Bony Orbit Flashcards
(29 cards)
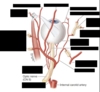
Identify the bones that make up the orbit


Identify the important passage points through the orbit


What is the difference bewteen the orbital axis and the visual (optical) axis?
23 degrees

How many layers are there to the eyeball?
What are their components?
- Outer: fibrous
- sclera
- white of eye
- maintains shape of eye
- attachment point for muscle
- cornea
- transparent
- avascular
- sclera
- middle: vascular
- choroid
- heavily pigmented to prevent scattering of light
- ciliary body
- helps lens stay in position (accomodation)
- iris
- constrictor pupillae
- dilator pupillae
- choroid
- Retina
- Neural layer
- optic disk
- macula
- pigmented layer
- Neural layer

What is the clinical term for pupil contstriction? Which autonomic system controls this action?
What is the clinical term for pupil dilation? Which autonomic system controls this action?
- Constriction
- miosis
- parasympathetic
- Dilation
- mydriasis
- sympathetic
Identify the compartments of the eyeball and their components.
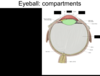

What is the impact of lens shape when the chilary muscles contract?
when the ciliary muscle is contracted, the zonular fibers are relaxed, and the lens becomes more conved (fatter) which provides focus for near objects.

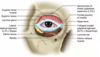
What are the layers of the eyelids?
- Thin skin
- obicularis oculi
- palpebral part
- orbital septum (Periosteum to tarsi)
- tarsus
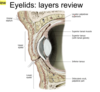
What muscle is indicated?
What is its function?
Attachment?
Innervation?

Levator palpebrae superioris (LPS)
- What is its function?
- elevates upper eyelid
- Attachment?
- Innervation?
- cranial never III
What muscle is indicated by the photo?
What is its function?
Attachment?
Innervation?

Superior tarsal
- What is its function?
- helps keep eyelid open (helps LPS)
- Attachment?
- origin: LPS
- Innervation?
- smooth muscle
- sympathetic
What are the squiggly lines indicated it the photo?

Tarsal glands
What is the name of the mucus membrane tha tlines the sclera and the eyelid? What is it called when the different parts meet?
Conjunctivia
- Bulbar: lines sclera
- palpebral: lines eyelids
- fornicles:
where they meet: canjunctival fornix
Describe the route of the lacrimal apparatus and identify the structure.

From the gland to the duct, superior conjunctional fornix
2 gaps = puncta
superior/inferior canaliculi to the lacromal sac, which drains into the
nasolacrimal duct

What are the 3 axis of eye movemet?
vertical, anterior/posterior, and transverse

Identify the extrinsic muscles of the eye shown in the image.


Identify the extrinsic muscles of the eye shown in the image.


What muscles are indicated by the photo?
What is its function?
Innervation?
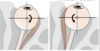
Lateral rectus
- ABDuction
- innervation (CN VI ABDucens)
Medial rectus
- ADDuction
- Innervation (CNIII)
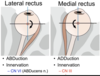
What is the common attachement point for all the rectus muscles? What nerves are located within?
common tendinous ring
- inferior branch of oculomotor nerve (III)
- Abducent nerve (VI)
- nasociliary branch of opthalmic nerve (VI)
- supeiror branch of oculomotor nerve (CNIII)
- ophthalmic artery
The only muscle that has nothing to do with the CTR is the inferior oblique

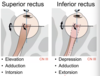
What muscles are indicated by the photo?
What is its function?
Innervation?

Superior rectus
- Function
- elevation
- adduction
- intorsion
- Innervation
- CN III
Inferior rectus
- Function
- depression
- adduction
- extorsion
- Innervation
- CN III
What muscles are indicated by the photo?
What is its function?
Innervation?
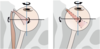
Superior Oblique
- Function
- depression
- abduction
- intorsion
- Innervation
- CN IV
Inferior Oblique
- Function
- elevation
- abduction
- extorsion
- Innervation
- CN III
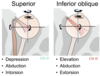
How to test:
- LR
- MR
- SR
- IR
- IO
- SO
- LR
- look laterally
- MR
- look medially (toward nose)
- SR
- look toward ear (close gap)
- look up
- IR
- look toward ear (close gap)
- look down
- IO
- look toward nose (close gap)
- look down
- SO
- look toward nose (close gap)
- look up
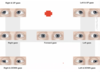
Nerves of the orbit
- Optic
- sensory
- Oculomotor
- eye muscles
- Trochlear
- superior oblique
- Abducens
- lateral rectus
- Opthalmic
- anterior orbit
LR6SO4R3 –> chemical formula to remember
What structures do the Optic Nerve pass through?
What types of fibers does it carry?
- through optic canal and common tendinous ring
- ensheathed in meninges
- high intracranial pressure
- can lead to edema around the nerve
- sensory nerve
Describe the path of the oculomotor nerve.
What are the symptoms when there is damage to this nerve?
Splits into an inferior and superior division
- Superior
- Superior Rectus
- LPS
- Inferior
- inferior oblique
- medial rectus
- inferior rectus
- Also controls accomodation and pupil constriction
- If there is a lesion
- “down and out” appearance (only lateral rectus and superior oblique are working)
- ptosis (when upper eyelid droops over eye)
- myadriasis
- issue w/ accomodation
- diplopia (double vision)
- “down and out” appearance (only lateral rectus and superior oblique are working)