Epithelia and Connective tissue Flashcards
Four basic tissue types that compose all organs
Epithelial, Connective, Muscular, Neural
The polarity of epithelial cells
Basal Pole
apical pole
lateral domains
The basal surface of the epithelium is in contact with what other tissue type?
Connective tissue
How do you classify epithelial cells
1- Shape of the most superficial cell layer when sectioned perpendicular to exposed surface
- Squamous (flat/thin cells)
- Cuboidal (cells as thick as they are wide)
- Columnar (cells taller than they are wide)
2- Number of layers
- * Simple epithelium (single layer)
- Pseudostratified - Simple epithelium that appears stratified – all cells touch basal lamina, all do not reach exposed surface
- Stratified epithelium (two or more layers)
- Urothelium – special features allow distension
3- Apical surface specializations
- Cilia, Keratinization
Function of eptithelial cells
…
Types of stratified squamous epithelium
keratinized
nonkeratinized
Merocrine
vesicle contents released via exocytosis
- acinar glands of pancreas
Apocrine
vesicle contents released along with some plasma membrane
- mammary glands
Holocrine
entire cell fills, dies (apoptosis) and releases contents
- sebaceous glands of hair follicles
Endocrine Cells realease into..
the blood stream via exocytosis
Paracrine release onto…
neighboring cells via exocytosis
What are microvilli
fingerlike projection that increases the surface area of the cell.
Absorptive role
present in intestinal tract, kidney
When dense on apical surface, forms ‘brush border’
visible by light microscopy
What is the composition of microvilli?
- Composed of bundles of actin filaments (microfilaments)
- Barbed end of actin filament anchored to villin at tip of microvillus
- At base (apical cytoplasm of cell) actin filaments of microvillus extend into terminal web
- Actin filaments in microvillus are crosslinked by actin-bundling proteins (fascin, espin, fimbrin)
- Myosin I connects actin filaments to plasma membrane
- Myosin II provide contractile ability to terminal web
What is the composition of cilia?
Axoneme = inner core of microtubules
* Central pair of microtubules surrounded by nine peripheral pairs of microtubules (9+2 pattern)
* Extends from basal body (recall MTOC; 9 triplets)
Movement of cilia due to movement of microtubule doublet
Dynein bridges (between each microtubule of the doublet) use ATP to slide along doublet
Basal bodies (feet) coordinate cilia movement
3 basic categories of cilia
Motile cilia
Primary cilia (monocilia)
Nodal cilia
Motile cilia
typical 9+2 microtubules
move fluid – trachea, bronchi
Primary cilia
9+0 arrangement of microtubules
no active movement (immotile) but passively bend to fluid flow,
lack associated motor proteins
chemosensors, osmosensors, mechanosensors
Nodal cilia
9+0 arrangement of microtubules
motile cilia (active rotational movement)
bilaminar embryonic disc at primitive node (L-R asymmetry)
Stereocilia
Long processes (significantly longer than microvilli)
Not very motile (immotile)
Ultrastructure like that of microvilli
Bundles of actin filaments crosslinked by fimbrin, but villinabsent
where is stereocilia found?
- Absorptive function in epididymis & ductus deferens
- Mechanoreceptor function in hair cells of inner ear
Basolateral Epithelial cell specializations
Essential for barrier function
Important for cell-cell communication
Tight junctions (zonulae occludens)
The most apical of the cell-cell junctions in epithelia
Junctions form network of bands that completely encircle the cell
Extent of zonulae occludens determine strength of…
- barrier to flow of materials into space between epithelial cells
- barrier to apical and basal lateral diffusion of membrane proteins
Membrane seal between epithelia cells is due to…
transmembrane proteins (occludin, claudin, JAM)
intracellular proteins (zonula occludens – ZO-1, ZO-2, ZO-3)
Adherent Junctions (Zonula adherens)
Located basal to (i.e. “below”) zonulae occludens, encircles cell
Adhesion mediated by transmembrane cell adhesion molecules (CAMs)
Cadherin-cadherin binding (homophilic)
Intracellular domain of cadherin binds catenin, catenin bind vinculin & α-actinin, and then actin cytoskeleton
Ca2+ dependent adhesion
Desosome (Macula Adherens)
Disc shaped structure at a localized site (i.e. a “spot-weld”), does not form a band that encircles the cell
Transmembrane cadherins (desmogleins, desmocollins)
– homotypic binding
Intracellular domain of desmogleins & desmocollins bind anchoring proteins, plakophilin, plakoglobin, desmoplakin, that bind intermediate filaments (not actin)
Gap Junctions (communicating junctions)
Found between cells in almost all mammalian tissues
Circular patches of aggregated protein complexes
Gap junctions are formed by connexin proteins. Connexins form a hexameric complex (connexon). Each connexon has a hydrophilic core about 1.5nm in diameter that aligns with a connexon on the adjacent cell.
Permit bidirectional exchange of small molecules (<1.5nm) such as cAMP, cGMP, and ions

Hemidesmosomes
Adhesive structure found on basal surface of epithelial cells; between epithelial cells and the basal lamina
Resembles a half desmosome
Transmembrane integrins bind to the basal lamina
Cytoplasmic domain of integrins binds to plaque proteins (desmoplakin, plectin, BP230, erbin) which bind to intermediate filaments

Focal adhesions
Small cell attachments that anchor actin filaments to the basal lamina
Integrins bind to extracellular matrix proteins (e.g. fibronectin) and intracellularly to the actin cytoskeleton

