Histology of peripheral and nervous system Flashcards
Autonomic
Function and components
- Involuntary motor innervation to smooth muscle, glands, viscera
- Involuntary sensory from viscera
- Unmyelinated fibers (some nerves can be myelinated)
Somatic
Function and components
- Sensory and motor innervation
- Myelinated fibers
(myelinated nerves moves faster)
Categories of neurons
sensory
motor
interneurons
Types of Sensory neurons
somatic afferent
visceral afferent
Types of motor neurons
somatic efferent
visceral efferent
Multipolar neurons
One axon; two or more dendrites
Motor and interneurons
Found in ventral horn
Biopolar neurons
One axon, one dendrite
Retina and ganglia of CN VIII
Unipolar neurons
One axon
Sensory neurons
Dorsal root ganglia and cranial nerve ganglia
characteristics of neuron cell body
– Euchromatic nucleus
– Perinuclear cytoplasm
- Abundant rER and free ribosomes
- Ribosomal content appears as Nissl bodies in light microscope
- Numerous mitochondria, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, neurofilaments, and transport vesicles
– Axon hillock
- Free of cytoplasmic organelles

Characteristics of Dendrites
- Receive info and convey to cell body
- Greater diameter than axons
- Unmyelinated
- Form extensive arborizations called dendritic trees
- Cytoplasm of dendrites is similar to that of the neuron cell body
Characteristics of Axons
- Convey info away from cell body
- Only one axon/nerve
- Originates from the axon hillock
- Contain microtubules, neurofilaments, mitochondria and vesicles
- Myelinated
- Initial segment is where action potential is generated
- Carries action potentials to dendrites, cell bodies or axons
Function of synapses
Facilitate transmission of impulses from:
- Presynaptic to postsynaptic neurons
- Axons to effector cells (muscle and glands)
What is a terminal bouton
terminal branch of axon
Categories of Synapses
Axodendritic (b)
- Axons and dendrites
Axosomatic (a)
- Axons and cell body
Axoaxonic (c)
- Axons and axons

Types of synapses
(based on the signal used)
Chemical: Neurotransmitters
Electrical: Ion (cardiac and smooth muscle)
Components of chemical synapses
Presynaptic knob
- Synaptic vesicles which contain the neurotransmitters
Synaptic cleft
- Space that separates the presynaptic and postsynaptic neurons
Postsynaptic membrane
- Contains receptor sites for the neurotransmitter
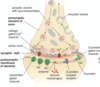
Types of axonal transport
Anterograde
retrograde
slow
fast
Anterograde transport
Carries materials from the cell body to the periphery
Kinesin is motor protein used
Retrograde transport
Carries materials from the axon terminals and dendrites to the cell body
Dynein is motor protein used here
Slow transport
From cell body to terminal bouton (0.2-4mm/day)
Only anterograde system
Fast transport
Rate of 20-400mm/day
Both anterograde and retrograde
Neuroglia of CNS
Oligodendrocyte
Astrocyte
Microglia
Ependymal cells

Function of Oligodendrocytes
form and maintain myelin
myelinate one or several axons
Function of astrocytes
Physical and metabolic support for neurons
Cover “bare areas” of myelinated axons
Maintain tight junctions of capillaries forming blood-brain barrier
Protoplasmic (gray matter) and fibrous (white matter)
Both types of astrocytes are identified via GFAP
Function of microglia
Phagocytic cells
Originate from bone marrow monocyte precursors
Function of Ependymal cells
Line ventricles of the brain and prosuce cerebrospinal fluid
Peripheral nervous system
What is it, what is the function
Collection of nerve fibers held together by connective tissue
Carry sensory and motor info
PCS cell body categories
Motor cell bodies
- Located in CNS (brain, brainstem and spinal cord)
Sensory cell bodies
- Located within or outside of the CNS in peripheral ganglia
- Dorsal root ganglia of spinal nerve
- Cranial nerve ganglia
- Autonomic nerve ganglia
Endoneurium
Innermost PNS tissue
Connective tissue surrounding individual nerve fibers
Bind fibers together into a bundle or fascicle
Schwann cells found here
Perineurium
Connective tissue surrounding nerve bundles
Contributes to formation of a nerve-blood barrier
Squamous, contractile cells found here
Epineurium
outermost PNS tissue
Dense connective tissue surrounding nerve bundles
blood vessels travel in this layer
Neuroglia of PNS
Schwann cells
Satellite cells
Function of Schwann cells
Produce myelin sheath (80% lipids)
- Ensure rapid conduction of nerve impulses
- Junctions between two adjacent Schwann cells are Nodes of Ranvier
- saltatory conduction
function of satellite cells
Support cells for neuron cell bodies of ganglia
Provide electrical insulation and promote metabolic exchange
Usually nuclei is only visible in H&E images
what determines the thickness of myelin sheath of the PNS
the diameter of the axon
Steps of the myelination in the PNS
Develops from compacted layers of Schwann cell mesaxon
- Cytoplasm is squeezed from between the membrane of the concentric layers of the Schwann cell
- Inner collar of Schwann membrane is next to the axonal plasma membrane
- Outer collar of Schwann cell membrane contains most organells of schwann cell
Diseases that cause demyelination
Guillian-Barre
Multiple sclerosis
Characteristics of Guillain-Barre
Autoimmune disorder
Effects the PNS
Large segments of the myelin sheath are damaged
Muscle paralysis, loss of muscle coordination, and loss of cutaneous sensation
Characteristics of multiple sclerosis
Autoimmune disorder
Effects the CNS
Myelin and oligodendrocytes are damaged
Plaques are apparent in white matter of CNS
Symptoms depend on region of CNS effected
Autonomic nervous system
Function and Categories
Conduct impulses to smooth muscle, glands, and cardiac muscles
Categories
- Sympathetic
- Parasympathetic
- Enteric
Sympathetic ANS
function and location
Responsible for fight or flight response
Neurons in thorax and lumbar regions (paravertebral) and abdominal (prevertebral) regions
Parasympathetic
function and location
counterbalances the action of the sympathetic nerves
Neurons in the brainstem and sacral spinal cord
Enteric ANS
function and location
Neurons found in the wall of the gut
Controls motility, exocrine and endocrine secretions and blood flow in the gut
Neuronal degeneration
Axon degenerated distal to injury (Wallerian degeneration)
Axons and myelin sheath fragment. Removed by Schwann cells (PNS) and microglial (CNS)
Loss of Nissl substance (chromatolysis) in cell body
Neuronal Scar formation
Occur between parts of severed nerve
- Connective tissue and Schwann cells in the PNS
- Glial cells in the CNS
Neuronal Regeneration
Schwann cells help bridge the gap in a severed nerve
- Form tubes which guide regenerating nerve sprouts
Gray matter in the spinal cord is found in
Ventral and dorsal horn
white matter in the spinal cord is found in
ascending and descending spinal cord tracts


