Histology: Epithelial and Fibrous Connective Tissue Flashcards
Functions of epithelial tissue
- Physical protection
- Permeability
- Secretion
- Sensation
Characteristics of epithelia
- Cellularity
- Polarity
- Attachment
- Avascular
- Innervation
- Regeneration
Location of epithelium
basement membrane
(thin extracellular, felt-like sheet of macomolecules)
epithelium primarily involved in secretion
glands
Epithelial polarity
- apical surface - faces exterior surface/lumen of enclosed cavity
- basal surface - rests on basement membrane
- lateral surface - communicates/attaches to adjacent cells

Name 3 types of inter-cellular junctions.
- tight/occluding junction
- gap/communicating junction
- anchoring junction

Describe tight/occluding junctions.
- impermeable: allows cells to function as barrier
- encircle cells near apical surface
- increased junctions means decreased permeability
- ptns: occludins and claudins
Describe gap/communicating junctions.
- fluid-filled channels that connect apposed cells
- mediate communication
- connexin aggregates
Name 3 types of anchoring junctions.
- adherens
- desmosomes
- hemidesmosomes
lateral adhesions involving cadherins that interact with actin filaments
adherens
lateral adhesions involving cadherins that interact with intermediate filaments
desmosomes
basal adhesions involving integrins and intermediate filaments that anchor to basal lamina
hemidesmosomes
- Bacteria that cause food poisoning target ____ in the intestine.
- This causes _______.
- tight junctions
- loss of tissue fluid into intestinal lumen
- Helicobacter pylori causes gastric ulcers by binding to ____ in the stomach.
- This causes ______.
- tight junctions
- increasing permeability
- Pemphigus vulgaris (autoimmune disease) causes abnormal ____ function.
- This reduces ____ and causes _____.
- desmosome
- (reduces) cell-to-cell adhesion, (causes) blister of oral mucosa
Describe the basement membrane.
- specialized sheet of extracellular material
- located adjacent to basal domain
- selective barrier between tissue permits diffusion of nutrients

basement membrane

- apical specializations - microvilli
- cytoplasmic processes
- specialized for absorption
- number and shape correlate to cell’s absorptive capacity
- 1 mm long with up to 100k present on a single cell
Celiac disease is caused by ______.
loss of microvilli on absorptive cells in the small intestine

- apical specializations - stereocilia
- microvilli of unusual length, long, less mobile
- microtubule structure with actin core
- increases S:A for absorption/secretion
- restricted location: epididymis and hair cells of inner ear
- Type
- Location
- Function

- Simple squamous epithelial cell
- Location:
- (endothelium) lining of blood and lymphatic vessels
- (mesothelium) lining alveoli in the lungs, loop of Henle in kidney, variou ducts - Function: exchange, barrier, lubrication
- Type
- Location
- Function

- Simple cuboidal epithelium
- Location: kidney tubules, glands and associated ducts, terminal bronchioles, covering of the ovary
- Function: absorption, barrier, secretion
- Type
- Location
- Function

- Simple columnar epithelium
- Location: auditory tubes, uterus, oviducts, stomach, SI/LI
- Function: absorption and secretion
- Type
- Location
- Function

- Pseudostratiied Columnar Ciliated
- Location: lining of nasal cavity, pharynx, trache, bronchi
- Function: absorption and secretion, debris, particulate movement
- Type
- Location
- Function

- Urothelium
- Location: urinary bladder, ureters, urethra
- Function: barrier, distensible property
- Type
- Location
- Function
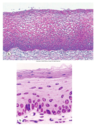
- Nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelial cells
- Location: oral cavity, portions of the pharynx, esophagus, anus, vagina, urethra, cornea
- Function: barrier and protection
- Type
- Location
- Function

- Keratinized straitifed squamous epithelial cells
- Location: epidermis of the skin
- Function: barrier and protection
- Type
- Location
- Function

