Clinical Flashcards
Fragile X repeat cutoffs
normal <50,
Pre 56-200,
Path = 200 (methylated)
Fragile X premutation phenotypes
Female: Premature Ovarian Failure.
Males and females: Ataxia/Tremor
Coffin Lowry
X-linked - RPS6KA3
ID
Broad hands with tapered fingers
Frontal bossing, flat nasal bridge, downslanting PF, wide mouth
Transcription Coupled Repair disorder
Cockayne syndrome
Gene: CSA, CSB
Face: Sunken eyes RP, SNHL, ID, Intracranial calcifications, short stature, photosensitive
Think: similar to XP but no cancer + dysmorphci facies
Syndromes with nuchal translucency
>3.4mm cutoff
Turner, Down Syndrome, Noonan
Most common genes in non-syndromic HCM
MYBPC3, MYH7
Down syndrome dysmorphic features
Upslanting PF
Burshfield spots
Small ears
Short 5th digit
Sandlegap toes
epicanthal folds
Single palmar crease
Ddx: epicanthal folds
Asian descent
Down syndrome
Fetal Alcohol
Zellweger
Down Syndrome association
Endocardial cushion defect (AV canal)
Duodenal atresia
Hirschsprungs
Leukemia
Alzheimers
hypothyroidism
Marfan diagnostic criteria
GHENT criteria:
If no FHX:
root dilation + lens,
FBN1,
systemic score >7,
OR lens + FBN1
If positive FHX: lens, root, or systemic score
Homocystinuria vs Marfan
AR inheritance,
rigid joints,
strokes,
ID
Turner syndrome dysmorphic features:
Webbed neck
low hair line
low set ears
lymphedema
cubitus valgus
Madelung deformity
Noonan Dysmorphology
Downslanting PF
low set, posteriorly rotated ears with creases
Turner features (webbed neck, board chest, pectus, short, cubitus valgus)
Noonan associations
Pulmonic stenosis
HCM
Bleeding/clotting
Trisomy 18 dysmorphology
microcephaly with prominent occiput
rocker bottom feet
short sternum
thumb/radius agenesis/hypoplasia
clenched fist with overlapping fingers
horseshoe kidneys
Trisomy 13 dysmorphology
cutis aplasia
holoprosencephaly
midline cleft
polydactyly
Cutis aplasia associations
Trisomy 13
Adams Oliver
Fragile X dysmorphology
Long, triangular face
flattened nasal bridge
protruding ears
macro-orchidism
Treacher collins dysmorphology
Downslanting PF
eyelid coloboma
absent bottom eyelashes
microtia
conductive hearing loss
NORMAL intellect
22q11 Dysmorpohlogy
tubular nose with hypoplastic nares
long tapering fingers
Cleft
CDLS dysmorpology
hirsutism
Synophrys/arched eyebrows
down-turned corners of mouth
Limb reduction defects
Achondroplasia dyrmorphology/associations
Trident Hand
Macrocephaly
Frontal bossing
Mid face hypoplasia
Foramen magnum stenosis
OSA
Beckwith Wiedemann Dysmorphology
Macroglossia
umbilical hernia
ear pits/creases
hemihyperplasia
BW Syndrome Cancer risks
Wilms
hepatoblastoma
embryonal
Williams syndrome dysmorphology
Broad forehead
short nose with broad tip
full cheeks
wide mouth with full lips
Puffy full upper eyelid
blue eyes with stellate irides
Waardenburg dysmorphology
white forelock
iris heterochromia
cochlear deafness
dystopia canthorum (lateral displacement of inner canthi)
CAL spots
NF1 Mccune-albright
Lip pits
Van Der Woude syndrome
Freckled penis
PTEN - Bannayan-Riley-Ruvalcaba syndrome
Persistent Fetal pads and arched split eyebows
Kabuki (also ITP)
Deafness genes
GJB2 and 6
Connexin 26 and 30
GJB2 can be AR or AD
Also biallelic inheritance possible
Common GJB2 mutation
35 Del C
Deafness + Goiter
Pendred Syndrome, SLC25A4
Deafness + RP
Usher
Deafness + Conduction defect (long QT)
Jerveil and Lange Nielson syndrome
Management of carrier mothers for DMD
TTE for cardiomyopathy
Germline mosiacism risk for DMD
14%
DMD treatment
Steroids between 5 and 15yo, Exon Skipping: Antisense (Etiplirsen) skip Exon 51, ACEi/BBlocker,
Gardner
FAP +
CHRPE,
osteomas,
soft tissue tumor,
supernumery teeth
Turcot
FAP +
CNS (medulloblastoma)
FAP surveillance
Start at age 10-12 q2 years;
EGD start at 18-25
Attenuated FAP definition
<100 polyps, start colonoscopy at age 20 If APC gene negative, look at MYH
Familial Hypercholesterolemia diagnosis
Clin: Arcus, Xanthomas, xanthelasma, arthritis/tenosynovitis
Cholesterol: 300 (het), 600 (homo)
Treatment of familial hypercholesterolemia
Statin,
Bile acid sequestrant,
aphoresis,
nicotinic acid (niacin)
Phenocopy for familial hypercholesterolemia (LDLR)
Apo B,
PCSK9
Repeat for Fragile X, where is it located
CGG,
5’ UTR
Fragile X Stablizer
AGG repeats
Top 4 most common genetic causes of ID
Down,
22q11,
Williams,
Fragile X
Recurrence risk for ID is increased if proband is:
Male
X Linked causes of ID
XALD
MPSII
FRAX
Pelizaeus-Merzbacher
ATRX (Alpha Thal + ID)
Coffin Lowry
MECP2
Coffin Siris
Absent nail,
hypoplastic 5th digit
Simpson-Colabi-Behmel
Overgrowth
+ cardiac conduction defects
+ polydactyly
+ Wilm’s tumor, neuroblastoma
MECP2 duplication syndrome
Can affect males
- severe ID, hypotonia, seizures, pseudo GI obstruction
Intracranial calcification syndromes
TORCH
Aicardi-Goutieres (TREX1; + encephalopathy, HSM, thrombocytopenia)
COL4A1 and COL4A2 - vascular basement membrane
Cockayne (CSA, CSB, ERCC; sunken eyes, retinopathy, SNHL)
Adams-Oliver (cutis aplasia)
Gorlin (PTCH1: BCC, teeth)
Most common causes of leigh syndrome
SURF1 (most common)
mtATP6 (T8993G/C)
PDH (X linked, common in males)
mt tRNAlys mutation causes
MERRF
Short rib, short limb, ectodermal dysplasia, polydactyly
Ellis Van Creveld, (EVC gene)
Most common Pulm HTN gene
BMPR2
Broad forehead, deep set eyes, triancular chin, pulm stenosis, cholestasis
Alagille syndrome
Sparse facial hair, hypertelorism, low set ears
CFC syndrome (BRAF, Rasopathy)
Heart defects associated with:
- Down syndrome
- 22q11
- Turner
- Williams
- Noonan/Costello/CFC
- AV canal
- TOF, interrupted AA, Truncus
- Outflow defects (Bicusp AV, Coarct, Root dilatation, dissection)
- Supravalvular AS
- Pulmonary stenosis, HCM, coagulopathy
First CHD gene
NKX2.5 - Tinman (has no heart in book)
5 syndromes with HCM
Fabry
Noonan
Friederich’s
Pompe
Danon
Most common causes of familial dilated cardiomyopathy
TTN (20%) LMNA (6%)
5 syndromes with dilated CM
DMD
Barth
LGMD
Emery dreifuss MD
Kearns-Sayre
AD Long QT genes
KCNQ1
KCNH2
SCN5A (events occur during sleep)
Jervell and Lange-Nielsen Syndrome
Long QT + SNHL
AR: KCNQ1, KCNE1
Brugada syndrome
Short QT
SNC5A + other Na, Ca, and K channels
Loeys-Diets vs Marfans
Craniofacial: Bifid Uvula, HyPERtelorism, craniosynostosis
Genes: TGFBR1, TGFBR2, SMAD3, TGFB2
COL5A1 and COL5A2
EDS type 1 and 2
COL3A1
EDS vascular
CHARGE heart defects
Dual outlet RV,
TOF
TBX5
Holt-Oram: AD
Cardiac (Conduction, ASD, VSD)
Limb defects
Alagille association
Peripheral pulmonary artery stenosis,
posterior embryotoxon,
butterfly vertebra
Triangular chin
Cholestasis
Jag1, Notch2: AD inheritance
What condition on quad screen does NIPS NOT cover
NT defect
When can CVS be performed
10-13 weeks (end of 1st trimester)
When can Amnio be performed
15-20 weeks
What factors determine effect of teratogen?
Fetal stage at exposure
Genotype of fetus
Dose/duration of exposure
When is all or nothing period of teratogen effect
0-2 weeks embryonic (2-4 wks) -> either death or nothing due to pluripotent cells
When is fetal period of greatest vulnerability
3-8 weeks embryonic (5-10 wks) -> organogenesis
Cat A drug
Controlled human studies show remote risk
Cat B drug
No controlled human studies, animal studies low risk
Cat C drug
Animal studies show risk, but may be acceptable
Cat D Drug
Risk in human studies, but may be necessary
Cat X Drug
Studies show major risk, do not give
Effects of radiation exposure in pregnancy
IUGR
microcephaly,
neuro
eye abnormalities
childhood leukemia
Effects of maternal hyperthermia
Exposure early (2-3 wks embryo age)
NTD
How do you convert embryo age into gestational age
Gestational age = embryo age + 2
Effects of maternal DM
11% risk (HgA1C >10) -> abnormal glycosolation
NTD,
cardiac,
renal/GI,
skeletal
Caudal regression/Sirenomelia
Maternal PKU
