GI Flashcards
VACTERL
Vertebral
Anorectal
Cardiac
Tracheal
Esophageal
Renal
Limb Anomalies
Esophageal atresia commonly occurs with what other anomaly?
Tracheoesophageal fistula
-distal esophagus connects with posterior trachea-
What is this? When does it present?
Esophageal atresia - maternal poly hydramnios
Vomiting up first feed
Reflux, back arching, stiffness, and torticollis
Sandifer’s Syndrome = GERD
What percentage of kids with GERD resolve without treatment by age 2?
60%
What is the most common cause of esophagitis?
Candida
How do you treat GERD?
Positioning after feeds
Thicken formula w/ rice cereal
Antacids, H2 blockers, PPIs
Motility agents = metoclopramide, erythromycin
How do primary gastric ulcers present in the first month of life, neonatal period, preschool, and > 6 yrs?
1st month: GI bleed/perforation
Neonatal: recurrent vomiting, slow growth
Preschool: Periumbilical, postprandial pain + vomiting
> 6 yo: epigastric abdominal pain, + blood loss/anemia
Gastric ulcers following surgery or head trauma?
Cushing
Stress gastric ulcers or those related with burns?
Curling ulcers
Colic
Frequent, complex abdominal pain and crying in infants < 3 months
Sudden onset loud crying
Circumoral pallor
Distended tense abdomen
Feet cold
*Relief with passage of feces/flatus*
Colic
R/o other causes
When and how does pyloric stenosis present?
Nonbilious vomiting
After 3 weeks, up to 5 months
What is the “olive” felt on exam of a pt. with pyloric stenosis?
Duodenal bulb
How do you diagnose pyloric stenosis?
U/S - 90% Senstive
What is this?

Pyloric stenosis
Also look for
string sign, double tract sign, shoulder sign
How does duodenal atresia present?
Bilious vomiting without abdominal distention
**First day of life**
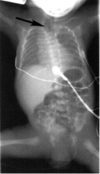
What is this? How do you treat it?

Duodenal atresia - double bubble sign
NG tube, IVF, surgery
**Associated with malrotation, esophageal atresia, and heart disease**
Moms with polyhydramnios might have an infant with what?
GI atresia
How does volvulus present?
Gastric: Severe abrupt epigastric pain, intractible emisis - failure to pass NG tube
Intestinal: Vomiting, abdominal pain
What is the most common cause of acute intestinal obstruction under 2 yo?
Intussusception - Ileocolic (90%)
What things can cause “lead point” for intussusception to develop? (6)
Viral illness
Meckel’s diverticulum
Polyp
Lymphoma
Henoch-Schonlein purpura
CF
Intermittent colicky abdominal pain, bilious vomiting, and currant jelly stool.
Classic triad of Intussusception
Who do you diagnose intussusception?
US: Target/donut sign, Pseudokidney
Impression: Paucity of bowel gas in film, air enema partially reduces it in film B.

