Gene 500 Flashcards
What are the 3 most common chromosomal abnormalities in recognized pregnancies?
1) Triploidy (100% SAB)
2) 45, X (99% SAB)
3) trisomy 16 (100% SAB)
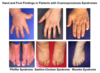
Large tongue, excess nuchal skin, auricular dysplasia, upslanting palpebral fissure, clinodactyly, hyperextensibility, single palmar crease, hypotonia
Down syndrome
47,XX,+21 (95%)
46,XX,rob(14:21) (4%)
Mosaic trisomy 21 (1%)
What are the complications of down syndrome?
Hearing problems (narrow ear canals)
Vision porblems
Cataracts, OSA
CHD
hypothyroidism
Leukemia
atlantoaxial instability
dementia
Small fingernails, short sternum, clenched hands (2 over 3, 5 over 4), micrognathia
Edwards Syndrome
Trisomy 18
- look for CHD, horshoe kidney, cerebllar hypoplasia, microphthalmia, central apnea
Sloped forehard, cutis aplasia, hypoterloirsm, cleft L/P, omphalocere, polydactyly, HPE
Patau, Trisomy 13
- Heart, CNS, renal, general anomalies
What are the most common karyotype findings for Turner Syndrome?
45,X - 50%
46, X, i(Xq) - 15%
45,X/46,XX mosiac - 15%
45X/46,X,i(Xq) - 5%
other
Low posterior hairline, renal anomalies, cardiovascular anomalies, short stature, edema in infancy
Turner Syndrome
+ gonadal dysgenesis, webbed neck, widely-spaced nipples
- Lack of secondary sex characteristics/ammenorhea in puberty
- Monitor for aortic root dilation
Hypogonadism, tall, gynecomastia, decreased muscle mass, osteopenia, low libido
Klinefelter
47 XXY (85%)
Mosaic 47XXY/46XY (15%)
- Increased risk for learning disabilities
What is the phenotype for 47XYY
Not dysmorphic
Tall, at risk for langage delay/low verbal IQ
- ~10-15 IQ points lower than siblings
What is 47XXX phenotype?
Tall, 70% have learning porblems
- no dysmorphic features
How is gonadal sex determined?
SRY -> SOX9
- established around 6 weeks gestation

When does X inactivation occur?
2 weeks post-fertilization
What gene is expressed in the inactive X but not active X?
XIST
in Xq13
- produces large RNA molecules that coat inactive X
Which X is usually missing in 45X?
paternal 75%
Cystic hydroma, ovarian dysgenesis, low hairline, aortic root dilation
Turner Syndrome
Haploinsufficiency of PAR genes
- 2 Xs needed for ovarian development -> inactive X is reactivated in oogoina during meiosis (starts in fetal life)
When are patients witt Turner Syndrome at risk for gonadoblastoma?
When mosaic for 45X and 46XY and external genetalia is female or ambiguous
- okay if external genetalia is male
What does a ringed chromosome in turner syndrome mean?
Need to do FISH to determine if X or Y and if XIST is present
- if Y risk for gonadoblastoma
- if X and XIST is present -> PAR haploinsufficiency -> Turner
- if X and XIST is absent -> X disomy -> severe ID, OCD, dysmorhpic features, and congenital malformation
-
Xp21 deletion syndrome
DMD, RP, adrenal hypoplasia, ID, glycerol kinase
What does Xp duplication involving DAX1 do?
46XY females
- increased DAX1 dose can overcome sry
- w/ ID
In X-Autosome translocations, which X is inactivated?
If balanced; normal X nonrandomly inactivated
If unbalanced: abnormal X is nonrandomly inactivated

What is the reproductive consequence of X-autosome translocation?
Half of females infertile
All males infertile
Which chromosomes can be involved in robertsonian translocation?
Acrocentrics
13, 14, 15, 21, 22
What is the clinical consequence of balanced translocation?
Usually multiple miscarriages due to unbalanced offspring
- Phenotype depends on size, genes involved, monosomy vs trisomy
What type of segregation is most common in a quadrivalent?
Adjacent 1 (chromosomes next to each other with different centromeres go together)
- Alternate results in normal/balanced offspring

