Geometry Ch 3 - Parallel and Perpendicular Lines Flashcards
(42 cards)
What is a Transversal?
A line that intersects two coplanar lines at two distinct points.
Example: The diagram shows the eight angles formed by a transveral t and two lines l and m.

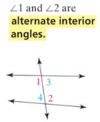
What are Alternate Interior Angles?
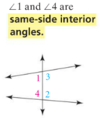
What are Same Side Interior Angles?
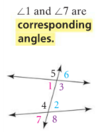
What are Corresponding Angles?
What is the Corresponding Angles Postulate?

What is the Alternate Interior Angles Theorem?

What is the Same-Side Interior Angles Theorem?

What is the Alternate Exterior Angles Theorem?

What is the Same-Side Exterior Angles Theorem?

What is the Converse of the Corresponding Angles Postulate?

What is the Converse of the Alternate Interior Angles Theorem?

What is the Converse of the Same-Side Interior Angles Theorem?

What is the Converse of the Alternate Exterior Angles Theorem?

If two lines are parallel to the same line, then…
they are parallel to each other.

In a plane, if two lines are perpendicular to the same line, then…
they are perpendicular to each other.

What is the Triangle Angle-Sum Theorem?
The sum of the measures of the angles of a triangle is 180.

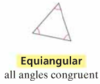
What is an Equiangular Triangle?
A triangle with all angles congruent.
What is an Acute Triangle?
A triangle with all angles acute.

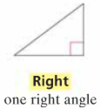
What is a Right Triangle?
A triangle with one right angle.
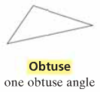
What is an Obtuse Triangle?
A triangle with one obtuse angle.
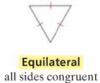
What is an Equilateral Triangle?
A triangle with all sides congruent.
What is an Isosceles Triangle?
A triangle with at least two sides congruent.
What is a Scalene Triangle?
A triangle with no sides congruent.

What is the Exterior and Interior Angles of a Polygon?