Mirocephaly,
ID,
cardiac
Keep Phe <360 u mol/L (6mg/dL)
Fetal mercury exposure
neurological and muscular injury
Fetal Polychorinated Biphenyls (cooking oil, some freshwater fish) exposure
DD, FTT, ectodermal dysplasia
Fetal lead exposure
Growth retardation, ID
TORCHES stands for:
Toxo
Other (Varicella, parvo B19, HIV)
Rubella
CMV
HErpes
Syphilis
Fetal B19 infection
Anemia,
thrombocytopenia
Tx: transfusion
Fetal Varicella
CNS and PNS
Fetal Rubella
Rash, hearing loss, liver
Features of fetal alcohol syndrome
Poor growth
DD
microcephaly
short palpebral fissures
short nose
smooth philtrum
thin upper lip
cardiac
small 5th fingernails
Fetal dilantin exposure (other AEDs similar)
Fetal Hydantoin syndrome (~10% of exposed)
(may have pharmacogenetic modifier -> dilantin epoxide)
Growth and mental delay
Wide fontanel
metopic ridging
hypertelorism
bowed upper lip
cleft l/p
hypoplastic distal phalanges/nails
hirsutism
Fetal VPA exposure
1% NTD
Fetal warfarin exposure 6-9 weeks
Nasal hypoplasia, depressed bridge
Stippling of epiphyses
Nail/fingertip hypoplasia
IUGR
ID
Fetal retinoic acid (accutane)
Ears: (microtia, anotia)
Mouth (micrognathia)
hypertelorism
conotruncal heart defects
CNS (hydrocephalus, microcephaly, DD)
Fetal thalidomide
Limb (amelia, finger/toe reduction)
CV
GI
NORMAL intellect
Fetal Tetracycline
Teeth/bone dyscoloration
Fetal SSRI
CHD (VSDs)
Neonatal irritability
Fetal AceI exposure
2nd Trimester -> Renal tubular dysgenesis
Fetal exposure to illicit drugs
Mostly not teratogens, but risk for IUGR, growth delay, vascular related placental issues
Presentations and inheritance pattern of G6PD
Kernicterus or hemolytic anemia X linked
What are the alleles for HFE
Cys282Tyr (higher risk)
His63Asp (only risk allele unless high risk allele also present)
Both incomplete penetrance
Most common mutation in Hemophilia A
Inversion in F8
Factor IX leiden
Variant Hemophilia B due to promoter mutation ->
severe in childhood, spontaneous improvement in adulthood
Major gene for isolated hirschsprung’s Which gender is more likely affected?
RET (AD, reduced penetrance)
Male > Females
4 most common genes in holoprosencephaly (AD)
SHH (35%)
ZIC2 (5%)
TGIF and SIX3 (1.5%)
HD repeat cutoffs
10-26 normal
27-35 premutation
36-39 incomplete penetrance
40-59 HD
60+ Juvenile HD
Which HD allele is more likely to expand?
Paternal
Where is the HD repeat expansion?
CAG in exon 1
Open fontanelle + exorbitism
Cruzon
FGFR2
+? SNHL, teeth abnormalities, frontal bossing, midface hypoplasia
Open fontanelle + small clavicles
Cleidocranial dysostosis
RUNX2
+ delayed/hypoplastic teeth, short stature, brachydactyly
Open fontanelle + stippled epiphysis
Zellweger
Check VLCFA
First test when differences in isomerism/laterality is found in baby
TTE - many CHD associated; heart loop is first morphological sign of assymetry in embryogenesis
Leukodystrophy with macrocephaly
Canavan (ASPA)
Alexander (GFAP)
Tay Sachs (HEX A)
Leukodystrophy + peripheral neuropathy
Metachromatic (ARSA) -posterior predominant
Krabbe (GALC)
Mitochondrial - DARS 2 w/ spinal cord involvement
Prodominantly anterior leurkodystrophy with macrocephaly
Alexander Disease (GFAP)
Leukodystrophy + intracranial calcifications
Aicardi-Goutieres
TREX1, RNASEH2A/2B/2C
CNS + fever, thrombocytopenia, HSM, anemia
Hypomyelination, sunken eyes, photosensitivity
Cockaye
ERCC1 and ERCC2
Also retinopathy, deafness, calcifications
X linked hypomyelinating disorder
Pelizaeur Merzbacher
PLP1
Teratogens that cause limb reduction defects
Thalidomide (+ CHD, phenocopy TBX5)
VPA
Phenytoin
Warfarin
Cutis aplasia + Limb reduction
Adams Oliver
AD: ARHGAP31 (rho GTPase), RBPG, Notch1, DLL4
AR: EOGT, DOCK6
Also neuro, cardiac, ophtho (retinal vascular disease)
Radial Ray + Heart defects
Hold Oram
TBX5
Thalidomide can look the same
Common Non-genetic causes of limb reduction
Amniotic band
VACTERL
Moebius syndrome (CN affected)
Poland (absent sternal head of pectoralis major)
Limb reduction + IUGR + synophyrys
CDLS
NIPBL, SMC1, SMCA, SMC3
+ hirsutism, anteverted nares, long smooth philtrum, micrognathia, cardiac defects, CNS
3 common genes for isolated and syndromic lisencephaly
PAFAH1B1
TUBA1A,
DCX (males, dual cortex in females)
Lisencephaly + hypertelorism, long/broad/think upper lip
Miller Dieker
PAFAH1B1 (17p13 deletion)
Dysmorphic: tall forehead, bitermporal narrowing, hyperteloric, short nose, iverted vermilion with prominent upper lip
CHD, omphalocele, contracture
Multiple brain malformations - lisencephaly, thin CC, BG abnormalities, polymicogyria
Tubulinopaties
TUB1A1, TUBB2A, etc
Cobbleston lisencephaly, retinal problems, hypotonia
Congenital musclular dystrophies
Muscle eye brain/walker warburg/fukayama
O-linked glycosylation disorders
macrocephaly + polymicrogyria
PIK3CA
mosiac
Lipoma + overgrowth of limbs
Proteus syndrome
AKT1
Mosiac
Skin Ca + GI/GU cancer
Muire Torre
MSH2, MSH1 (Lynch genes)
DDx: gardners
Cone shaped epiphysis + subcutaneous calcified nodules + hand abnormalities
Albright hereditary osteodystrophy
GNAS
+ short 4th/5th metacarpels, short distal phalanges of thumb,
Most common cause of 46XX, ambiguous genetalia
CAH
21 hydroxylase deficiency
NBS: high 17-OHP
Evaluate for salt wasting
Penile freckling + macrocephaly
Cowden/Bannayan-Riley-Ruvalcaba Syndrome
PTEN
Hamartoma syndrome - vascular, lipoma, breast, thyroid, endometrial, GI
2/3 toe syndactyly
SLOS
DHCR7
BIochem: measure 7 dehydrocholestrol level
FTT, microcephaly, ID, cleft palate, CHD, ambiguous genetalia
Monitor: AST/ALT, cholesterol
Femur/tibia bowing, 46 XY sex reversal
Campomelic dysplasia
SOX 9 (autosomal SRY activator)
Cleft palate, CHD
monitor: Gonadoblastoma
Wilms tumor, aniridia, ambiguous genetalia, ID
WAGR
11p13 del (WT1 and PAX6)
Also look for ESRD
Wilms tumor, ambiguous genetalia, renal failure
Denys-Drash
WT1 gene
Ambiguous genetalia, renal failure, gonadoblastoma
Frasier syndrome
WT1
CHD, radial ray defect, anal anomalies
VACTERL
Unknown, ZIC3 (X linked)
Vertebral
Anal
Cardiac
TEF
esophageal atresia
Renal
Limb
imperforate anus, triphalangeal/hypoplastic thumb
Towns Brock
SALL1 (zinc finger)
+ ear tags, SNHL
- ESRD, CHD
Imperforate anus, polydactyly, hypothalamic hamartoblastoma, hypopituitary
Pallister Hall
GLI3
- Bifid epiglottis
Manage endo issures
PAX6
aniridia
Ch 11p13
Contractures/arthrogryposis, marfanoid habitus, crumpled ears
Congenital Contractural Arachnodactyly (beals)
FBN2
- Watch for kyphoscoliosis
heart defects (interrupted aortic arch, root dilation)
SCA + Parkinsonism
SCA3
Portugese
SCA + RP
SCA7
SCA + Oculomotor apraxia
SCA2
Which SCAs are repeat expansions?
CAG repeats
SCA1, 2, 3, 6, 7
Ataxia + neuropathy + Cardiomyopathy
Friedreich’s ataxia
Frataxin (FRDA)
GAA intronic repeat
Normal : 6-34
Disease: 67-1700
Ataxia + low Vit E
TTPA
Alpha-tocopherol transfer protein
Treatable
brachydactyly with shawl scrotum
Aarskog
FGD1
+ short stature (rhizomelia)
Broad thumbs with bifid nails/distal phalanges, duplicated hallux with syndactyly of 1-3 toes, macrocephaly, high forehead
Greig cephalopholysyndactyly
GLI3
Coronal craniosynostosis, broad thumb
Pfeiffer syndrome
FGFR1 or FGFR2 (more severe)
- May have cloverleaf skull
Broad thumb and hallux, beaked nose, with columella below ala nasae
Rubinstein Taybi
CRBBP, EP300
Cryptorchidism, CHD, FTT, ID
Cardiomyopathy, wrinkled palms, ulnar dev of hands, coarse face
Costello syndrome
HRAS
Monitor for pelvic rhabdomyosarcoma
Myopathy, cardiomyopathy, neutropenia
Barth syndrome
X linked
Taffazin
Cerebellar hypoplasia, deep posterior interpeduncular fossa (molar tooth)
Joubert
Ciliopathy
Dysmorphic - low set ears, high eyebroas, triangular shaped mouth
Renal cystic disease
Elevated 8-dehyrocholesterol and 8,9 cholestenol
XL-RCDP in females (Male lethal)
EPB gene
+ assymetric limb involvement

