GI Neoplasia II Flashcards
Molecular association?

KRAS mutation
(Serrated lumens = hyperplastic polyp)
List some factors associated with DECREASED risk of CRC
High calcium, folate, fiber, postmenopausal HRT, selenium, vegetable and fruit-heavy diet, ASA/NSAID use
Inheritance pattern of FAP?
AD
(Inherit loss of one APC allele)
Left or right CRC: frank bleeding
Left
Biopsy of the associated GI lesion would reveal:

Hamartomas = mass of tissue indigenous to site
(Peutz-Jehgers syndrome = colonic hamartomas + oral hyperpigmentation)

A 75 year old patient had a polypoid adenocarcinoma surgically removed 5 years ago. He now presents with occult bleeding and anemia. First step in management?
CEA to monitor for recurrence
Dx?
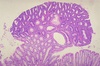
Tubular adenoma
(Notice the pedunculated mass with crowded, hyperchromatic glands)
How can this present?

Single rectal polyp in kid; can prolapse out of anus
(Juvenile/retention polyp = large cystic spaces/dilated glands
Left or right CRC: tenesmus
Left
(Feeling of incomplete emptying)
List some factors associated with INCREASED risk of CRC
Age, Fhx, lack of physical activity, low fiber/high fat diet, obesity, consumption of red meat, smoking, EtOH
This finding is associated with:

FAP
(Multiple retinal pigmented areas)
Left or right CRC: occult bleeding
Right
What does CRC look like on barium enema?
Apple core lesion

Treatment options for CRC
- If localized to head of polyp = endoscopic polypectomy
- Surgery
- If node positive = surgery
Left or right CRC: polypoid carcinoma
Right
A 40 year old whose mother died of CRC at age 45 wants to undergo a colonoscopy, which is normal. A year later she presents with weight loss, anemia, and occult fecal blood. First step in management?
Screening for microsatellite mutations + check for ovarian, endometrial, urinary, and gastric cancers
(Development of CRC without polyps [indicated by normal colonoscopy] + Fhx of CRC <50 yo indicates HNPCC, which is caused by microsatellite instability, more associated with right sided CRC; also has increased risk of the above listed cancers)
Which is heritable: oncogene or tumor suppressor gene abnormalities?
Tumor suppressor genes
(Oncogenes usually turned on via enviornmental stimuli)
Left or right CRC: obstruction
Left
Describe the adenoma-carcinoma sequence
Polyp to dysplasia to adenocarcinoma to invasive cancer
An 80 year old patient presents with fever, hematachezia, and abdominal pain. On physical exam, you notice several splinter hemorrhages and oral mucosal petechiae. Cause?
Strep bovis endocarditis caused by CRC
Dx?

Villous adenoma
(Tall glands, crowded cells)
Left or right CRC: anemia
Right
When does FAP present? Most common lesion?
2-3 decade (AD so in adulthood)
Adenomatous polyp (they have >100 so 100% chance of developing CRC if colectomy not performed)

Mutation of FAP? Of HNPCC?
FAP = loss of APC
HNPCC = mutation in DNA mismatch repair enzymes (microsatellite)


