General Flashcards
(42 cards)
what are the two forms of reticulocytes in cats? How long do they last?
aggregate- 12hr-4-7d punctate- 10-12days
What species is more likely to get oxidation of Hb?
Cats- have more sulfahydryl groups that are targets for oxidation
In what breed of dog is von Willebrand’s deficiency common?
Dobermans
In which species is it normal to see small amount of heinz bodies?
cats
In which species are Howell-Jolly bodies normal?
horses & cats
In dogs, lithium heparin can overestimate which value?
albumin
What is greater in plasma vs. serum
more in serum- K, P, LDH (AST and CK in cattle/sheep
more in plasma- total proteins, globulins
What are the three things we need to be cautious about when using EDTA in terms of blood values?
- more K
- chelate divalent ions- Ca & Mg and effect enzymes (ALP, CK, glucose, amylase, lipase)
- acidosis (bicarbonate low)
On blood work, I see an increased glucose and diluted electrolytes- what does that indicate?
dextrose solution contamination
What are the three things that will happen with old blood?
cell lysis
RBC swelling (MCV, MCHC, PCV)
Platelet activation (MPV & platelet count)
What does long term storage do to blood?
decrease glucose
increase K as leaks from cells (horses, most LA, japenese dogs)
What is the corrected WBC count formula?
WBC x 100/ 100 + nRBC/100 WBC
Exposure of blood to light will decrease what values?
bilirubin
What analysis type is better at dealing with icterus & hemolysis?
reflectance chemistry
What are the things that affect absorbance?
lipolysis
hemolysis
icterus
hyperproteinemia
drug-KBr (hperhloremia)
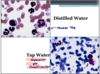
What is the abnormal slide due to?

WBC count calculation?
Avg #/100x x 10,000 (or square of objective)= cell/uL in 10 fields
In what animals are large platelets norma?
cats, Cavalier king charles spaniel
What is the min # platelets/100x field normal?
dog and cats- 7-10 platelets/100x hpf
IF a horse of ruminant has pale-yellow plasma, what does that indicate?
normal- from caretenoids in diet
What is it?

reactive lymphocyte
With lipemia, what values are affect?
decrease electrolytes
increased Hb
What is the formula for Hct? What can falsely decrease it?
Hct= MCV x RBC conc/10
autoagglutination
Formula for MCHC
Hb/PCV x 100= g/dL









