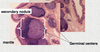
What is a lymphoid nodule? Describe its formation.
- Transient area of lymphocyte differentiation found in peripheral tissues (mucosa)
- Formation
- primary lymphoid nodule (follicle)
- secondary nodule
- mantle
- germinal center: B cell proliferation
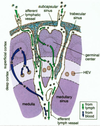
What are the lymphoid organs?
- primary
- bone marrow
- thymus
- secondary (terminal differentiation)
- lymph nodes
- spleen
- tonsils
- adenoids
- peripheral mucosa (MALT)
- appendix
- Peyer’s patches
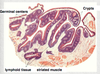
Describe a Peyer’s Patch.
- lymphoid nodules found in intestine
- developed lymphocytes can interact with specialized M cell on epithelial wall to have antigen presented
- **also found in mucosa of appendix