IBD Flashcards
distinguishing features b/t UC and Crohn’s disease


ulcerative colitis
- crytabcesses, cryptitis = chronic inflammation
differences in age and sex distrib in UC and Crohn’s
more males have Crohn’s, similar age distrib (highest onset rate in 20s-30s)

genetic susceptibility - which has more, Crohn’s or UC?
Crohn’s! much higher twin concordance
environmental risk factors for crohn’s and UC
smoking: protective in UC, risk in Crohn’s
appendectomy protective for UC
high sanitation level in childhood - risk for CD
UC - distribution of disease
- colon only
- continuous distribution
- rectal involvement
- mucosal inflammation

sx of UC
- rectal bleeding (hematochezia)
- diarrhea
- abdominal pain
- tenesmus and urgency
- systemic sx: fever, night sweats

Crohn’s: nodulatiry, ulceration, exudate, luminal narrowing
complications of UC
- hemorrhage
- toxic megacolon
- perforation
- colon cancer
lympocytic colitis
- a type of microscopic colitis
- watery diarrhea
- occurs in middle age adults, M =F
- normal endoscopy, but inflammation on microscopic level
collagenous colitis
type of microscopic colitis
- watery diarrhea but no bleeding
- predominantly older women
- normal endoscopy but inflammation on microscopic level
Crohn’s disease distribution and distinguishing feature
- transmural inflammation
- granulomas
- strictures
- skip lesions
- can have small bowel involvement
- rectal sparing
- perineal disease


Crohn’s
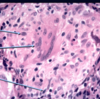
non-caseating granuloma in Crohn’s
Crohn’s clinical patterns
- inflammation: pain, tenderness, diarrhea, low-grade fever, weight loss
- confined perforation: mimics appendicitis (ileum), mimics diverticulitis (sigmoid colon)
- obstruction: cramps, distension, borborygmi, vomiting
- fistulization: to anywhere
- perineal complications
childhood presentations of IBD
- fever
- anemia
- arthritis
- failure of growth and development

apthous stomatitis - assoc w/ IBD
skin conditions assoc w/ IBD
- erythema nodosum: more w/ Crohn’s
- pyoderma gangrenosum: more w/ UC
extraintestinal manifestations of IBD
- aphthous stomatitis
- episcleritis and uveitis
- arthritis
- vascular complications
- skin: e. nodosum, p. gangrenosum
- hepatobiliary: primary sclerosing cholangitis

primary sclerosiing cholangitis - assoc w/ IBD
ddx IBD vs IBS


crypt abcesses in ACUTE (INFECTIOUS) COLITIS
*architecture intact (unlike UC)

Cryptitis

crypt abscess