What do integrins bind to?
Bind primarily ECM components
Binding promiscuity (i.e. multiple ligands can bind receptor heterodimer, multiple heterodimers can bind same ligand)
also binds RGD (arginine-glycine-aspartic acid) sequences
Generally low affinity binding to extracellular ligand
function of integrins
Mediate cell-cell and cell-matrix adhesive interactions
Recall focal adhesion sites, hemidesmosomes
Intracellular signaling – linked to actin cytoskeleton
“Inside out” activation – cytoplasmic tails change conformation of extracellular ligand binding site
Binds to many molecules
Cadherin function
Regulates calcium
Recall adherens junctions, desmosomes
Do not interact with ECM
Homophilic binding:
Like-like cadherin interactions greater
than like-nonlike cadherin interactions
Bidirectional signaling
Linked to cytoskeleton (actin, intermediate filaments)
Cadherin-catenin signaling – misregulated if adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) mutated = tumor
“Contact inhibition” – loss of E-cadherin in tumor progression
Immunoflobulin function
Homotypic and heterotypic interactions
Trans- and Cis-interactions
Trans-interactions can result in bidirectional signaling
Activate intracellular signaling cascades
Selectin function
Ca2+ dependent lectin domain – binds oligosaccarides
Binds mucin-like glycoproteins
high tensile strength (a few binding interactions sufficient to tether)
low binding affinity (hence leukocyte rolling)
Importance in leukocytes and platelet function
3 classes of connective tissue
cells
fibers
ground substance
What is the major component of connective tissue?
the extracellular matrix
Function of connective tissue
Encompass the major structural constituents of the body
Connects and binds tissues and cells in organs
Mechanical / Structural role
Medium for diffusion of nutrients and waste
Cells in connective tissue
Fibroblasts
Adipocytes
Macrophages
Mast cells
Plasma cells
Lymphocytes
Fibroblasts
Predominant cell type found in connective tissue
Synthesize collagen, elastin, glycosaminoglycans, proteoglycans, glycoproteins (i.e. produce fibers and ground substance)
Adipocytes
specialized for storage of neutral fats
Macrophages
phagocytic cells
Mast cells
promote local inflammatory response
Plasma cells
produce antibodies
lymphocytes
immune function
How do you characterize adult connective tissue
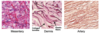
1- Loose (areolar): flexible, not resistant to stress
2- Dense
- Regular- collagen bundles, definite organization
- Irregular – collagen bundles, 3D network
3- Specialized
- Reticular: 3D mesh
- Adipose- 3D network reticular fibers
how do you characterize embryonic connective tissue?
mucous
mesenchyme
3 types of connective tissue fibers
Three types of connective tissue fibers:
Collagen fibers (collagen)
Reticular fibers (collagen)
Elastic fibers (elastin and fibrillin)
Composition of Fibers in connective tissue
Fibers in connective tissue are proteins that polymerize into elongated structures
collagen
Most abundant protein in human body (30% dry weight)
Type IV collagen is 50% of all basal lamina protein, part of basal lamina, form long fibrils, forms anchoring fibrils, form networks
Assembly of Collagen into triple helix
Repeating amino acid sequence of Glycine-X-Y
Most often X=proline, Y=hydroxyproline
Glycine is small, allowing tight association of the chains

Reticular fibers
Extensive network of extremely thin fibers (‘threadlike’)
Around parenchyma of various organs
Abundant in hematopoietic organs (spleen, lymph nodes, bone marrow)
Type III collagen
Elastic fibers
Thinner than collagen fiber; branching pattern
Sparse networks intersperse with collagen in tissues/organs that are subject to bending or stretching (i.e. arteries)
Composed of fibrillin and elastin
different proportions of fibrillin and elastin provide different resiliency to connective tissue
Extracellular matrix of connective tissue
Fibers (e.g. collagen, reticular), Proteoglycans,Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs)
Ground Substance
Part of Extracellular Matrix (ECM)
Highly hydrated and transparent (i.e. “gel-like”)
Fills the space between fibers and cells in Connective tissue
3 molecule classes of ground substance
Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs)
keratin sulfate, dermatan sulfate, etc…
* Proteoglycans
aggrecan, syndecan, etc….
* Glycoproteins (multiadhesive proteins)
fibronectin, laminin, tenascin, osteopontin, etc…..
Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs)
Repeating disaccharide of hexosamine (glucosamine or galactosamine) and uronic acid (glucuronic or iduronic) Forms linear polysaccharide
Highly hydrophilic
Highly viscous
All GAGs, except hyaluronic acid, are…
*covalently attached to proteins (to form proteoglycan)
*synthesized in Golgi
*rich in sulfate
*10-40kDa
Glycosaminoglycans: Hyaluronic acid (Hyaluronan
largest (100+ to 1000+kDa)
most ubiquitous GAG
synthesized into ECM by enzyme (hyaluronatesynthase)
located in plasma membrane
4 primary Components of basal lamina
Collagens
Laminins
Entactin/nidogen
Proteoglycans
Laminins
Cross-shaped glycoprotein composed of three polypeptide chains (α, β, γ)
Bind to integrins (receptors) on cell
Bind to nidogen/entactin to link to collagen
Bind to collagen IV

Entactin/Nidogen
Glycoprotein that contains three globular domains
Binds to laminin, collagen IV, fibronectin, fibrinogen
Links laminin and type IV collagen
Binds Ca2+