RCDP + hypoplasia of distal phalanges
XL RCDP - males
ARSE
- Can also be seen in pseudo-warfarin embryopathy (vit K eposide reductase)
RCDP with assymetric limb involvement
XL RCDP (females, male lethal)
high 8 dehydrocholesterol and 8,9 cholestanol
RCDP + nasal hypoplasia
Warfarin embryopathy
Cleft lip/palate laterality
L>R
Midline clefting DDX
Oralfacialdigital syndrome
Ellis Van Creveld (short rib, polydactyly, CHD)
holoprosencephaly
Cleft L/P + lip pits
Van Der Woude
IRF6 (interferon regulating factor) AD
Cleft l/p + myopia, deafness, hypermobility, arthritis
Stickler
COL2 and COL9, AD
Croase facies, short/obese, small hands/feet
Smith Magenis
RAI1
isochromosome 12p
Pallister Killian
Moasic (47+12p)
Need skin biopsy
Coarse face, hypertelorism, ID
Overgrowth syndrome + polydactyly, supernumery nipples
Simpson-Colabi-Behmel
Glypican 3 (X linked)
-Wilms tumor risk
Hypoplasia of distal 5th digit, DD, sparse scalp hair
Coffin Siris
SMARCA4, ARID1A, ARID1B
Coarse face
Bushy eyebrows
Cardiac, GU anomalies
22q11 marker -> tetrasomy 22q11
Cat eye syndrome
Anal, ear pits/tags, CHD, coloboma, renal, ID
4p16 deletion
Wolf Hirschorn
FTT, ID, greek-helmet face (short nose/philrum, high forehead, hypertelorism), coloboma
Coloboma of lower eyelid, micrognathia, malar hypoplasia, downlanding PF
Treacher Collins
TCOF1, POLR1D
Also ear abnormalities (microtia), cleft l/p, Pierre Robain sequence
Normal intellect
Peripheral Pulm artery stenosis, Posterior embryotoxon, butterfly vertebra
Alagille
JAG1, Notch2
hypoplasia of bile ducts -> jaundice
also TOF
Branchial cleft, hearing loss
Branchio-oto-renal syndrome
EYA1 (AD)
Also reonal dysplasia/agenesis
Hearing loss + RP
Usher syndrome
MYO7A
RP usually symptomatic in teens
Low set, prominent, posteriorly rotated ears with deficiency cartilage and hypoplastic lobes. “Cup shaped”
CHARGE
CHD7
Coloboma, heart, atresia choanae, growth retardation, genetal, ear anomaly
ear pit + imperforate anus
Towns brock
SALL1 (AD)
+ triphalangeal or hypoplastic thumb
FTT + dry/lax skin
RASopathy
CFC (pulm stenosis)
Costello (wrinkled hands, HRAS)
Assymetric growth restriction, triangular face, relative macrocephaly
Russel Silver
Hypomethylaton of 11p Imprinting control region (ICR1)
Maternal UPD7
May have hypoglycemia, GU anomalies
Wormian bones (extra bones between sutures)
Type I OI
COL1 deletions (other variants cause more severe phenotype - type II OI - due to dominant negative effect)
Blue sclera
Tx with bisphosphonates
Most common albinism in caucasians
OCA1
TYR (tyrosinase)
White hair at birth
Most common albinism in Africans
OCA 2
P gene
Some pigment at birth, gets lost with age
Albinism + syndromes
PKU (PH, low tyr)
Homocystinuria (CBS)
Prader Willi (P gene is by ch 15)
Menkes (ATP7A, copper metab, kinky hair)
Cheidack Higashi (LYST, giant melanosomes, + infection/neuro/bleeding)
Hermansky Pudluck (HPS, pale, bleeding, Puerto Rican + pulmonary fibrosis)
Cystinosis (CTNS)
Hemihypertrophy + epidermal nevi
Proteus syndrome
AKT1
- vascular malformations, lipomas, lymphatic malformations
Wilms tumor surveillance
US every 3-4 monhts until age 8
holoprosencephaly + polydacytly + hypothyroidism
Pallister hall
GLI3, AD
Hypothalamic hamartoma, hypothyroidism
aqueductal stenosis, CAL spots
NF1
Beighton scoring and cutoffs for abnormal
9 total
2 each for pinky, thumb, elbow, and knees
1 point for touching floor w/ palms
Abnormal cutoffs:
>6 pre puberty
>5 post puberty
>4 over 50
hypermobile + high arched palate w/ dental crowding
Marfan
FBN1
hypertrichosis + nail hypoplasia
Coffin-Siris
ARID1B
Coards, sparse hair, nail hypoplasia (5th digit)
Hypertrichosis cubiti
Wiedemann Steiner
KMT2A (AD)
ID, excess hair at elbow, back, legs
hypertrichosis + broad thumbs
Rubinstein taybi
CREBBP, EP300
postnatal short stature, microcephaly, broad thumbs/halluces
hypoglycemia, macrocephaly, jaundice
SOTOS
NSD1 (AD)
ID, hyptotonia
Dysmorphic: Long narrow face w/ long chin
Overgrowth
What does G6PD do?
First enzyme of hexose monophosphate shunt - generate nicotinamide edenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) -> glutathione regeneration
Heinz bodies in erythrocytes
G6PD defciency
Limb reduction + thrombocytopenia
Thrombocytopenia-absent radius syndrome
RBM8A
- thumbs are present
- may have renal and cardia cfindings
Limb defect + hypohydrosis + sparse hair + hypodontia
Ectrodactyly-Ectodermal dysplacia -Clefting (EEC)
TP63 (AD)
-Absent eyelashes/eyebrows
Cardiac myxoma, cutaneous myxoma, schwannomas
Carney complex
CNC1 (AD)
Dolichocephaly, prominent forehad, long/narrow face, long chin + DD + overgrowth
Sotos syndrome
NSD1 (AD)
Monitoring: Cardaic, renal, scoliosis, hearing loss
microcephaly, cleft palate, syndactyly
SLOS
7 dehydrocholesterol reductace (DHCR)
2/3 toe syndactyly, ambigous genetalia, DD
microcephaly + broad thumbs and halluces
Rubenstein Taybi
CREBBP, EP300
Postnatal growth restriction, ID
Downslanting PF, beaked nose
Micrognathia, cleft palate, upper airway obstruction
Pierre - Robin sequence
2/3 isolated
1/3 complex (22q, stickler, etc)
Robin sequence + myopia, deafness
Sticker
COL2, COL9, COL11
-myopia, deafness, arthropathy
Robin sequence + CHD
22q11
- look for hypocalcemia, immunodeficiency
CHD: arch abnormalitites - IAA or truncus
Micrognathia + inferior eyelid coloboma
Treacher Collins
TCOF, POLR
+ microtia, malar hypoplasia, SNHL
- Intellect normal
anophthalmia + polydactyly + cleft
Trisomy 13