What are 3 mechanisms of isochromosome formation?
Centromere misdivision - isochromosome w/ identical arms
U-type exchange in meiosis 1 (most common) - isodicentric chromosome w/ homologous arms
U-type exchange in meiosis 2 -isodicentric chromosome w/ identical arms

Which type of inversion involves the centromere? Which type is more likely to result in abnormal offspring?
Pericentric involves centromere and is more likely to result in liveborn but abnormal offspring

What is the significance of segmental duplications?
Seg Dup = Low copy repeats
- Non-homologous recombination -> recurrent Del/Dup syndromes

Name the syndrome associated with:
5q35 deletion
7q11 deletion
15q11q13 deletion
17p11. 2 deletion or duplication
22q11. 2 deletion
5q35 deletion - Sotos
7q11 deletion - Williams
15q11q13 deletion - PWS/AS
17p11. 2 deletion or duplication - Smith magenis, HNPP/ CMT
22q11. 2 deletion - DiGeorge
75% of chromosome rearrangements come form which parent?
father
Exceptions:
- novo markers (associated w/ advanced maternal age)
- De novo robertsonian (90% mom)
- interstitial del/dup -> 50/50
What are alpha-satellites? Why are they relevant?
Alpha-satellite is a 171bp repeated region at centromeres -> different by 2-3% between chromosomes and allow chromosomes to be distinguished on FISH
- Exceptions: 13 and 21, 14 and 22
What are the advantages of interphase FISH?
- Fast - no need to culture cells (takes 1-2 days vs 7-14 days for karyotypes)
- better for Tandem duplications
What is the best FISH probe for philadelphia chromosome?
Dual fushion -> for when both tranlsocation breakpoints are known
What can SNP array tell that CGH array cannot?
- UPD, loss of heterozygosity
Why would you follow up CMA results with FISH?
- confirm finding
- provide location of duplications
- identify balanced translocations in parents (recurrence risk)
According to ACOG, when should a pregnant woman be offered CMA?
- if U/S abnormal get CMA
- if U/S normal can do karyotype or CMA
- offer to women of all age groups (most findings are not AMA related)
What is the resoluation of:
- Karyotype
- high resolution karyotype
- CMA/FISH
- Sequencing?
- Karyotype - 5-15MB
- high resolution karyotype - 1-3MB
- CMA/FISH - 20-250KB
- Sequencing? - 1-100bp

What is the signfiicance of JAK2?
Driver mutations in essential thrombocytopenia and polycythemia vera
What is the significance of MYC ?
Burkitt lymphoma
Protooncogene on Ch8, multiple translocation partners
What is the significance of ALK, EGFR, and KRAS?
Amplified in lung cancer
- ALK inversion is drug target
- EGFR can betargered by Cetuximab
- KRAS is downstream of ALK and EGFR and can negate effects of targeted therapy
Which aneuploidies are more likely to be paternal origin?
45X, and XYY

Which aneuploidies are more likely to be MII errors?
Trisomy 18, XYY

Which aneuploidy is 50/50 in parent of origin?
XXY

Most aneuploidies originate from which parent?
Maternal M1

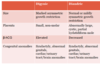
Small placenta, high B-hCG, severe growth restriction, syndactyly, multiple congenital anomalies
Digynic triploidy
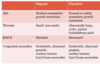
mild growth restriction, large cytic placenta, low B-hCH, syndacytly, multiple congential anomalies
Diandreic triploidy
- Partial hydatiform mole
Which phase of cell cycle are cellular contents duplicated?
G1
- chromosomes duplicated in S
Recombination occurs in what stage of meiosis?
Porphase 1 - Pachytene
When does meiosis start?
Males: after puberty
Females: 3rd month of gestation -> arrest at prophase 1 -> continue at menstration -> arrest at metaphase 2 -> complete if fertilized
TTAGGG repeat
Telomere cap sequence -> critical in meiotic pairing
In a karyotype G banding, which bands are GC rich?
Light bands = gene rich, GC rich, more euchromatic
Dark bands = gene poor, AT rich, more heterochromatin

