GUT Women's Health Anatomy & Radiology Part 2 (& Commentary) Flashcards
Know the structures on the slide

What is a a hysterosalpingogram and what is it used for?
- Injection of radiographic contrast goes into the cervical os to see the uterine cavity and if the fallopian tubes are open (normally open to the peritoneal cavity)
- For fertility studies
- Open uterine cavity means a chance for successful implantation of fertilized egg
Abnormalitites of the tubes and uterus can cause infertility such as?
- scarring in the uterus
- masses in the uterus
- scarring in the tubes 2/2 PID
Does VUR cause renal damage?
Not necessarily!
What is primary VUR?
- Genetic predisposition to short ureteral tunnel through the bladder
- Small chance of renal damage from VUR
What is secondary VUR?
- To the bladder and/or urethral dysfunction ie: neurogenic bladder or posterior urethral valves
- Have the most problems and have increased chance of renal damage
If there is no stasis of urine in the GUT does VUR predispose a patient to UTIs?
NO - VUR does not predispose if there is no stasis of urine
What is required if a Hydronephrosis is found on prenatal US?
Requires a f/u evaluation after birth to determine etiology
What percentage of children <5 y/o with UTI’s have VUR?
30-40%
What conditions increase the chance of renal scarring?
- Febrile UTIs
- VUR plus UTIs
T/F: Surgery to reimplant ureters and/or prophylactic ABX do not necessarily prevent UTIs and/or renal damage
True
Greater grade of reflux is associated with ___ chance of renal damage
increased
What is the bottom Line of VUR and UTIs?
They require individual evaluation and tx as these are complex entities with still evolving knowledge of their associations
Grading of VUR

What should a workup of VUR include? What are you evaluating?
- VCUG or Isotope Cystogram and a Radionuclide DMSA Renogram
- Evaluating renal parnchyma and presence of reflux
- In utero US evaluation is important to ID prenatally the presence of hydronephrosis and/or kidney size
What are the 2 causes/types of Vesicoureteral Reflux?
- Due to immaturity with a short ureteral tunnel in the bladder
- Due to a congenital anomaly at the UV junction
- no tunnel, adjacent bladder diverticulum, or displaced orifice
What happens in VUR if reflux is present with a UTI and the cause is a short ureteral tunnel?
- Pyelonephritis and renal damage can result
- An immature short tunnel usually resolves with age
What happens in VUR if reflux is present with a UTI and the cause is a congenital anomaly at the UV junction?
Same thing as a short ureteral tunnel - pyelonephritis and renal damage can result
*If reflux of any etiology is present with a UTI, pyelonephritis & renal damage can occur
Posterior Urethral Valves or a Neurogenic Dysfunctional Bladder does not necessarily occur if the ureteral tunnel is ___?
normal
*if the tunnel is abnormal, reflux occurs
When prenatal fetal hydronephosis occurs or the patient has documented pyelonephritis, VCUG or Radionuclide Cystogram, is indicated to determine what?
- If underlying anatomic or functional abnormalities are present
- If so, depending on findings, treat
In Hydronephrosis what will you see on VCUG or Cystomgram secondary to ureteral obstruction?
Dilated urinary collecting systems, calyces, infundibula, renal pelvis, ureters
High pressure in the urinary collecting system 2/2 to obstruction can cause?
rupture of the collecting system
*this is not a concern & spontaneously resolves
Bladder stone (bladder calculi) 2/2 to bladder urinary stasis and contributes to ___?
infection
What defects in the ureter and bladder indicate malignancy?
Filling defects
What is the key clinical finding in urinary tract transitional cell malignancy?
Painless hematuria!
*renal cell CA can cause hematuria as well
In what disease does a patient have enlarged ovaries with thick sclerotic capsules and an abnormally high number of follicles?
Polycystic Ovary Disease (PCOD)/ Stein-Leventhal Syndrome (PCOS)
What sx will you see in patients with Stein-Leventhal Syndrome?
- ammenorrhea
- infertility
- hirsutism
- enlarged polycystic ovaries
What would you expect to see on US in a PCOD patient?
Increased central stroma with multiple small subcapsular follicles
What is on your DDx for Pelvic or Low Abdominal Pain in a female patient?
- PID/Tubo-ovarian abscess
- Ovarian torsion
- Ectopic pregnancy
- Appendicitis
- Ruptured ovarian cyst
- Diverticulitis
- Endometriosis
- Dysmenorrhea
If you note a blue ovary 2/2 to obstruction of veins and/or arteries in the ovary and the Doppler US shows no blood flow to the ovary what Dx are you thinking of?
Ovarian torsion
If a patient’s bHCG level is >1000 IU/mL (2IS Standard) or >2000 IU/mL (IRP Standard) what should be identifiable on a Transvaginal Sonogram?
intrauterine gestational sac
An intrauterine gestational sac should be present by how many weeks?
5 wks
An intrauterine gestational sac should show embryonic cardiac activity by 5+ weeks on a transvaginal when the sac is at least 16mm long or?
embryonic crown rump length is at least 5mm
What are the criteria for an Ectopic Pregnancy?
- If no intrauterine gestational sac is seen at all
- If a live, extrauterine embryo is identified
- There is free fluid in the pelvis or peritoneum
- There is an adnexal mass
- There is a hematosalpinx (blood in fallopian)
T/F: PID can be anything from a mild inflammation to an extensive abscess within the tubes and ovaries (tuboovarian abscess)
True!
*may see fluid collections and pus on CT and US
Why can there sometimes be both benign or malignant tumors including hair, teeth, fat, etc. in dermoid cysts of the ovary?
Because the ovary contains plenipotential cells (can develop into any type of organ)
What type of ovarian tumor can be very large and is benign?
Cystadenoma