What assessment should be performed in patients with bilateral ear pits?
Hearing assessment
Renal US if dysmorphic
- Treacher collins, Brachio-oto-renal
What should you think about when seeing inverted nipples?
CDG
Propionic acidemia
Flat nasal bridge + myopia, vitreous gel anomaly, cleft palate, deafness
Stickler Syndrome
COL2, 9, 11
nasal hypoplasia + RCDP
Warfarin
high nasal root, short nose, short phildrum, DD, FTT, hypotonia
Wolf Hirschhorn
4p delesion
Beaked nose (columella below alae nasi), broad thumb, downslanting PF
Rubenstein Taybi
CREBBP, EP300
hooked nose, exorbitism
Crouzon syndrome
FGFR2
neonatal encephalopathy, alopecia, rash, hypotonia
Biotinidase deficiency
EIEE + apnea + burst suppression
NKH
EIEE + lens dyslocation
Sulfite oxidase deficiency or Molybdenum Cofactor Deficiency
Alexander disease genetics
GFAP
AD (de novo)
Microcephaly, hirschsprung, hypospadias
Mowat Wilson
ZEB2
-Also ear anomalies, agenesis of CC
Bilaterally posterior ear pits, and creases
Beckwith Weidemann
FHx: Triple neg breast ca, ovarian cancer, melanoma, endometrial ca, prostate ca
BRCA1/2
Higher risk of breast and ovarian cancer in BRCA1
Higher risk of male breast ca in BRCA2 (8% vs 2%)
What % of pancreatic and ovarian ca can be attributed to BRCA1/2?
10% epithelial ovarian Ca and 5% of pancreatic
What are the NCCN high penetrance Breast and Ovarian ca genes
BRCA1, BRCA2, (breast, ovarian)
CDH1, (Diffuse gastric cancer + lobular breast ca)
PALB2, (allelic with fanconi, breast and ovarian ca)
PTEN (Cowden - GI hamartoma + macrocephaly + endometrial/breast/thyroid)
TP53 (Li frameni - soft tissue sarcomas, less ovarian)
NCCN High risk breast/ovarian Cancer screening
age 25: clinical exam every 6-12 months
25-29 - annual MRI (exposure to radiation before age 30 associated with increased risk of ca)
30-75- annuam mammo or MRI
- Discuss mastectomy
- SP Oophorectomy after childbearing ~ 35-40
Macrocephaly, GI hamartomas, Endometrial/breast/thyroid cancer
PTEN
Cowden Syndrome
Can also have neurodevelopmental phenotype in childhood
+ lipomas, colon ca, RCC, mucoutaneous skin lesions
Should TP53 patients get Bilateral salphingo-oophorectomy?
Li Frameni
- Multiple soft tissue sarcomas (including breast ca)
BSO NOT recommended prophylactically, low risk of ovarian cancer
GYN cancer syndromes
BRCA1, BRCA1
Lynch
Peutz Jegher (STK11)
Gorlin
DICER1
Colon Ca + ovarian Ca + endometrial ca + gastric Cancer
Lynch syndrome
MLH1, MSH2, MSH6, PMS2
Endometrial up to 60%, Ovarian 25%
- Also intestine, CNS, urothelial, pancreatic, and prostate
Tx: Gene specific recommendations:
- TAH-BSO in MLH1 and MSH6
Colonoscopy starting at 20 -25
Ovarian fibroma + BCC + jaw cysts + medulloblastoma
Gorlin
PTCH1
Hypotonia and FTT in infancy -> truncal obesity and small hands/feet
ID, hypogonadotropic hypogonadiam
Prader Willi
15q11 (pat genes)
Causes: 75% pat deletion, 25% maternal UPD, 1% imprinting defect
Obesity, DD, retinopathy, nephropathy
Barbed Beidl
BBS
Ciliopathy
+ preaxial polydactyly
Obesity, short stature, shortening of distal phalanges and metacarpals, coned epiphysis, ID, subcutaneous nodules
Albright hereditary osteodystrophy
Inactivating GNAS mutations AD
Tissue specific imprinting:
Maternal mutations -> pseudohypoparathyroidism (resistance to PTH -> PTH high)
Paternal; -> Pseudopseudohypoparathyroidism (labs are normal)
Obese, short stature, small hands/feet
Sleep disturbance, self hugging, self harm
Smith Magenis syndrome
17p11 deletion: RAI1
- Prader Wili like + prominent sleep/behavioral phenotype
- Check for this whenever PWS is negative
Hypertelorism, macrocephaly, high forehead, bifid thumbs and toes
Greig cephalopolysyndactyly
GLI3
Hypertelorism, rhizomelia, hyperextendable PIP joints, shawl scrotum
Aarskog,
FGD1 (XL)
Syndromic causes of edema infancy
Noonan, Turner, GM1 gangliosidosis
Variable: Proteus (AKT1)
TEF + radial limb defect
VACTERL
(Small percentage due to ZIC3, Kynureniase deficiency - tryptophan metabolism)
Vertebral
Anal atresia
Cardaic
TracheoEsophageal Fisula
Renal
Limb
TEF + dysplastic external ear, Coloboma
CHARGE (CHD7)
Coloboma
Heart
Atresia of chloanae
Regardation (growth and intellect)
Genital
Ear anomalies
What condition do you need to exclude in babies with duodenal atresia
Down syndrome
Overgrowth + dolicocephaly, ID, fronto-temporal hair sparsity, hypotonia
Sotos syndrome
NSD1 (AD)
- Also cardiac, renal anomalies and seizures
Overgrowth, macrocephaly, hemangiomas, follicular thyroid tumor, breast ca, lipoma
PTEN hamartoma syndrome
Bannayan-Riley-Ruvalcaba - childhood w/ penile freckling
Cowden - adult form -> multiple hamartomas
Overgrowth + syndactyly, midline groove in lower lip
Simpson-Golabi-Behmel
GPC3 (XL)
Overgrowth
Dysmoprhic
Hand anomalies
Congenital anomlaies: Heart, renal, Congenital diaphragmatic hernia
Tx: Surveillane for embryonal and wilms tumor
Overgrowth, abd wall defects, ear creases/posterior pits
Beckwith-Wiedemann
11p15 epigenetics
monitor for wilms tumor
Regional overgrowth syndromes
Mosiac disorders:
PIK3CA (brain malformations, hemimegaencephaly)
Proteus - ATK1 - cerebriform naevi, linear epidermal naevi, vascular/lymphatic malformations
Duodenal atresia, diaphragmatic hernia, corneal clouding, nail hypoplasia
Fryns syndrome
unknown gene
Jejuno-Ileal atresia
Cystic Fibrosis
CFTR
hypopigmented macule + ependymoma + epilepsy
TSC
Hypopigmented macule = ash leaf spot
Raised leathery patch = Shagreen’s patch