What is the difference between a polymorphism and variant?
Polymorphism is >1% pop frequency
Variant is < 1% pop frequency - may or may not be disease causing
Locus vs alleleic heterogeneity
Locus heterogeneity = multiple genes -> same phenotype
Allelic heterogeneity = multiple variants in same gene -> same phenotype
Definte autosomal dominant
phenotype seen in heterozygotes
Definte autosomal dominant
Phenotype only seen in homozygotes
What does X-Linked mean?
If recessive: No father -> son transmission
If dominant: affected males have no affected sons but all affected daughters
Co dominant vs incomplete dominant
Codominant = both A and B show up (Ie ABO blood type)
Incomplete dominant = hets are intermediate to homozygotes
What does g.112931A>T mean?
genomic sequence change
What does c.112931A>T mean?
coding sequence change
What does r.112931A>T mean?
RNA sequence change
What does p.112931A>T mean?
Protein sequence change
What does m.112931A>T mean?
mitochondrial DNA sequence change
What does n.112931A>T mean?
noncoding RNA transcript change
What does c.9A>G, p.Lys3 mean?
synonymous A>G in DNA -> Lys 3 position
- May still affect splicing
What does c.100+1G>T mean?
Intronic change 1 nucleotide downstream from nucleotide 100 in coding sequence
What does c.100-2A>T
Intronic change 2 nucleotides upstream from nucleotide 100 in coding sequence
LMNA c.1824 C>T, p.Gly608
Synonymous change in LMNA that creates cryptic splice site
-> Hutchinson-Gilford Progeria
FGFR3 p.G380R
Achondroplasia
C.1138G>A (98%) or G>C (2%)
Name the stop codons
UAA
UAG
UGA
When does a nonsense mutation result in a truncated protein?
When stop codon is downstream of the last 50bp of penultimate oxon (50bp from the last exon junction complex)
- If stop codon is too early -> nonsense mediated decay
- If gene has 10 exons, nonsense variant in exon 1-8 will trigger nonsense mediated decay -> no protein -> likely pathogenic
- If nonsense if in exon 10 or last 50bp of exon 9 then it MIGHT NOT trigger decay and may make protein -> MIGHT have some function
What is the correct nomenclature?
c.locus is 1521-1523

p. Phe508del
c. 1521_1523delCTT
- > not delTCT because you push to the right

What is necessary to make a variant pathogenic?
1 very strong + 1 strong, 2 mod, or 1 mod + 2 sup
2 strong
1 strong + 3mod, 2mod +2 sup, 1mod + 4 sup

What evidence is necessary to classify variant at LPATH?
Very strong + mod
strong + 1-2 mod
strong + 2 sup
3 mod
2mod + 2 supporting
1 mod + 4 supporting

What evidence classified variant as benign?
1 stand alone strong OR 2 strong

What evidence classified variant as likely benign?
1 strong + 1 sup
2 supporting

Variant classification: allele frequency >5% in pop database
stand-alone benign

Variant classification:
- allele frequency > expected for disease
- observed in healthy individuals expected to have condition based on penetrance/age
- not damaging in in-vivo funtional studies
- no segregation
Strong Benign criteria

Variant Classification:
- MIssense variant in gene where mostly truncating variants cause disease
- Observed in trans with AD disease causing allele or in cis with known disease causing allel
- in-frame del/dup in repetitive region
- computations data -> benign
- alternative molecular diagnosis found in case
- reputable source reports variant as benign
- synonymous variant not predicted to affect splicing
Supporting benign criteria

