Embryology Flashcards
Define ovum. What are its structural components?
- unfertilized egg
- ovum nucleus in center, surrounded by zona pellucida and corona radiata cells on outer layer
Define sperm. What are its structural components?
- male gametocyte
- head w/ acrosomal cap, mitochondrial sheath, tail
Define embryo.
developing human until the 8th week of gestation
Define fetus.
developing human from week 9 to birth
Define conceptus.
all structures that deveop from zygote
What are the general steps that occur in fertilization?
- ovum suspended in meiosis II released into oviduct
- sperm enters oviduct and undergoes capacitation (loss of glycocalyx)
- sperm meets egg, genetic mingling takes 24 hours
- once fertilized, egg completes meiosis II and is activated
- zygote is now diploid, has a genetic sex
- cleavage initiated
What are the specific steps that occur when sperm first meets egg?
- sperm penetrates corona radiata
- enzymes: hyaluronidase, tube enzymes
- sperm tail wagging
- sperm penetrates zona pellucida
- sperm acrosome releases enzymes
- lysosomal enzymes from cortical granules in egg released
- zona reaction: becomes impermeable to other sperm
- ovum-sperm membrane fusion
- ovum completes meiosis II
- sperm mitochondria destroyed
- ovum activation
WEEK ONE: What happens during cleavage?
zygote undergoes division in oviduct, becomes morula (compaction) and then **blastocyst **(cavity organizes) which then hatches
WEEK ONE: What happens during hatching & implantation?
blastocyst hatches out of the zona pellucida & implants in the uterine lining (endometrium) via the blastocyst’s cytotrophoblast cells
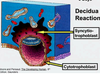
WEEK TWO: What happens during the final stages of implantation & the decidual reaction?
- Cytotrophoblast cells give rise to syncytiotrophoblastic cells: mass of cells without cell walls that spreads out from inner cell mass, and engulfs the uterine glands, releasing nutrients that encourage growth in conceptus, and maternal blood vessels, which create lakes of blood (lacunae coalesce)
- Decidual Reaction: maternal cells undergo change to contain nutrients and lipids to feed conceptus
- envelopment of maternal blood vessels establishes utero-placental flow
WEEK TWO: What happens during the formation of the bilaminar disk?
- former contents of the inner cell mast (hypoblast and epiblast) combine to form the bilaminar disk

WEEK TWO: What happens during the formation of amniotic cavity & yolk salk?
spaces form between inner mass cells to create amniotic cavity; yolk sac begins to expand to form embryonic mesoderm
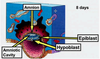
What does the Epiblast become?
- EMBRYO
- embryonic ectoderm
- embryonic mesoderm
- embryonic endoderm
What does the Hypoblast become?
- extra-embryonic endoderm of yolk sac –> extra-embryonic mesoderm
What is the amnion?
- large sac containing amniotic fluid in which the fetus is suspended by the umbilical cord
- fluid: absorbs jolts, allows for fetal movements, prevents adherence of embryo to surrounding tissues

