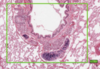
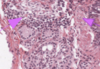
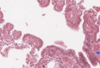
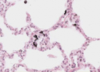
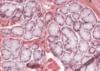
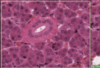
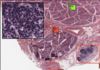
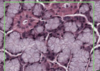
Histology Flashcards
What is this slide stained with? What stains blue with this stain?

Alcian blue
- GAG rich structures
- Mucous
- Mast cells
- Cartilage
What is this slide stain with?
What stains pink with this stain?
Eosin
- Colloidal proteins
- Plasma
Eosinophilic = Acidophilic
What is this slide stained with?
What stains black with this stain?

Iron haematoxylin
- Nuclei
- Elastic fibres
What is this slide stained with?
What stains magenta with this stain?
- Hexose sugars
- Goblet cell mucins
- Cartilage matrixs
- Glycogen
- Basement membranes
- Brush border
What is this slide stained with?
What stains:
- Purple
- Red/pink
- Pale blue
- Dark blue

Purple = chromatin/nuceli and netrophil granules
Red/pink = Erythrocytes/eosin granules
Pale blue = Lymphocyte/monocyte plasma
Dark blue/purple = Basophil granules
What is this stained with?
What stains:
Dark blue
Pale blue
Bright purple
Toludine blue
Dark blue = nuclei/ribosomes
Pale blue = cytoplasm
Bright purple = cartliage/matrix/mast cell and GAG rich
What is this slide stained with?
What stains:
Pink Red
Yellow/Olive green
Dark brown

Van giesons trichrome with haemotoxylin counter stain
Pink red = collagen
Cell cytoplasm = yellow/olive green
Nuclei = black
Elastic tissue = dark brown
What is this slide stained with?
What stains blue with this stain?
Haemotoxylin
- Nuclei
- RNA
What is this slide stained with?
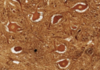
Silver stain
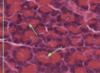
Describe neurones?
Neurones are large
25-60 microns
Because of the thickness of slides cannot see all processes
1 to 5 dentritic processes
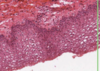
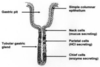
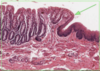
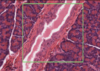
Where is the epithelium from?
What type of epithelium is it and describe it?
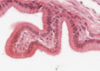
From the gall bladder
Simple columnar
- Height > width
- Oval nucelus
- Longer axis perpendicular to base of the cell
- Often microvilli or cilia at the apical membrane
- GUT ENTEROCYTES and RESPIRATORY TRACT
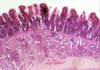
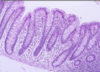
What type of epithelium is this?
Describe?
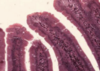
Intestinal epithelium
- Enterocytes with goblet cells
- Epithelia sit on BM permeability barrier between epithelium and connective tissue
- Microvilli at the apical surface (brush border)
- Brush border increases surface area
- Small intestine = simple columnar
Larger intestine > goblet cells
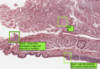
What is this a slide of?
What stain has been used?
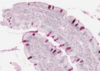
Microvilli/intestinal
Stained with PAS and haematoxylin
- Microvilli with carbohydrate rich glcocaylx
- Goblet cells and basement membrane rich in hexose
- The stain is magenta
What type of epithelium is this?

Cuboidal epithelium
- Square
- Round nucleus
- Ducts at exocrine glands: sweat glands, salivary, pancreas and kidney tissue
What type of epithelium is this?
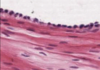
Squamous (serosa at outer wall of intestine)
- Outer surface of most thoracic and abdominal organs
- Simple squamous epthielum = serosa
- Also lines pleura and peritoneal cavities
- Air sacs of lungs
- Flattened
- Cylindrical ellpitical nuclei at the base
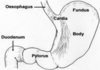
What type of epthielium is this where is it founf?
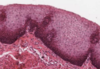
Stratified squamous non keratinsing epithlium (left is mouth)
Found in:
- Mouth
- Throat
- Oesophagus
- Anus
- Vagina
What type of epthielium is this?
Where is it found
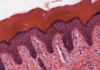
Keratinised stratified squamous epithelium
- Epidermis
- Lower layers are similar to stratified squamous
- Upper layers synthesise a unique collection of proteins - interact with cytoskeleton of cell to produce keratin
- Keratin: a dense protein that fills the cytoplasms of cells = tough and waterproof
- When the cell is full of keratin they die and are sloughed off
Left = Hairless skin at lower lip
pink = dead keratinised squames
Boundary later with blue keratohyaline granules STRATUM GRANULOSUM
What type of epthlium is this?
Where is it found?

Pseudostratified
Multilayered but stretches when flattened
Slide = trachea
Also found in urinary tract
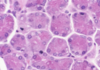
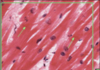
What is this slide showing?
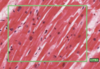
Caridiac muscle (myocardium)
- Branching chains of cardiac myocytes (15 x 100 microns)
- Striations (myofibrils and repeat sarcolemmas)
- Dark intercalated disks
How does cardiac muscle differ from skeletal?
Structurally
- Branched mononuclear with no stem cells
Phyisologically
- Contract and relax without rest, secrete hormones (ANP when stretech excessively, increases water/Na+/K+ excretion and inhibits RAAS)
What is this slide showing?

