Hernias Flashcards
Define what a hernia is
Any protrusion of a viscus (any large interior organ) or part of a vicus through a defect of the walls that contains it into an abnormal position
What are the risk factors for the development of hernias ?
- Anatomical e.g. sites where structures exit through an opening in the cavity.
- Inherited collagen disorders
- Sites where surgical incisions are made
- Obesity
- Ascites
- Increasing age
List the different types of abdominal wall hernias
- Epigastric
- Umbilical
- Paraumbilical
- Inguinal Hernia
- Femoral Hernia
- Spigelian Hernia
- Lumbar Hernia
- Incisional Hernia
- Parastomal Hernia
- Port-Site Hernia
- Obturator hernia

Ignoring the classification based on anatomical location what are the different classifications of abdominal wall hernias ?
- Reducible - Hernia can be easily pushed back into the abdomen.
- Incarcerated or Irreducible hernia - When a hernia cannot be manipulated back to the abdomen.
- Strangulated Hernia - Vascular supply to the contents contained within the hernia is compromised, resulting in ischaemic and gangrenous tissue. Patient becomes toxic and requires surgery
- Obstructed hernia - bowel contents cannot pass through the hernia, classical symptoms of intestinal obstruction soon appear
What defect results in an epigastric hernia ?
A fascial defect in the linea alba between the xiphoid process and the umbilicus.

What are the typical features of an epigastric hernia ?
- Lump in the midline between umbilicus and the xiphisternum
- Asymptomatic (75%) or can present with pain.
- If incarcerated or strangulated symptoms depend on organ involved.
- Most common in men aged 20-30 years
What is the management of epigastric hernias ?
Either conservative or surgical.
What are the risk factors for paraumbilical hernias and what age group do they occur in ?
- Occur in all age groups.
- Risk factors include stretching of the abdo wall by obesity, multiple pregnancy and ascites.
What are the typical presenting features of paraumbilical hernias ?
- Asymmetrical bulge - half the sac is covered by skin of the abdomen directly above or below the umbilicus
- Often painful

What usually causes umbilical hernias ?
Persistent elevation of intra-abdo pressure
What are the typical presenting features of an umbilical hernia ?
- Symmetrical bulge under the umbilicus
- Often painful

What is the management of paraumbilical & umbilical hernias and why ?
Surgical - because they do not resolve spontaneously and have a high incidence of incarceration and strangulation.
Who is at greatest risk of infantile umbilical hernia development and how are they managed ?
- Symmetrical bulge under the umbilicus
- More common in premature and Afro-Caribbean babies
- The vast majority resolve without intervention before the age of 4-5 years
- Complications are rare
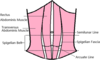
Describe the anatomy of the inguinal canal, specifically its:
- Start and finish
- Borders
- What it transmits
Starts at deep inguinal ring and ends in superficial inguinal ring.
Boundaries:
- Anterior –External oblique aponeurosis
- Floor – ligament
- Roof – Conjoint tendon
- Posterior – Transversalis fascia
Transmits the spermatic cord and ilioinguinal nerve in males and the round ligament of the uterus and ilioinguinal nerve in females

What are the 3 coverings of the spermatic cord ?
- Internal Spermatic Fascia
- Cremasteric Fascia
- External Spermatic Fascia

What are the 6 contents of the spermatic cord ?
- Vas Deferens
- 3 Arteries: Testicular Artery, Artery to the Vas and Cremasteric Artery
- Pampiniform Plexus (Veins)
- Lymphatics
- Nerves: Genital branch of Genitofemoral nerve + Sympathetic Twigs
- Remains of the Processus Vaginalis
What are the 3 things that form the hesselbach triangle ?
- Laterally: Inferior Epigastric Artery
- Medially: Lateral Border of the Rectus Muscle
- Inferiorly: Inguinal Ligament

What are the 2 types of inguinal hernias ?
Direct & indirect
Describe the anatomy of a direct inguinal hernia
- A direct inguinal hernia pushes directly forward through the posterior wall of the inguinal canal (transversalis fascia), into a defect in the abdo wall (hesselbachs triangle)
- They sit within hesselbachs triangle medial to the inferior epigastric vessels & lateral to the rectus abdominus

Describe the anatomy of an indirect inguinal hernia
They pass through the deep inguinal ring & if large out through the superficial ring

Who is much more commonly affected by inguinal hernias - M or F?
Males - 95%
What is thought to be the underlying cause of inguinal hernias ?
- Patent processus vaginalis + pathological change in connective tissue
- Anything that increases intra-abdo pressure or past abdo surgery are also risk factors
What are the characterisitc features of an inguinal hernia ?
- Groin swelling located above and medial to the pubic tubercle
- usually disappears when lying down.
- Discomfort/ache on activity - severe pain and strangulation is rare
- Cough impulse - swelling expands upon coughing
- May cause intestinal obstruction
- More common to present on the Right side of the groin

What investigation can be done if you are unsure a swelling is an inguinal hernia or not ?
Dynamic US