Craniovertebral Joints/Pharynx Flashcards
What type of joint is the atlas and occipital bone?
What type of motion does this joint permit?
synovial
axis of rotation
flexion and extension
What are the 3 joints the compose the atlas-axial joint?
- Inferior articular surface ofo lateral mass of axis with superior articular facet of atlas x2
- slope of superior articular facet is important relative to fractures
- 45 degrees is normal rotation movement
- Dens and anterior arch of atlas
- pivot joint
- 2 synovial cavities
What artery perforates the posterior atlantooccipital membrane?
vertebral artery
Identify the indicated cerbical ligaments


Identify the indicated cervical membranes/ligaments.
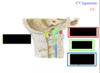

Identifiy the indicated cervical ligaments


What are the 3 types of fractures that can occur to the atlas and the axis?
- Burst
- vertical load through vertebral column
- at least 2 fracture points
- Hagman’s fracture
- fracture of pars interarticularis
- due to hyperextension
- Fracture of the Den’s
- cand fracutre are different places
Identify the sections of the pharynx. Where is the pharynx located with regards to the vertebral column?

anterior to the vertebral column
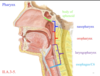
What is the priamy motor nerve innervatign the pharynx? Sensory?
Motor: vagus (CN X)
Sensory: Glossopharyngeal (CN XII)
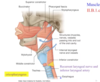
Identify the 3 muscules indicated in the photo. What is their function? What is their common posterior attachment?
Which is most superficiel?

Function: they constrict to propel structures down towards the esophagus; involved in swallowing & phonation
Attached Posterioly to pharyngeal raphe
Open anteriorly
inferior is most superficial

What are the 2 arteries that feed the pharynx?
Ascending palatine artery
ascendign pharyngea artery (ECA)
What are the anterior and posterior attacment points for superior constrictor?
What are the contents of the superior gap?
- Posterior
- Pharyngeal tubercle
- pharyngeal raphe
- Anterior
- Pterygoid hammulus
- pterygomandibular raphe
- Superior Gap
- pharyngobasilar fascia
- levator veli palatini (muscle)
- pharyngotympanic Tube

Attachment point for middle constrictor
Contents of gap between superior constrictor and middle constrictor
- Anterior
- greater and lesser horn of the hyoid
- stylohyoid ligament comes between the superior and middle constrictor
- Posterior
- pharyngeal raphe
- Gap between middle and superior constrictor
- stylopharyngeus
- innervated by glossopharyngeal nerve
- stylohyoid ligament
- stylopharyngeus

Attachment of inferior constrictor muscle
Contents of gap between inferior constrictor and middle constrictor
- anterior
- oblique line on thyroid cartiledge to cricoid cardiledge
- posterior
- pharyngeal raphe
- Gap between inferior and middle constrictor
- thyrohyoid membrane
- superior laryngeal arter
- internal laryngeal neve
What is the most inferior portion of the inferior pharynx. What nerve name change occurrs at this muscle?
cricipharyngeus
- Location
- cricoid cartiledge and start of esophagus
- Function
- reduce reguigitation of stuff back up the esophagus
- Nerve
- Recurrent laryngeal nerve turns into inferior laryngeal nerve
- inferior laryngeal artery
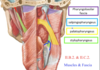
Idenify the indicated internal muscles

Salpingopharyngeus: “from tube to pharynx”
palatopharyngeus: “lateral porion of uvula” “from palate to pharynx”
stylopharyngus: btw gap between superior and middle constrictor; attach to thyroid cartiledge
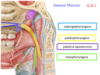
Identify the indicated internal pharynx muscles

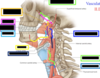
Identify the arteries that supply the pharynx
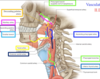
What venous system does the pharynx vasculature drain into?
WHat about the lower pharynx?
Ptergygoid plexus
external jugular
What veins drain the palatine tonsils adn tonaillar bed?
external palatine vein
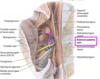
In what form do nerves innervate the pharynx? What nerves contirbute?
pharyngeal plexus
(from vagus adn glosopharyngeal)
glossopharyngeal : sensory
Vagus: motor
maxillary nerve in superior pharynx (V2) rest is glossopharyngeal sensory

What is the key lymph node of the pharynx?
Where is it located?
jugulodigastric node: behind parotid above, over internal carotid artery behind SCM, primary feeded for most pharynx
Identify the indicated nasopharynx components




