HaDSoc Flashcards
(58 cards)
Define an adverse event
An injury caused by medical management rather than underlying disease, and that prolongs hospitalisation, produces disability or both
Describe the Swiss Cheese Model of Accident Causation (aka James Reason’s Framework of Error)
There are successive layers of defences, barriers and safeguards. However errors occur because of active failures that are acts that directly lead to the patient being harmed (e.g. drug overdose) or because of latent conditions (predisposing conditions which mean active failures are more likely e.g. poor training, poor supervision)
How does systems-based approach promote patient safety and quality in healthcare?
- Avoid reliance on memory
- Make things visible
- Review and simplify processes
- Standardise common processes and procedures
- Routinely use checklists
- Decrease reliance on vigliance
Define clinical governance
A framework through which NHS organisations are accountable for continuously improving the quality of their services and safeguarding high standards of care by creating an environment in which excellence in clinical care will flourish
Define clinical audit
Quality improvement process seeking to improve patient care and outcomes through systematic review of care against criteria and implementation of change
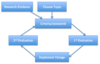
Label the clinical audit cycle
Give examples of quantitative methods of research
- Questionnaires
- RCT
- Cohort studies
- Case-control studies
- Cross-sectional surveys
What are the advantages of using questionnaires?
Good for describing, measuring and finding relationships and allows for comparisons to be made
What are the disadvantages of using questionnaires?
- Force people into inappropriate categories
- Don’t allow people to express things in the way that they want
- May not be effective in establishing causality
Give some methods of qualitative research methods
- Observation and ethnography - studying human behaviour in nature context
- Interviews
- Focus groups
- Documentary and media analysis
What are the advantages of qualitative research methods?
- Understanding patient’s perspective
- Explaining relationships between variables
What are the disadvantages of qualitative research methods?
- Not good at finding consistent relationships between variables
- Not good for generalisability
What is the benefits of systematic reviews and meta-analysis?
- Help offer to highlight gaps in research and poor quality research
- Offer authorative, generalisable and up-to-date conclusions
- Save clinicans from having to locate and appraise the studies themselves
Explain the practical criticisms of EBP
- Impossible to create and maintain systematic reviews across all specialities
- Challenging and expensive to distribute and implement findings
- Choices of outcomes very biomedical - limits interventions trialled (e.g. complementary and alternative medicine)
- Requires ‘good faith’ in pharmaceutical companies
Explain philsophical criticisims of EBP
- Doesn’t align with most doctors’ mode of reasoning
- Population-level outcome may not apply to individual
- May make professionals ‘unreflective rule followers’
- Can be seen to be undermining the doctor-patient relationship and the NHS
What are some of the difficulties of getting evidence into practice?
- Evidence exists but doctors don’t know about it
- Doctors know evidence but don’t use it
- Organisational systems can’t support innovation
- Commissioning decisions reflect different priorities
- Resources not available to implement change
Explain the artefact explanation with regards to health inequalities and socio-economic background
Health inequalities are evident due to the way statistics are collected
Explain the social selection explanation with regards to health inequalities and socio-economic background
Sick individuals move down social hierarchy and health individuals move up (health status = social position rather than other way around)
Chronically ill and disabled people are more likely to be disadvantaged
Explain the behavioural-cultural explanation with regards to health inequalities and socio-economic background
Ill health due to people’s choices/decisions, knowledge and goals. Choices made freely from range of options
What are the limitations of the behavioural-cultural explanation?
- Behaviours and outcomes of social processes are not a simple individual choice
- Choices may be difficult to exercise in adverse conditions
- Choices may be rational for those whose lives are constrained by their lack of choices
Explain the materalist explanation with regards to health inequalities and socio-economic background
Inequalities in health arise from differential access to material resources (low income, unemployment, work environment)
Explain the difference between inequality and inequity
Inequality = when things are different e.g. men don’t get access to cervical screening
Inequity = inequalities that are unfair and avoidable
What is a lay belief?
How people understand and make sense of health and illness
Describe the negative, functional and positive definitions of health
Negative definition = absence of illness
Functional = ability to do certain things
Positive = state of well-being and fitness