Intussusception
What is the rule of 2’s for Meckel’s diverticulum?
2% of the population
2 inches long
2 feet from iliocecal valve
< 2 yo
2% symptomatic
What are the signs of symptomatic meckel’s diverticulum?
Intermittent painless rectal bleeding
Obstruction
Diverticulitis
**Can mimic appendicitis**
What is the perforation rate in kids with appendicitis after 48 hours?
>65%
**Can’t localize pain**
Pain first, then V/D or anorexia
Which kids with possible appendicitis get CTs?
Indicated if diagnosis is equivocal
How do you treat appendicitis?
Surgery
Broad spec antibiotics if perfed for 7 days
What are causes of constipation in the neonatal period? (5)
Hirschprungs
Intestinal pseudo-obstruction
Hypothyroidism
Cows milk protein intolerance
Low K, High Ca
What is the cause of Hirschprungs Megacolon? What is associated with?
Absence of ganglion cells in bowel
M > F, Down Syndrome
How do you diagnose and treat Hirschprung’s Disease?
Rectal suction biopsy - need submucosa
Rectal manometry
How do you treat an anal fissure?
Sitz baths, fiber supplements, increased fluid
What is appropriate initial management of the following: 14 yo girl with 2-month hx of crampy diffuse abdominal pain with anorexia nad 4.5 kg weight loss. Pain unrelated to meals no diarrhea or constipation.
Rectal exam, stool exam
CBC, ESR
Review of family/emotional stress
**Do not refer to eating disorder clinic**
True or false: Extraintestinal manifestations of IBD are more commonly seen in Crohn’s.
True
Perianal fistula, sclerosing cholangitis, pyoderma gangrenosusm and ankylosing spondylitis are seen with what?
Crohns
IBD + bloody diarrhea, anorexia, weight loss, pyoderma gangrenosum, sclerosing cholangitis is most likely what?
Ulcerative colitis
How do you treat Crohns?
Steroids
Aminosalicylates
MTX
AZA
Cyclosporine
Metronidazole
Sitz baths
TNF-α inhibitors
How do you treat UC?
Aminosalicylates
Steroids
Colectomy
Abdominal pain with intermittent diarrhea and constipation without organic basis
Irritable Bowel Syndrome
Must exclude other pathology
CBC, ESR and FOBT
What is the most common cause of diarrhea in children?
Viral - rotavirus
Diarrhea and emesis =
Diarrhea and fever =
Diarrhea and tenesmus -
Non-inflammatory
Inflammatory
Large Colon Involvement
What does fecal leukocytes infer?
Invasive cytotoxin organism
Shigella, Salmonella
Patients with enterohemorrhagic E. coli and Entamoeba histolytica have ___________ fecal leukocytes.
Minimal to none
What is the BRAT diet for diarrhea?
Bread
Rice
Applesauce
Toast
If a kid has E. coli 0157:H7 do you treat with antibiotics?
No - higher incidence of HUS
Pseudomembranous colitis
Post-antibiotic c diff infection
Treat with PO metronidazole or PO Vanc
When is surgery indicated for abdominal umbilical hernias?
Symptomatic
Strangulated
Grows larger after age 1 or 2
Perianal itching at night
Enterobius vernicularis - pinworm
Albendazole or mebendazole
Mild anemia, abdominal pain, diarrhea tenesmus
Perianal itching
Trichuris trichuia - whipworm
Albendazole or mebendazole
Pneumonia
Intestinal obstruction
Liver failure
Ascaris lumbricoides
Albendazole or mebendazole
Intense dermatitis
Loeffler’s pneumonitis
Anemia/GI symptoms
Necator americanus & Ancylostoma duodenale
Hookworm (skin penetration)
Albendazole or mebendazole
Dermatitis, pneumonitis
Anemia, GI symptoms
Diarrhea 3-6 weeks
Superimposed bacterial sepsis
Strongyloides stercoralis (skin)
Ivermectin
Myalgias
Facial periorbital edema
Conjunctivitis
Pneumonia, myocarditis, encephalitis, nephritis, meningitis
Albendazole
What is a weird cause of irreversible developmental delay in kids?
Intestinal worms
Necator or a. duodenale - hookworms
Strongyloides
What is the most common type of inguinal hernia?
Indirect > direct > femoral
How can you distinguish an inguinal hernia from a hydrocele?
Hernia increases with straining
15 yo girl with spots on her lips has crampy abdominal pain + bleeding
Peutz-Jeghers
Multiple intestinal polyps, tumors of soft tissue/bone (mandible)
Gardner’s syndrome
Aggressive surgical removal of polyps - high malignant potential
Carcinoid Tumors
Tumors of Enterochromaffin cells in intestine
Appendicitis
Carcinoid Syndrome
Carcinoid Syndrome
Inc. serotonin
Vasomotor disturbances
Bronchoconstriction
Familial Polyposis Coli
AD - APC mutation
Hematochezia, cramps, diarrhea
Resection of affected colonic mucosa
Juvenile polyposis coli
2-10 years
Bright red painless bleeding with bowel movement
Iron deficiency
What is the most common childhood bowel tumor?
Juvenille polyposis coli
When does short bowel syndrome occur
With loss of at least 50% small bowel
Dec. Na and K
Acidosis - loss of bicarb
How do you treat short bowel syndrome?
TPN
Small feeds PO
Metronidazole to treat bacterial overgrowth
5 yo girl presents with protuberant abdomen and wasted extremities
Gluten induced enteropathy
Celiac disease is asociated with which genetic types?
HLA-B8
DR7, DR3, DQW2
Bx: Vilous shortening inc. crypt depth, increased inflammatory cells in lamina propria of small bowel
Tropical Sprue
Abx 3-4wks
Folate and B12
Explosive watery diarrhea with abdominal distention in response to lactose
Lactose deficiency (AR)
Eliminate from diet
Gilbert Syndrome
Benign - unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia
Crigler Najjar I (AR)
Glucuronyl Transferase mutation
Unconj. bili in first 3 days of life
**Absence of hemolysis**
Need liver transplant
Crigler Najjar 2 (AD)
Glucuronyl transferase mutation
Kernicterus unusual
Unconj. bili in first 3 days - resolves
Phenobarbital for 7-10 days
Alagille Syndrome
Absence or dec. # of bile ducts
Occular, vertebral, and CV abnormalities
Unusual facies
Zellweger Syndrome AR
Progressive degeneration of liver and kidneys
Fatal in 6-12 months
**Absence of peroxisomes on hepatic cells**
Extrahepatic Biliary Atresia
Acholic stool, polysplenia, malrotation
Drain or liver transplant
Which is the only hepatitis virus that is a DNA virus?
Hep B
What causes most of the cases of hepatitis in children?
Hep A
10 yo boy is diagnosed with Hep A, how would you treat the parents and siblings not sick?
IVIg
What causes neonatal hepatitis?
Most from systemic disease i.e. sepsis
CMV, HSV, HIV
Congenital syphilis & toxo
How do you treat neonatal hepatitis?
Abx for bacterial associated
Acyclovir for HSV
Ganciclovir and foscarnet for CMV
How do you treat chronic (autoimmune) hepatits?
Steroids
Azathioprine
What causes Reye’s Syndrome?
URI/chicken pox or ASA
Improvement
Abrupt protracted vomiting 5-7 days after illness onset
How do you treat Reye’s Syndrome?
Control ICP 2/2 cerebral edema
Supportive management
What is the most likely manifestation of α1-antitrypsin deficiency in the newborn?
Jaundice (neonatal cholestasis)
Jaundice
Portal HTN, liver failure
Tremors
Delayed puberty
Wilsons Disease - Excessive copper deposition in brain and liver
Low ceruloplasmin
High serum copper
Kayser-Fleischer rings
How do you treat Wilson’s Disease
Zinc - block Cu absorption
Penicillamine
Restrict copper
Hepatoblastoma
Associated with Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome
Large abdominal mass, R lobe
αFP, CT, MRI
Resect, cisplatin and doxorubicin
Inc. abdominal girth, hmegaly, vomiting, pain
or
Chest pain, coughing, hemoptysis
Echinococcus - domestic and wild canines
Liver and/or lungs
Anaphylaxis 2/2 rupture and spillage
Surgery or albendazole
Abd. pain, distention, hmegaly
Anemia, inc. ESR, nonspecific ALT
slightl leukocytosis
Amebic abscess - from disseminated infection
Metronidazole
Chloroquine
Aspiration