Variant Classification:
- Same amino acid change as a previously established pathogenic variant regardless of nucleotide change
- De novo (both maternity and paternity confirmed) in a patient with the disease and no family history
- funcitonal studies support damaging effect
- The prevalence of the variant in affected individuals is significantly increased compared with the prevalence in controls
Strong pathogenic criteria

Variant interpretation:
- Located in a mutational hot spot and/or critical and well-established functional domain without benign variation
- Absent in controls (AD), rare (AR)
- Detected in trans w/ pathogenic variant (AR)
- Protein length changes as result in in frame del/dup
- Novel missense in residue where missense has been seen before as disease causing
- assumed de novo
Moderate pathogenic criteria

Variant Classification:
- Cosegregation with disease*
- Missense in gene w/ low missense frequency and where missense is common mechanism
- Computational -> deleterious
- Phenotype is specific for this gene
- Reportable source interpreted this variant as pathogenic
Supporting pathogenic criteria
* segregation can become moderate/strong depending on size of pedigree

How do you detect variable number tandem repeat polymorphisms (minisatellites, microsatellites)?
Multiplex PCR
- highly informative genomic variation since each locus has many possible alleles
- Used in linkage and DNA fingerprinting
Which SCAs are repeat exapnsion disorders?
1, 2, 3, 6, 7, 17
- CAG repeats
What are the 3 main types of non-random mating?
- inbreeding
- assortive mating
- negative inbreeding (small population, people actively avoid kin)
What does identical in state mean?
Alleles that have the same phenotypic affect
How can heritability be estimated?
2x Parent-offspring correlation
h2=2Ppo
or
2(monozygotic twin concordance - dizogotic twin condordance)
h2=2(Pmz-Pdz)
How is relative risk (λ) calculated?
Frequency in relatives/ Freuqency in general population
What does a high λ mean?
High relative risk ratio = more heritable
λs>2 = significant (s= sibling)
What is the difference between linkage and association?
Linkage = cosegregation of phenotype with chromosome region in multiple families - best for finding rare alleles of large effect
Association: presence of phenotype with specific allele in many famlities in population -> more frequence in cases than controls - best for findings common alles with small effect
What does linkage dysequilibrium mean?
Behavior of 2 loci violates law of independent assortment
- Excess of parental types (non-recombinants) in offspring
What needs to be true in order to perform linkage analysis?
One parent has to be hetrozygous and phase must be known
What is θ (recombination fraction)?
Prebability that a parent will produce a recombinant offspring (non-parental haplotype)
Recombinant haplotype/ total offspring
θ = 0 -> complete linkage
θ = 0.5 -> independent
θ < 0.5 = some linkage
What does θ = 0.5 mean?
50% of offspring have recombinant haplotype
- Independent assortment -> no linkage
what does θ = 0 mean?
No offpsring have recombinant haplotype
- complete linkage
Calculate θ

In generation 2 dad is heterozygote and we know phase (disease with A) -> linkage possible
Gen 3 unaffected AD daughter = recombination
θ = 1/8 = 0.125

Calculate θ

Gen 2 we know dad is BE. He is heterozygous and phase of disease is E -> linkage possible
- Gen 3 son BE unaffected is recombinant
θ = 1/4

Calculate θ

Phase unknown -> cannot calculate

Calculate θ

Unable to tell who is recombinant in third generation because both C and D could have come from either mom or dad.

How do you tell if θ of <0.5 is statistically significant?
Calculate LOD score
LOD 3 = 1000:1 odds favoring linkage
LOD 3.4 = genome wide significant linkage
What is the definition of association?
Lack of independence between 2 things
how can association (between phenotype and allele) and linkage (marker and phenotype) be uncoupled?
Recombination
Breech position, hypotonia, low birth weight, Thick saliva, hypoplastic genetalia, almond shaped eyes, small hands/feet, ID
Prader Willi
Paternally expressed (maternally imprinted) genes in 15q11q13 - pat deletion > mat UPD > methylation defects
– hyperphagai, fair skin/hair in deletions (P gene in area)