- Stratified cuboidal epithelial cells
- Location: sweat glands and ducts, ovarian follicles, salivary gland ducts
- Function: barrier and passageway
Name 2 types of membranes
- mucous
- serous membrane
epithelial tissue that secrete mucus
(lines many body cavities and tubular organs including the gut and respiratory passages)
mucous membrane
- epithelial tissue that lines internal body cavities
- (forms a smooth, transparent, 2-layered membrane, lubricated by a fluid derived from serum, includes peritoneum/pericardium/pleura)
- includes mesothelium
serous membrane
epithelial cells that produce and secrete a product as individual cells or as specialized organs
glands
classification based on how products are released
exocrine vs. endocrine
ways that glands are classified
- exocrine vs. endocrine
- arrangements and shape of cells and ducts
ways that signals are released
paracrine or autocrine
Name the gland and its characteristics

- unicellular glands
- simplest in structure
- single, secretory cells distributed among non-secretory cells
- goblet cells
mucus-secreting cell lining the intestines and respiratory tract

goblet cell
Describe exocrine glands.
- multicellular glands comprised of acini (secretory cells)
- product is secreted into a system of ducts for release
- parenchyma
- secretory units supported by stroma of CT
functional tissue of an organ, which does not include CT and other tissues
parenchyma
partitions that separate gland into lobules
septa
name of structure when entire gland is enclosed
capsule

serous acini

mucous acini

mucoserous acini
Name this gland.

parotid gland
Name this gland.

sublingual gland
Name this gland.

submandibular gland
secretion is delivered in membrane-bound vesicles to apical surface and undergo exocytosis

merocrine gland
secretion accumulates within a cell –> apoptosis
secretion and cell debris are released

holocrine gland
release of the apical portion of the cell, surrounded by cytoplasm within a plasma mebrane

apocrine gland
branched secretory portion

simple branched acinar
secretory cells form sac-like structures

simple acinar

simple branched tubular

simple coiled tubular
secretory cells from straight tube

simple tubular
coiled secretory portion

compound tubular
saclike seretory units

compound acinar
tubular and acinar secretory units

compound tubuloacinar
thyroid, anterior pituitary, adrenal, pancreas (islets of Langherans)
endocrine - glandular
major salivary glands, liver, pancreas (acinar tissue)
exocrine - glandular
sebaceous glands, Brunner’s glands of dudoenum, small salivary glands, breast, prostate
compound glandular
colon, stomach, eccrine sweat glands
simple glandular
lower urinary tract (renal pelvis, ureters, bladder, urethra)
transitional
gallbladder, collecting ducts on kidney, endocervix
simple columnar
respiratory tract including nose and sinuses
pseudostratified, ciliated
fallopian tubes
simple ciliated
collecting tubes of kidney, rete testis, small ducts of exocrine glands, surface of ovary
simple cuboidal
larger ducts of exocrine glands
stratified cuboidal
epidermis
keratinized stratified squamous
lining oral cavity, epiglottis, esophagus, anus, cervix, vagina, vulva, glans penis, cornea
non-keratinized stratified squamous
lining blood vessels (endothelium), lining body cavities (mesothelium), alveoli of lungs, Bowman’s capsule, and loop of Henle of kidney
simple squamous epithelium
- gel-like substance with embedded protein fibers
- mineralized in the bone
ECM
- not exposed to outside environment (separated by epithelium)
- separated from each other by ECM
- separated into embryonic and adult CT
types of fibrous CT
- loose
- dense regular
- dense irregular
- special: adipose, cartilage, bone, hematopoietic
functions of connective tissue
- structural framework of the body
- protection
- supports and interconnects other tissues
- energy storage
- transports fluids, cells, and dissolved chemicals throughout the body
- defense against invasion by microorganisms
produce collagens, proteoglycans, glycoproteins
fibroblasts
connective tissue stem cells
mesenchymal cells
store and release fats
adipocytes
produce and maintain cartilage components
chondrocytes
produce bone components
osteoblasts
produce RBCs and immune cells
hematopoietic stem cells
ECM of connective tissues (fibrous component)
- collagen: resist tension
- elastin: stretchable fiber (assembly of tropoelastin, fibulin-1, fibrillins 1/2)
- reticular fibers: form supportive meshwork
aligned and crosslinked to increase tensile strength