Skin hypopigmentation + white forelock + heterochromia
Waardenburg
Pax3
+ Deafness, synophorys, dystopia canthorum

Blistering lesions along lines of blaschko (first few days) ->
LE verrucous lesion (<6 months) ->
axillary/groin hyperpigmentation (>6 months) ->
pale atrophic streaks (childhood)
Incontentia pigmenti
IKBKG (XL, male lethal)
+ alopedia, dental problems
- Free melanin granules if hyperpigmented streak is biopsied
Tx: Retina exam, cosmetic dentistry

What are typical CAL macule findings in NF1 vs NF2
NF1 - 6 or more (5mm pre puberty, 15mm post puberty)
NF2 - <6
craniosynostosis + broad thumbs/halluces
Pfeiffer syndrome
FGFR1 (5%)
FGFR2 (95%)
Craniosynostosis + Cleft Palate + syndacytly
Apert syndrome
FGFR2
Ser252Try or Pro253Arg
Postaxial polydactyly + Retinal dystrophy + Obesity + renal dysfunciton
Bardet Biedl
BBS genes
Ciliopathy
Broad, duplicated thumbs, polydactyly, macrocephaly, hypertelorism
Greig Cephalopolysyndactyly
GLI3 (AD)
Mesoaxial polydactyly, imperforate anus, hypopituitarism, hypothalamic hamartoblastoma
Pallister-Hall (anocerebrodigital syndrome)
GLI3 (AD)
- bifid epiglottis
Triphalangeal Thumbs, absent thumbs, CHD
Holt Oram
TBX5 (AD)
- Upper limbs only
Triphalangeal thumbs, hypoplastic thumb, imperforate anus, dysplastic ears, SNHL
Towns brock
SALL1
+ CHD
UGT1A1 homozygosity for A(TA)7TAA promotor insertion
Gilbert syndrome
Most common cause of mild unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia
~50% of north american’s are carriers, 9% homozygous
UGT1A1 LOF mutations
Crigler Najjar syndrome
- Non-hemolytic unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia
Tx: Phototherapy
Neonatal jaundice, prominent/pointed chin, deep set eyes, straight nose w/ bulbous tip,
Alagille syndrome
JAG1, NOTCH2
Slit lamp exam -> posterior embryotoxon
Peripheral pulmonary artery stenosis
Face: Prominent forehead, deep set eyes, hypertelorism, pointed chin, saddle/straight nose w/ bulbous tip

Jaundice, large fontanelle, hypotonia
Zellweger Spectrum
PEX genes
VLCFA up, Plasmalogen low, Phytanic high
Neonatal jaundice, hepatmegaly, neurodegeneration, cherry red macula
Niemann Pick A
Acid Sphingomyelinase (SMPD1)
NPB presents later
Jaundice, overgrowth, dolichocephaly, pointed chin
Sotos Syndrome
NSD1 (AD)
- Look for microdeletion 5p35 in japanese patient
Assymetric coronal suture craniosynostosis, low frontal hairline, ptosis, proximally inserted thumb, small ears w/ prominent crus
Saethre-Chotzen
TWIST1
- look for skin syndactyly, broad halluces

What do you need to look for in patients with blepharophimosis, ptosis, and epicanthus inversus syndrome?
Premature ovarian failure
Overgrowth + CHD + polydactyly
Simpson Golabi Behmel
GPC3, GCP4
Neonatal jaundice + adult COPD
Alpha 1 antitrypsin
SERPINA1
Rhizomelia, ptosis, hypertelorism, hyperextendable PIP, shawl scrotum
Aarskog
FGD1

