Adipose and blood Flashcards
Funtion of adipose tissue
- energy storage (homeostasis)
- insulation
- cushioning
- hormone secretion (leptin)
- conversion of steroid hormones (estrogen, testosterone, glucocorticoids) to active forms
- thermogenesis
Characteristics of white adipose
Single lipid inclusion (unilocular)
‘signet-ring appearance’ – cell nucleus at eccentric position
Few blood vessels
Few mitochondria

Characteristics of brown adipose
Multiple lipid inclusions (multilocular)
UPC-1 (Uncoupling protein) is unique to brown adipose
Numerous mitochondria (cytochrome oxidase)
Numerous blood vessels
Sympathetic (norepinephrine) innervation regulates thermogenesis
5% total body mass of an infant

What is the relationship of plasma to interstitial fluid?
Higher protein content but there are equivalent amounts of solutes
Components of blood
Plasma
Erythrocytes
Buffy Coat: platelets and leukocytes
Components of blood plasma
mostly water
protein:
- albumin (70kDa protein) - colloid osmotic pressure
- Water is pulled from interstitial space
- globulins = immunoglobulins (γ-globulins), nonimmune
globulins (α-globulin, β-globulin)
- fibrinogen (340kDa protein) → fibrin (323kDa)
- Clotting factor
other solutes
Plasma vs Serum
Serum is plasma without fibrinogen and clotting factors
Erythrocyte
Function and structure
Function
- transport of O2 and CO2
- hemoglobin (96% in adult is HbA tetramer = 2α&2β globulin chains)
Structure
- Anucleate
- biconcave discs
- all are the same size - 7.5 um
What does the ABO blood group system use
glycoproteins & glycolipids attached to the extracellular domain of glycophorins (integral membrane proteins) on plasma membrane surface of erythrocytes

2 groups of leukocytes
Granulocytes: Eosinophil, Neutrophil, Basophil
Agranulocytes: lymphocyte, monocyte
Characteristics of neutrophil
granulocyte
most numerous WBC
multilobal nucleus
granules in cytoplasm not strongly stained
uses phagocytosis

characteristics of eosinophil
granulocyte
bilobal nucleus
eosinophilic stain of granules in cytoplasm pink bumpy part

characteristics in basophil
granulocyte
least numerous WBC
lobed nucleus (usually obscured by granules)
basic dyes stain granules in cytoplasm

characteristic of lymphocyte
most common agranulocytes
three groups based on size: S, M, L
‘spherical’ nucleus
little cytoplasm
Three distinct functional types:
T lymphocytes, B lymphocytes, Natural killer
cells

characteristics of monocytes
largest WBC
differentiate into phagocytotic cells (macrophages, osteoclasts)
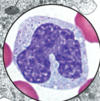
Platelets (thrombocytes)
Structure and function
Structure
anunclear, intact membrane
derived from megakaryocytes
Function
forms blood clots
involved in the maintenance and repair of blood vessels
red bone marrow means…
its is active
yellow bone marrow means…
its inactive and contains adipose cells


