Geometry Ch 11 - Surface Area and Volume Flashcards
Polyhedron
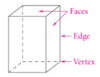
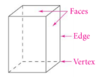
A three-dimensional figure whose surfaces are polygons. Each polygon is a face of the polyhedron. An edge is a segment that is formed by the intersection of two faces. A vertex is a point where three or more edges intersect.
Euler’s Formula
The numbers of faces (F), vertices (V), and edges (E) of a poolyhedron are related by the formula F + V = E + 2
Cross Section of a Solid
The intersection of a solid and a plane.
Note: You can think of it as a very thin slice of a the solid.

Literal Equation
An equation involving two or more variables.
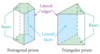
Prism
A polyhedron with exactly two congruent, parallel faces, called bases. Other faces are lateral faces. You name it by the shape of its bases.
A prism may either be right or oblique.
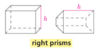
Right Prisms
The lateral faces are rectangles and a lateral edge is an altitude.
Oblique Prism
A prism with bases that are not aligned one directly above the other. The lateral faces are parallelograms.

Lateral Area of a Prism
The sum of the areas of the lateral faces.
Surface Area of a Prism
The sum of the lateral area and the area of the two bases.
Lateral and Surface Areas of a Prism

Cylinder
A solid geometric figure with straight parallel sides and a circular or oval cross section. It has two congruent bases that are circles.
Altitude of a Cylinder
A perpendicular segment that joins the planes of the bases. It is the height of a cylinder.

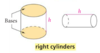
Right Cylinders
A cylinder with the bases circular and with the axis joining the two centers of the bases perpendicular to the planes of the two bases.
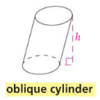
Oblique Cylinder
A cylinder that ‘leans over’ - where the sides are not perpendicular to the bases.
Lateral and Surface Areas of a Cylinder
The rectangle resulting from “unrolling” the curved surface of a cylinder. The surface are of a right cylinder is the sume of the lateral area and the areas of the two bases.
Lateral Area = 2πrh = πdh
Surface Area = Lateral Area + 2B = 2πrh + 2πr2

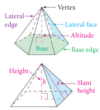
Pyramid
A polyhedron in which one face (the base) can be any polygon and the other faces (the lateral faces) are triangles that meet at a common vertex (called the vertex of the pyramid). You can name it by the shape of its base. The altitude is the perpedicular segment from the vertex to the plane of the base. the length of the altitude is the height h of the pyramid.
Regular Pyramid
A pyramid whoe base is a regular polygon and whose lateral faces are congruent isosceles triangles.
Slant Height of a Pyramid
The length of the altitude of a lateral face of the pyramid.
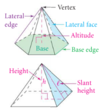
Lateral area of a pyramid…
The sum of the areas of the congruent lateral faces.
Note: You can find the formula for the lateral area of a pyramid by looking at its net.

Lateral and Surface Areas of a Regular Pyramid

Cone
It’s “pointed” like a pyramid, but its base is a circle.

Lateral and Surface Areas of a Cone

Volume
The space a figure occupies. It is measured in cubic units such as cubic inches (in3), cubic feet (ft3), etc…
Cavalieri’s Principle
If two space figures have the same height and the same cross-sectional area at every level, then they have the same volume.