Bilateral thumb anomalies, CAL spots, microcephaly
Fanconi amenia
- Chromosomal breakage analysis
Radial ray anomalies, growth retardation, anemia
Diamond Blackfan Anemia
RPS and RPL genes
Tx: transfusion, HSCT
Radial ray defect, tracheal esophageal fistula, renal agenesis, anal agresia
VACTERL
Vertebral
Anal
Cardiac
TEF
Renal
Limb
Autosomal dominant radial ray defect + CHD
Holt Oram
TBX5
- Always bilateral, can be any upper limb anomly
+ CHD
DDx: thalidomide
Retinal dystrophy + hydrocephalus + neuronal migration defects
Congenital Muscular dytrophy (Walker warburg, muscle - eye-brain)
POMT (O linked CDGs)
RP + deafness
Usher (+ balance issues)
Refsum disease (+ high phytanic acid, neuropathy, skeletal changes)
Cockayne (+photosensitivity, growth failure, intracranial calcifications)
RP + obesity + renal dysfunction
Bardet Biedl
Ciliopathy, BBS genes

High ornithine, night blindness, myopia
Gyrate atrophy
OAT (ornithine aminotransferase)

RP + seizures + neurodegneration
Neuronal Ceroid Lipofucsinosis
CLCN 1, 2, 3
Enzymes: Palmitoyl-Protein thioesterase (PPT), Tripeptidyl-peptidase (TPP)
Transverse limb defect + scalp defect
Adams Oliver
ARHGAP31, DLL4, NOTCH1, RBPJ (AD)
DOCK6,EOGT (AR)
- may have developmental delay or pulmonary HTN
What gene accounts for short stature in Turner Syndrome?
SHOX haploinsufficiency
Short stature, triangular face w/ assymetry, disproportionately large head
Silver-Russell syndrome
60% hypomethylation of ICR1 on chromosome 11p15
10% maternal UPD7
Short stature, rhizomelia, hypertelorism, brachydactyly with hyperextensible PIP joines
Aarskog
FGD1 (XL)
+ Shawl scrotum

Short stature, obesity, short 4th/5th metacarpals, subcutaneous nodules
Albright hereditary Osteodystrophy
GNAS LOF
Postnatal short stature and microcephaly, ID, broad thumbs, pilomatrixoma
Rubinstein Taybi
CREBBP, EP300 - abnormal histone acetylation
+ beaked nose, cryoporchidism, CHD, sleep apnea
Tumors: Meningioma, pilomatrixoma, leukemia

short stature, microcephaly, hirsutism, limb reduction, ID, diaphragmatic hernia
CDLS
NIPBL (AD), SMC1A, SMC3, HDAC8, RAD21
+ synophorys, pulmonary valve stenosis

agenesis of the corpus callosum, hypertelorism, pointed chin, prominent columella, broad medial flared eyebrows, uplifted earlobes, hypospadias
Mowat Wilson
ZEB2
+ CHD
craniosynostosis with syndactyly
Apert syndrome
FGFR2
+ ID
Absent sweating, dry skin, sparse hair, peg shaped teeth
Hypohydrotic ectodermal dysplasia
EDA (XL) - also AR and AD forms
Death due to hyperpyrexia during infections
What are the non-skin findings in Incontinentia pigmenti?
NEMO (XL)
skin: blistering -> verrucous -> Hyper -> Hypopigmented
Non skin: Nail dystrophy, dental anomalies, patchy alopecia, seizures all ectodermal stuff
Sparse hair, nail hypoplasia (5th digit), coase facies
Coffin Siris
ARID1B - chromatin remodeling - AD de novo
Wormian bones, sparse steely hair, pili torti, neurodegeneration
Menke’s disease
ATP7A (XL) -> copper metabolism
FGFR3 c.1138G>C, p.G380R
Achondroplasia
rhizomelic short stature
trident hard (wedge shaped gap between 3rd and 4th digit)
- OSA, cervical instability, hydrocephalus
FGFR3 c.1620C>A, p. N540K
Hypochondroplasia
milder achondroplasia, X rays may be normal until age 2
What is the pathophysiology of achondroplasia?
GOF -> constitute activation of normally inhibitory function of FGFR3
What disease and how much enzyme activity do homogyzotes with GLu342Lys in SERPINA 1 have?
A1AT deficiency
Glu342 = Z variant = 85% enzyme reduction
Glu264Val = S variant = 40% enzyme reduction
wt = M variant
What disease and how much enzyme activity does someone homozygous for Glu264Val in SERPINA1 have?
A1AT deficiency
Glu342 = Z variant = 85% enzyme reduction
Glu264Val = S variant = 40% enzyme reduction
wt = M variant
Progressive childhood hematuria + deafness + anterior lenticonus
Alport syndrome
85% XL - COL4A5
15% AR - COL4A3 or A4
- can have renal failure and retinal findings
- Contiugous gene delesion on X can cause alport + leiomyomatosis
What external and interal differences do you expect between CAIS, PAIS, and 46XY females due to SRY?
CAIS/PAIS - complete/partial androgen insensitivty syndrome due to AR mutations
CAIS: 46XY w/ normal external female genetalia and testes w/ blind vaginal pouch
PAIS: 46XY w/ ambiguous genetalia and testes
SRY: 46XY w/ normal female genetalia and ovaries/uterus
- remove testes due to gonadoblastoma risk
What % of Angelman syndrome mutations should be detectable by methylation analysis?
~80%
70% - deletion of maternal 15q11-13
5% - paternal UPD
5% - imprinting defect
- 10% w/ UBE3A mutations and 10% unknown will be missed
When/what should genetic testing in pursued for individuals with autism?
If there is intellectual disability: CMA and fragile X
If dismorphic: CMA
If developmental normal -> regression: MECP2
If seizures -> MRI + TSC
Exome role unclear
In an adult patient with renal, liver, pancreatic, and splenic cysts and positive family history, what other complications are likely?
ADPKD
- screen for renal function, hypertention, and aneurysms if family history is present
- CTD: hernias and colonic diverticula are also common
What features can help distinguish CFC, Costello, and Noonan w/ multiple lentigenes?
CFC: Sparse hair/eyebrows, eczema/ichthyosis
Costello: Papillomata, soft and loose skin w/ deep palmar creases
Noonan w/ multiple lentigenes: Lentigenes + deafness
Nail dysplasia, elbow/knee exostosis, V shaped lunula
Nail-Patella
LMX1B gene -> regulate COL4A3 and COL4A4
What is pseudoachrondroplasia?
- No craniofacial involvement.
- Normal at birth -> short stature w/ short limbs
- COMP gene
In androgen insensitivity syndrome, what happens in puberty?
- normal breast development - testosterone -> estrogen
- sparse hair
- no menses
What are the first and second line genetic tests for BWS?
1) 11p15.5 methylation -> detects paternal UPD or methylation abnormalitites
2) CDKN1C mutation analysis (5-10%)
Name 4 molecular causes of BWS
1) epimutation in IC1 (10%)
2) epimutation in iC2 (50%)
3) paternal UPD 11p15 (20%)
4) CDKN1C mutation (10%)
What gene causes X linked Charcot Marie Tooth?
GJB1 -> connexion 32
Retinal degeneration, renal, respiratory, CNS malformation, situs inversus, infertility, liver cysts, diabetes, polydactyly, obesity, skeletal
Ciliopathies
Compare Male vs Female presentation of 21 hydroxylase deficiency
CAH
21 hydroxylase converts 17OH-progesterone into 11 deoxycortisol; deficiency means 17OHP turns into androstenedione -> testosterone instead
Females: Ambiguous genitalia, salt wasting
Males: salt wasting, early puberty
What is the definition of a consanguinous relationship?
second cousin or closer
What is the probability of a recessive disorder in offspring of general public, 1st cousin marriages, and 2nd cousin marriages?
general: 2%
2nd cousin: 3%
first cousin: 4%
Craniosynostosis w/ severe syndactyly (mitten hands), developmental delay
Apert syndrome
FGFR2
Craniosynostosis w/ exorbitism (shallow orbits) and hooked nose
Crouzon Syndrome
FGFR2
Craniosynostosis w/ exorbitism (shallow orbits) and hooked nose
+ Acanthosis nigricans
Crouzon w/ Achanthosis nigricans
FGFR3 (Ala391Gln)
Most common genetic coronal synostosis
Muenke syndrome
FGFR3 (Pro250Arg)
- May have deafness/brachydactyly/carpal fushion
- Rule out in ALL coronal synostosis (uni and bilateral)
Craniosynostosis w/ cloverleaf skull or broad thumbs/halluces
Pfeiffer syndrome
FGFR2 or FGFR1 (rarer, mild)
- can also have beaked nose and exorbitism like crouzon
Craniosynostosis w/ prominent crus, facial assymetry, ptosis, low anterior hairline
Saethre-Chotzen
TWIST1 - transcription factor
- also can have broad thumb -> distinguish from pfeiffer by facial features
- can be part of 7p21 deletion syndrome + ID