type I collagen fibers
amorpous ground susbtance
- ECM of CT
- includes proteoglycans, hyalouronan, glycoproteins, and extracellular proenzymes
types of proteoglycans
- chondroitin sulfates
- heparan sulfates
- keratan sulfates
types of glycoproteins
- cytokines
- growth factors
- structural proteins
cell-ecm interactions
- integrin receptors (bind ECM components and initiate intracell. signaling)
- syndecans
- cd44
- selectins
- gfrs
- cytokine receptors
- rich in ECM
- rich in mesenchymal stem cells
- some collagen/reticular fibers
- UC: “warton’s jelly”
embryonic connective tissue
self-renewing population serving as source of production of differentiated cells throughout life
stem cells
Adult mesenchymal stem cells are ____ stem cells.
multipotent
They can differentiate into variety of cell types including fibroblasts, muscle cells, osteoblasts, chodrolasts, adipocytes.
types of fibrous connective tissue classes
- loose CT
- dense CT
types of loose connective tissue
- areolar: low density tissue w/ fixed + wandering cells; widespread
- adipose: fat containing
- reticular: rich in reticular fibers; forms open framework for supportive mesh to hold free cells
types of dense connective tisse
- dense irregular CT: fibers deposited in random pattern
- ex: dermis
- dense regular CT: fibers deposited in regulated pattern
- ex: tendons connecting skeletal muscle to bone
- elastic conentive tissue: rich in elastin
cell types in loose areolar connective tissue
- fixed
- fibroblasts
- adipocytes
- mesenchymal cells
- wandering
- macrophages
- mast cells
- leukocytes/lymphocytes
- plasma cells
- functions to support and bind other tissues
- hold body fluids
- defensd against infection
- found beneath membranous epithelia and around blood vessels, muscles, nerves

loose CT

loose areolar CT

adipose connective tissue
- abdundant adipocytes and sparse ECM
- reserve energy source and insulation
- support and protect organs
- found under skin and around organs, within abdomen, breasts, buttocks
types of fat
- white fat: functions in energy storage, insulation, cushioning vital organs, hormon secretion
- brown fat: key thermogenic tissue, abundant in newborns, reduced in adults

brown fat

white fat

reticular conenctive tissue
- rich in reticular fibers
- forms open framework to create labyrinth for holding free cells
- found in liver, BM, lymph nodes, splen
- meshwork houses blood cells and immune cells

dense irregular connective tissue
- ECM of tithglty packed, interwoven collagen fibers running in random pattern
- fibroblasts = principle type
- found in dermis of skin, capsules surrounding internal organs, perichondrium/periosteum, fascia

dense regular connective tissue
- ECM of tightly packed, regularly arranged collagen fibers
- fibroblasts = principle cell type
- resists pulling force
- poor vascularization
- wavy appearance (not under tension)
- found in tendons, ligaments, aponeurosis, dense fascia, joint capsules

elastic connective tissue
- high proportion of elastic fibers
- allows recoil of tissue following stretch
- found in BV walls, bronchile tubes, special ligaments
function to produce collagen, elastin, reticular fibers, proteoglycans, and glycoproteins in ECM

fibroblast
- closely packed with their nuclei pushed to side by large _ droplet
- removes _ from blood, stores, and releases it into bloodstream
- provides reserve energy source

adipocytes
- differentiate from blood monocyte
- function is phagocytosis and destruction of bacteria, damaged or sick cells, removal of cell debris, and antigen processing/presentation

macrophages
- secrete chemicals such as histamine to mediate allergic response and heparin (anti-coagulant)

mast cells
- differentiate from B-lymphocytes
- function to produce antibodies that mediate immunity

plasma cells


