Health Psychology Flashcards
1
Q
Health Psychology
A
- Emphasizes psychology’s role in establishing and maintaining health and preventing and treating illness
- Lifestyle choices, behaviors, and psychological characteristics can play important roles in health
2
Q
Health Promotion
A
- Helping people change their lifestyle to optimize their health and assisting them in achieving balance in physical, emotional, social, spiritual, and intellectual health and wellness
3
Q
Public Health
A
- Concerned with studying health and disease in large populations to guide policymakers (identify health concerns, set priorities, design interventions for health promotion)
4
Q
Behavioral Medicine
A
- Developing and integrating behavioral and biomedical knowledge to promote health and reduce illness
5
Q
Biopsychosocial Model
A
- How we look at concerns through Health Psychology
6
Q
Health Behaviors
A
- Practices that have an impact on physical well being
- Example: Exercising, eating, smoking, drinking, etc
7
Q
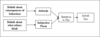
Theory of Reasoned Action
A
- Effective change requires individuals to have specific intentions about their behaviors, as well as positive attitudes about a new behavior, and to perceive that their social group looks positively on the new behavior as well
You smoke and you want to quit smoking, you will be more successful if you devise an explicit intention of quitting, feel good about it, and believe that your friends support you
8
Q
Theory of Planned Behavior
A
- Includes the basic ideas of the theory of reasoned action but “adds” the person’s perceptions of control over the outcome

9
Q
Stages of Change
A
- Model describing a process by which individuals give up bad habits and adopt healthier lifestyles

10
Q
Four ways Setting Goals Affects Outcomes
A
- Choice: Goals narrow attention and direct efforts to goal-relevant activities, and away from perceived undesirable and goal-irrelevant actions
- Effort: Goals can lead to more effort; for example, if one typically produces 4 widgets an hour, and has the goal of producing 6, one may work more intensely towards the goal than one would otherwise
- Persistence: Someone becomes more prone to work through setbacks if pursuing a goal
- Cognition: Goals can lead individuals to develop and change their behavior
11
Q
General Adaptation Syndrome
A
- Term for the common effects of stressful demands on the body, consisting of three stages; alarm, resistance, and exhaustion
- Alarm
- Resistance
- Exhaustion

12
Q
Alarm
A
- Temporary state of shock during which resistance to illness and stress falls below normal limits
- Body releases hormones that adversely affect the functioning of the immune system
- Body is prone to infections from illness and injury
13
Q
Resistance
A
- Glands throughout the body manufacture different hormones that protect the individual
- Immune system can fight off infection with remarkable efficacy
14
Q
Exhaustion
A
- Wear and tear takes its toll, vulnerability to disease increases
- Heart attach or death can occur
15
Q
Hypothalamic Pituitary Adrenal Axis
A
- Complex set of interactions among the hypothalamus, the pituitary gland, and the adrenal glands that regulates various body processes and controls reactions to stressful events