Intercalated disk
With desmosomes and adherant junctions (stick)
With gap junctions (electrical coupling)
Disc = Black
Myofibril = Blue/black
MIT/RBC = red
What are the functions of the intercalated discs?
Desomosomes anchor one cardiac muscle to the next by immediate cytoskeleton filaments
Gap junctions allow ion transfer between cardiac muscle - electrochemical coupling not cardiac conduction!
What is this slide showing?

Purkinje fibres (with PAS proceedure - magenta)
- Large modified muscles
- Large vacuoles
- Few myofibrils therefore pale H and E
- Stores of glyocogen (PAS)
Cardiac conduction
Describe valves?
- Thick collagen with occasional elastic tissue
- Both surfaces with endothelial cells
- Chordae tendinae = Fibrous
Describe pericardium?
- Single layer of mesothelial cells on the basement membrane with thin loose elastic/ fiberous tissue
Describe endocardium?
- Single layer on the heart
- Endothelial cellls are on the basement membrane with thin loose elastic/fiberous tissue
What is the slide showing?
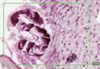
Artery = Left
Vein = right
3 layers
- INTIMA (innermost)
- endothelial cells on loose connective tissue with occasional myo-intimal cells - MEDIA (middle)
- smooth muscle, elastic and collagen - ADVENTITIA (outermost)
- dense collagen and elastic
What is the slide showing?

Muscular artery
- Well defined medial later (smooth muscle in concentric rings)
- Medial layer interspersed with elastic
- Media/intima divide = Wavy internal elastic lamina
- Adventitia = thick strands of collagen/elastic with vasa varsorum and nerves
- Adventitia/media divide = external elastic lamina only in large muscular
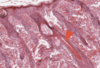
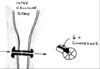
What is this slide showing?
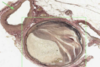
An artey with plaque and thrombus stained with iron haemotoxylin
What is this slide showing?

Elastic artery with mallory’s stain
- Elastic = red
- Collagen and muscle = blue
- Medial layer thick with concetric SHEETs of elastic interspersed with smooth muscle
- As vessels enlarge - contain their own blood supply = vasa vasorum
At the top = intima then i.e. vascular endothelial cells on basement membrane
What is this slide showing?

Arterioles
- 3 layers of fewer of muscle at the media
- No internal elastic lamina therefore may completely close when the muscles contracts
- Poor adventitia - mainly collagen and elastin
Function: highly responsive to vasoactive stimuli - regulation of peripheral resistace
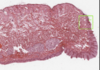
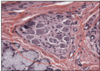
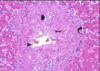
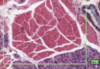
What is this slide showing?

Glandular acinus at the rectal mucosa
- Lined by enterocytes and goblet vells
n. b. mucosa does not ever contain blood vessels
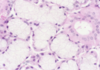
What is this slide showing?
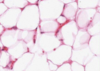
Mature adipose with capillaries
Describe capillaries?
- Sometimes have contractile pericytes
- Continous or fenestrated
Diameter is the size of an erythrocyte
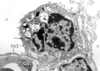
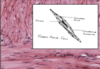
What is this slide showing?
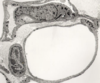
Enodthelial cells (electron micrograph)
- Specialised: released vasoactive substances
- Capillary at the centre - wall = 1 micron
Function of endothelial cells?
- Influence muscle tone
- Coagulation
- Produce cell adhesion molecules - influence lymphocyte/neutrophil migration
- AT of molecules acroos the cytoplasm
What is this slide showing?

Venules
- Thin walled
- Pericytes alongside them
- Pericytes become continuous as the vessel gets bigger
- In veins there are no pericytes, replaced by smooth muscle
- Irregular outline
What is this slide showing?

Veins, top left x2
- Same layers as arteries but thinner and poor boundaries
- Irregular outline, large lumen and therefore same blood at lower pressure
- Wider lumen than arterioles but slower flow therefore same vol/sec
What is this slide showing?
Large veins
- Thick wall
- Distinct intima/media layer
- Medial later with longitudinal smooth muscle
- Adventitia - thick with longitudinally arranged muscle fibres
What is this slide showing?
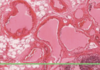
Lymph vessels
Describe lymph vessels?
- Pink staining blood plasma and valves
- Small = like cappillaires
- Large = like veins
- Walls = connective tissuse with some muscle
- Less pressure than in venules
- Somtimes lymphocytes
- Transports antigens and activates lymphocytes from tissue to lymph nodes and resident macrophages
- Drains excess fluid from tissue
- No nlood
What is this slide showing?

