Head and Neck Radiology Flashcards
identify the indicated features of the skull


Identify the indicated features of the skull


Identify the indicated features of the skull


Identify the indicated features of the radiograph
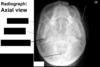

Identify the indicated features of the radiograph. How would you position a patient for this view? Why is this positioning done?

Head is extended backwards, so orbit is going up to ceilig, and temporal bones going inferior, so can see orbit and sinuses better

What are the 3 places to look for the type of Le Fort arch?
I: anterior lateral corner nasal apeture
II: inferior orbital rim
III: zygomatic arch

What fracture is showin in the image?
What are the 3 points of fracture?

Tripod Fracture
- zygomatic maxillary suture
- frontal zygomatic area
- zygomatico temporal suture

What type of fracture is shown in the image?
What is the the concerning feature indicated in the image on the bottom right?

Blow-out fracture
by definition, does not fracture orbit rim
blow to orbit, the eye globe makes its way posterior, so one of walls of orbit blows out
can be surgical emergncy
Lower Right: inferior rectus muscle is displaced
Identify the indicated feature of the radiograph


Identify the ndicated features of the skull


Identify the indicated features of the skull
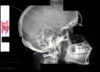

What is the features shown in the image?

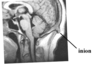
Identify the indicated feature of the pediatric skull? Why is it important to be cogniscent that this is a pediatric skull?


What are feature to identify a skull fracture from a suture?
know typical location of sutures
interdigitation seen in suture
margin of suture are soft, composed to hard margin (abrubt transition) of a fracture

Identify the feature indicated by arrows

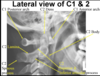
Identify the features indicate by the arrows. What features are looking for specifically?

symmetricla on either side of dens
the alignment of the latera masses wiht the superio articular facet of axis

What are the expected contours of the prevertebral soft tissue?
What situations could change this?
What superimposed image could make it look pathogenic?
concave
convex
convace
Obesity and phase of respiration
superimposed soft palate

What type of fracture is seen on the radiograph? What featuers are you looking for?

Symmetry on either side of the dens
alignment of lateral masses
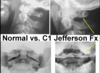
What type of fracture is seen in the image?
What bone is fractured?

Jefferson fracture (radiogrph and CT)
atlas
What type of fracture is show in the image?
What feature is fractures?

Pars interarticularis of axis

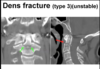
Where are fracture locations for type I, type II and type III dens fractures?
What type of fracture is shown in the image?

Type I: tip of dens (usually stable)
Type II: base of dense (unstable)
Type III: body of axis (unstable)

What type of fracture is shown in the image?
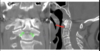
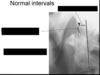
Identify the indicated features. What should be the maxium distance between the indicated intervals?

What was replaced in the CT shown?

The codyles were replaced in the axis after cervical dislocation

Why are frontal bone fractures concerning?

Sinus material/external material can make its way into the cranial cavity
Identify the indicated features of the CT.


Identify the indicated features of the CT

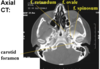
Identify the indicated features of the CT
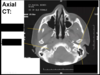

What features shuld you look for when you are concerned about a facial fracture?
Addition of air or blood

Identify the features indicated on the CT

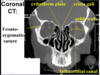
Identify the featues indicated on teh CT of the neck