craniosynostosis w/ bowed femors, joint anklylosis, radiohumeral synostosis, ambivuous genetalia
Antley Bixler
Cytochrome P450 (POR)

What does sweat chloride level of 30-60mM mean?
Borderline result, most likely atypical CF
<30mM is normal
What phenotype is associated with R117H in cis with 5T along with delta F509 in other alelle?
Classic
- 5T = very little expression
What phenotype is associated with R117H in cis with 9T along with delta F509 in other alelle?
CBAVD
Growth retardation, neonatal diabetes -> remission by 1 yr
Transient neonatal diabetes
Paternal UPD6
Paternal 6p24 duplication
Methylation defect
ZFP57 inactivation (6p22)
Early diabetes, RP, obesity
Bardel Biedl Syndrome (with renal disease)
or
Prader Willi
Name 2 XL causes of dilated cardiomyopathy
1) Dystrophin
2) Barth syndrome (Tafazzin)
What does APTX and SETX do?
DNA repair genes (SS break and DNA damage response)
- Ataxia w/ oculomotor apraxia
Immunodeficiency, ataxia, small stature, Cell cycle checkpoint inhibitor - Double stranded break repair pathway
Ataxia Telangiectasia
ATM
- Telangiectasias appear by age 4-8
- Avoid radiation
- Leukemia/lymphoma/ breast ca risk
Butterly rash, immunodeficiency, diabetes, chronic lung disease, Ashkenazi jewish
Bloom syndrome
BLM -> DNA helicase -> sister chromatid exchange
Deep set eyes w/ pinched appearing nose (loss of subQ fat). hearing loss, RP, photosensitivity
Cockayne
CSA, CSB, ERCC6, ERCC8
- Transcription coupled repair
FTT, pancytopenia, cafe au lait spots, radial ray anomalies
Fanconi anemia
FANC genes - including BRCA2 (AR), PALB2 (AR)
-broken chromatids and quadriradial formations
Trichorrhexis nodosa, short stature, ID, ichthyosis, sun sensitivity
Trichothiodystrophy
- TTDA, XPD
- DNA repair defect
- XPD -> decreased B globin production -> B thal trait
Corneal clouding, severe sunburn, skin cancers (BCC, SCC, melanoma)
Xeroderma Pigmentosum
- Avoid UV exposure
- Nucleotide excision repair
Large bowel perforation, urterine rupture, carotid dissection, thin translucent skin
Vascular EDS
COL3A1 (AD)
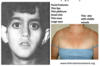
Widened atrophic scarring, joint hypermobility, hyperextensible skin, molluscoid pseudotumor
Classic EDS
COL5A1 (AD)
Neonatal hypotonia, premature rupture of membrane, joint dislocation, Globe rupture, congenital kyphoscoliosis
Kyphoscoliotic EDS
PLOD1 (AR - NOT a collagen subunit)
Genetics of FSHD
DUX4 expression
- Can be due to D4Z4 shortening + PolyA tail haplotype
OR
SMCHD1/DNMT3B variant (methylation controllers)

Fragile X premutation is more likely to expand if inherited from mom or dad?
mother
Screening guidelines for BWS
Abd US every 3 months until age 8 -> wilms tumor
AFP every 3 months until age 3 -> hepatoblasoma
Short rib, short limbs, cardiac malformation, polydactyly, small nails
Ellis- van creveld
ECV and ECV2
Short rib, short limbs, polydactyly, renal dysplasia, hepatic fibrosis, retinal degeneration
Jeune syndrome
IFT80, DYNC2H1, WDR60, WDR35, TTC21B, WDR19
Caniosynostosis, split/ridges in nails, hypertelorism, midline nasal groove.
X-linked Dominant
Craniofrontonasal syndrome (Frontonasal syndrome)
EFNB1
XL females more affected because ephrin protein defines cellular boundaries -> cellular interference
Craniosynostosis, scalp thickening
Bear Stevenson Syndrome
FGFR2
- Scalp thickness = cutis gyrata
What phenotype is associated with R117H in cis with 7T along with delta F509 in other alelle?
Non-classic CF
Continguous gene deletion involving dystrophin
DMD + glycerol kinase deficiency
- pseudohypertriglyceridemia + high urine glycerol
What % of Duchennes is de novo/germline mosiac?
De novo: 30%
Germline mosiac: 15%
Jemojuvelin (HJV), Hepcidin (HAMP)
Juvenile Hemochromotosis
Onset between 10 and 30
Neonatal hemochromatosis
Autoimmune disease
- High ferritin, low transferrin, high AFP
- May present as hydrops
HbSC disease
Compount HbC and HbS
What does 4 nonfunctional Hb A allese cause?
Hydrops (no HbA production in utero) - Hb Barts = 4 gamma globins
What does 3 nonfunctional HbA alleles cause?
HbH disaease
- Anemia, splenomegaly, hemolyss
HbE
E26K in B globin
- abnormal splicing -> decreased B globin synthesis
- Mild version of B thal when homozygous
- Severe disease when compound het w/ Beta Thal variant
How are hemophilia A and B inherited?
Both X linked
What is the mechanism of hypocoagulability in von Willebrand Disease?
vWF protects factor VIII from premature proteolytic cleavage at sites of vascular injury
When should you screen for Pul AVMs in HHT?
- After puberty (rare before)
- Also between pregnancies (tend to get worse)
HTT w/ aortic root dilation and polyps
SMAD4
ACVRL1, ALK-1, and ENG
genes for classic HHT
- form a homodimeric membraine glycoprotein that is surface receptor for TGFB superfamily
- SMAD 4 causes HHT w/ polyps and aortic root dilation
Isolated Hirschsprung
RET
- 50% familial and 20% sporadic cases
- Also causes in MEN2A (MTC, pheo, parathyroid) - hirschsprung can be part of this
Hirschsprung + upturned ear lobule, deep set eyes, prominent chin, flared eyebrows, microcephaly, ASD, GU anomalies
Mowat Wilson
ZEB2
Hirschsprung, IUGR, microphcephaly, distal limb anomalies
SLOS
DHCR7
- mother estriol low
- 2/3 toe syndactyly