RBCs stained with leshimans stain - a type of romanovsky smears
- 44% of blood
- 4-5 million per microlitre
- Anucleate = leads to biconcavity
- lifespan = 120 days
- 7.5 microns
What is this slide showing?
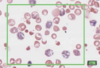
Reticulocytes
- Mature RBCs loose cytoplasm and nucleus
- Reticulocytes = immature RBC with some visible ribosomes, i.e. some dark staining granules
- <1% of circulating RBCs
- Increased number iwth increased RBC production in blood loss
What is this slide showing?
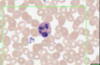
Eosinophils (romanovsky/leishman’s)
- 2 to 3 lobed nucleus
- Bright pink granules
- Acidophils
- Circulation for a few hours
- 5% of 1%
- Diurnal = highest in the morning
- Phagocytose antigen/antibody complexes associated with parsitic infection
- Neutralise histamine
What is this slide showing?

NEUTROPHILS (leishmans stain)
Polymorphonuclear leukocytes
- Multi lobar nucleus
- Most numerous (40-70% of 1%)
- Phagocytic
- Engulf and destory bacteria
- Leave blood stream to enter tissue at the infection site
Describe granulocytes?
Fine granules = Granulocytes
- Primary - lysosomes, acid hydrolases, antibacterial and digest
- Secondary - neutrophil specific, regulation of the inflammation response
- Teritiary - facilitate the insertion of proteins to cell membranes
What is this slide showing?

BASOPHILS
- Not multilobar
- Dark blue granules which appear to fill the cell
- Least common 1% of 1%
- Similar role to mast cells
- Secrete histamine and other vasoactive substances - increased blood flow locally
What is this slide showing?
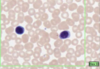
LYMPHOCYTES
- Small cells with dark staining nucleus
- 20-50% of 1% (most common non granulocyte)
- B and T indistinguishable
- Immature grow to be bigger than RBC, smaller than granulocytes
- Mature are roughy of equal size to granulocytes
What is this slide showing?

MONOCYTE
- Kidney shaped nucleus
- No granules
- Pale blue cytoplasm
- Immature cells with differentiate to various forms when the leave the blood and enter the connective tissue
- Many diff to a macrophage
In the blood and alveolar spaces
What is this slide showing?

PLATELETS
- Smaller than a red cell
- Anucleate
- Fragments
- From mutlinuclear megakaryocytes
- Blue
4 types of platelet granules?
- Alpha - clotting
- Dense
- Lysosomes
- Peroxisomes - elimation of oxygen radicals
What is this slide showing?
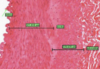
Muscular artery
- Circumferential smooth muscle at the media
- When this contracted reduces the diameter of .vessel
What is this slide showing?

Elastic tissue (elastic van giesons with iron haemotoxylin counter stain)
- Elastic tissue is in tube like sheets - elastic lamina
- Elastic = black
- Smooth muscle = mushroom
- Collagen = pink
What is this slide showing?
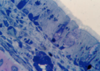
RESPIRATORY EPITHLIUM stained with toludine bone
SIMPLE/PSEUDOSTRATIFIEF COLUMNAR CILIATED EPITHLIUM
- Nuclei and ribosomes = dark blue
- Cytoplasm = blue
- Non ciliated goblet cells
- Underlying tissue rich in BVS and seromucous glands
- Mucous prevents the dehydration of epithelium and traps partical matter
What is this slide showing?
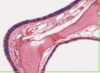
NOSE (H&E and Alcian blue)
- Mucous/cartilage = blue
- Central bone plate = pink
- Respiratory epithelium either side
- Thin walled blood vessels between epithlium and bone
- Mucous containing goblet cells stain bright blue
What is this slide showing?
NOSE
- Similar cillated respiratory epithelium except at the opening
- Concha covered in respiratory epithelium
- Swell bodies - thin arterioles/venules deep to the epithelium
- Thin skin allows the escape of water moistening air
What is this slide showing?
OLFACTORY EPITHELIUM
- Roof of the nose below the cribiform plate
- Pseudo-stratified columnar epithlium with basla and sustenacular (supporting cells)
- Bipolar neurons - dentric processes to surface
- Serous glands to surface( solvent to odourous substances)
- Thicker than respiratory epithelium
Speicialised cells = Bowman’s glands - small serous glands below the olfactory epithelium
What are sustenacular cells?
Tall narrrow cells in contact with basement membrane of olfactory epithelium
Bulky cytoplasm near lumen
Cytoplasm acculumates yellow/brown pigment
What does this slide show?

LARYNX
Respiratory epithelium except at the vocal folds
Vocal folds - stratefied squamous epithelium = more robust to with stand vibration
Below epiglottis larynx = 2 sets of folds
Describe the vocal folds?
Vocal folds
- Contain the free upper margin of elastic tissue (conus elasticus)
- Tensioned by voluntary skeletal muscle = vocalis muscle
FALSE FOLDS - upper = resp type
VESTIBULE - between = resp type
TRUE FOLDS = stratified squamous epithelium
What is shown on this slide?
TRACHEA
Pseudo-stratified, cilliated, columnar epithlium