Cell Cycle Flashcards
1
Q
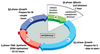
What are the cell cycle phases?
A
G1 –> S –> G2 –> M
2
Q
G1 Phase
A
- cells grow in size and functional output
- mRNAs and protein synthesis
- organelle expansion
- some cells remain in G1 for extended period (G0 phase)
- prepare for S phase
- make materials required for DNA synthesis: enzymes, nucleotides, ATP
3
Q
S Phase
A
- duplicate each chromosome once
- 2n –> 4n
- DNA packaging must also be copied: epigenetics
4
Q
G2 Phase
A
- cells grow in preparation for division
- prepare for M phase: make materials for cell division
- tubulin, mitotic spindle proteins, ATP
5
Q
M Phase
A
- mitosis or karyokinesis
- sister chromatid (DNA) separation
- prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase
- cytokinesis
- cytoplasmic division
6
Q
Describe the mitotic spindle.
A

7
Q
Prophase
A
- DNA condenses to form compact chromatids
- centrosomes move to poles of nucleus
- microtubules beign to organize into spindle
8
Q
Prometaphase
A
- nuclear envelope (membrane) disintegrates
- spindle microtubules begin attaching to kinetochores on sister chromatids
9
Q
Metaphase
A
- chromosomes are aligned at the spindle equator
- sister chromatids are attached to opposite poles of spindle
10
Q
Anaphase
A
- cohesins that hold sister chromatids together are destroyed
- sister chromatids are separated and move twoards opposite poles by 2 mechanisms
- kinetochore microtubules shorten
- spindle poles move further apart from one another
11
Q
Telophase
A
- chromosomes are funnly separated to opposite poles
- nuclear envelope reforms
- DNA decondenses
12
Q
Cytokinesis
A
- accomplished by progressive constriction and final scission of plasma membrane
- contractile ring of actin and myosin pulls plasma membrane inward as it constricts
- spindle equator (metaphase plate) determines location
- active membrane addition is required to accommodate increase in surface area
13
Q
How are cells stimulated to divide?
A
- mitogens
- erythropoietin
- antigen
- cytokines
- environmental stimuli initiate signal transduction cascade
14
Q
Cyclins
A
proteins expressed at different stages in the cell cycle and direct the events that occur duing that stage
15
Q
How do cyclins regulate transit of cell through cell cycle?
A
- bind w/ cyclin-dependent kinases (Cdk) to phosphorylate targets
- different cyclin-Cdk complexes are activated/ inactivated during each phase of cell cycle
- G1-cyclin
- S-cyclin: activates DNA synthesis machinery
- M-cyclin: activates spindle regulators, histones