Carcinoma of the ovary is a malginant tumor and on US could show?
- complex cyst
- thick walls
- mixed mass and cystic changes
Sister Mary Joseph Sign can be a sign of what type of tumor in females?
Carcinoma of the ovary
Endometrial tissue is the tissue within the uterine cavity that develops during the ___ ___
Menstrual cycle
In Endometriosis/Endometrioma, endometrial tissue can sometimes be located where?
- Outside of the uterus
- In the adnexa
- Even on bowel
*responds to menstrual cycle and can be very painful
What are uterine Leiomyomata/Fibroids?
- Smooth muscle benign tumor
- Very common - esp. in older pts
- Can be painful, bleed
- Can lead to infertility

What is uterine adenomyosis?
- endometrial tissue within the myometrium
- similar but different than Endometriosis
What are some sx of uterine adenomyosis?
- Can be painful
- Cramping
- Uterine bleeding
- Dyspareunia (painful intercourse)
- Infertility
*Note thickening myometrium
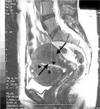
Painless, post-menopausal bleeding should be evaluated because?
It could be endometrial carcinoma!
Risk factors for Endometrial Carcinoma
- Obesity, DM
- BRCA
- Tamoxifen
- Nulliparity
- Inc age
- Inc levels of estrogen
- FHx, genetics
- PCOS
Risk factors and causes of Carcinoma of the Cervix (uterine neck)
- Squamous carcinoma
- HPV (90%)
- Oral contraceptives
- Multiple pregnancies
Carcinoma of the Cervix can obstruct what structure and lead to a renal death?
ureters
What is the supporting structure of the ovary that is a fold of peritoneum off of the Broad Ligament?
Mesovarium

What supporting structure of the ovary is a fold of peritoneum from the superiolateral pelvic wall and contains arteries, veins, and lymphatics?
Suspensory Ligament of Ovary
What supporting structure of the ovary is continuous with the Round Ligament of the uterus and attaches to the lower pole of the ovary?
Ligament of Ovary
Weakness of the bladder supporting structures causes the posterior portion of the bladder to drop down forming a ___
Cystocele
What fascia supports the bladder? What happens when this fascia weakens?
- Pubocervical Fascia
- When weakened, often 2/2 to childbirth, the support of the bladder weakens and a Cystocele (Prolapse) occurs
When the support structures of the uterus and vagina weaken, the vagina and/or uterus can?
Prolapse (drop) out
*this can also occur when the rectal support structures weaken (rectocele)
What are the 3 Levels of the Pelvic Support Structures?
Level 1: Cardinal, Uterosacral, and Anterior Pubocervical ligaments
Level 2: Levator ani and Arcus tendinous fasciae
Level 3: Urogenital diaphragm

A Cystocele can manifest with stress incontinence and on PE you can feel a bulge in the ___ vaginal wall accentuated when the patient coughs
anterior
What structure is a hollow canal connecting the fetal urinary bladder to the umbilical cord?
Urachus
Normally the Urachus obliterates during development to become what?
The Median Umbilical Ligament or Fold
What ligament is the obliterated Umbilical Artery that during fetal development connected to the Internal Iliac Artery?
Medial Umbilical Ligament
If the lumen of the Urachus remains open, a communicatin can occur between the Urinary Bladder and ___
- Umbilicus
- Or a Urachal Cyst can form