How does prenatal exclusion testing work?
For Huntingtons - a way for at-risk individual to not have HTT child WITHOUT finding out their own status
- Look at haplotypes of grandparents around HTT gene
- If haplotype of child is from unaffected grandparent then they are at population risk
What features suggest heritable retinoblastoma?
- Bilateral
- Family history
- < 1 year old
- Other ca: Osteosarcomas, melanomas
- germline RB mutation
What should patients with germline RB mutations avoid?
Radiation - including radiotherapy
>100 colon polyps
Congenital Hypertrophy of RPE
APC gene (AD)
FAP: Polyps + CHRPE + Thyroid/duodeum tumors (adenomas)
Gardner: FAP + desmoid tumor, dupernumerary teeth, osteomas
>3 hamartomaous polyps, mucocutaneous pigmentation
Peutz Jeghers
STK11
- increased breast, upper GI, ovarian, and pancreas Ca risk
Colon, stomach, pancreas, endometrial, ovarian ca, microsatellite instability
- How do you screen?
HNPCC
Mismatch repair
MHL1, MSH2, MSH6, PMS2
- Colonoscopy at age 20 (or 10 yrs before first ca in family)
- TVUS at age 30 (or 10 yrs before first ca in family) + Ca 125 every 6-12 months
HNPCC + sebaceous adenomas/carcinoma + keratoachantoma
Muire Torre
- MSH2 or MLH1 (subset of HNPCC)
Papillomatous papules, macrocephaly, trichilemmomas
+ breast, thyroid, endometrial, renal cancer
PTEN - Cowden/BRRS
- Pigmented macules in penis in BRRS
Clear cell renal carcinoma, pheo, endolymphatic sac tumors
- Tumor suppressor involved in degradation of HIF
VHL
Hereditary leiomyomatosis and renal cell carcinoma
Fumarase (fumarate hydratase) def, AD
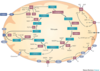
Renal Cell carcinoma, lung cysts, pneumothorax, fibrofolliculoma, trichodisocoma, acrochordons
Birt-Hogg-Dube
FLCN - folliculin
- Skin, lungs, renal
What tumor suppressor gene on ch17 regulates adenylyl cyclase in intracellular cAMP generation?
NF1
- Plexiform Neurofibtromas
- malignant peripheral nerve sheath
- optic glioma
- pheochromocytoma
- leukemia
- astrocytomas
- breast ca
Basal cell, jaw cysts, falx calcification
Gorlin
PTCH, SUFU (rare)
+ macrocephaly, skeletal abnormalities, medullloblastoma
Breast cancer, sarcoma before <45 w/ family hx
Li frameni
TP53
Breast ca most common ca in this syndrome (can mimic brca, lynch, other ca predisposition)
Hereditary paraganglioma
Succinate dehydrogenase
SDHB, SDHC, SDHD
- part of TCA cycle and complex II

SNHL, absent reflexs, acquired microcephaly, skin cancer, sun senstivity, keratitis
XP
Nucleotide excision repair
ERCC1-5, XPA, XPC
Cell cycle checkpoint kinase that regulates TP53, BRCA1, CHEK2, NBS1
- Radiation sensitivity
Low IgA, IgE, and IgG levels
- cerebellar hypoplasia
Ataxia Telangiectasia
ATM gene
- Breast, prostate, and pancreatic cancer
Defective double stranded break repair
Nijmegen breakage syndrome
NBN
- microcephaly, FTT, ID, immunodeficiency, lymphoma
- Heterozygotes at risk for breast and prostate cancer
Photosensitivity, microcephaly, immunoglobin deficiency, FTT
DNA Helicase disorder
Bloom syndrome
BLM gene -> genomic instability -> abnormal sister chromatid exchange
- Quadriradials on karyotype
- many cancers
Triangular face, dangling thumbs, imperforate anus, short stature, pancytopenia
Fanconi anemia
+ solid tumors and leukemia
- Chromosome breakage analysis
Ribosomal protein disorder
Short abnormal thumbs, cleft palate, macrotytic anemia, increased Hb F
Diamond-blackfan anemia
- associated w/ lung ca, choroid meningioma of the lung, AML, MDS, SSC (vaginal)
Parathyroid, pituitary, pancreatic islet ca, adrenocortical tumors
MEN1
(MEN1 gene)
- parathyroid is defining feature (100% of cases)
Medullary thyroid cancer, Pheo, hyperparathyroidism
MEN2A
RET
- Test RET in all individuals with MTC
- Ppx thyroidectomy asap in anyone with RET - 100% penetrance
Medullary thyroid ca, pheo, murosal neuroma, ganlioneuromatosis, marfanoid facies, hirschsprung
MEN2B
RET
- RET testing in ALL individual with MTC
- Ppx thyroidectomy asap in anyone with RET - 100% penetrance
How do you treat familial hypercholesterolemia
Statins (consider at age 10)
Aphoresis (for severe homozygotes/cmpd hets)
PSCK9 inhibitors
Hypercholesterolemia, phytosterol/sitosterols
Sitosterolemia/Phytosterolemia
- ABCG5, ABCG8 -> twinned sterol-half transporter
- Increased intestinal absorption/decreased biliary excretion of fish and plant sterols
- Xanthomas, artheroscerlosis, hemolysis
- Tx Diet
MYBPC3, MYH7, troponin mutations
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
50% MYBPC3
33% MYH7
Syndromic causes:
- Fabry (angiokeratoma, short PR)
- Danon (LAMP2 - pompe like + WPW)
- Friedreich (+ ataxia)
- Pompe,
- Ras-opathies (+ pulmonic stenosis)
Eczema, thrombocytopenia, immunodeficiency, lymphoproliferative disease/lymphoma
Wiskott aldrich
WASP (XL)
- regulation of actin cytoskeleton in blood cells
Tx: IVIG, tranfusion, splenectomy, BMT
Decreased T cells, hypocalcemia, TOF
22q11 del syndrome
- CD8 primarily affected
severe T cell lymphopenia, ear abnormalitites, Coloboma
CHARGE syndrome
CHD7
Coloboma, Heart, atresia choanal, retardation (growth and dev), general hypoplasia, ear anomalies
Early bacterial infections, low IgG, Low CD19 B cells
Bruton agammaglobinemia
BTK gene (XL)
tx: IVIG
Albinism, leukocytes w/ giant granules, easy bruising, cognitive delay, ataxia, neuropathy, parkinsonism
Chediak Higashi
LYST - lysosomal protein trafficking gene
- Albinism + immunodeficiency + neuro + easy bruising
Tx: BMT
Recurrent fevers, abd pain, joint pain, chest pain
Familial mediterranean fever
MEFV (Pyrin)
- Predisposed to amyloidosis
Tx: Cholchicine
What is the risk of disease in child of 1st degree relatives?
Genome 12.5% (1/8) IBD
Empiric risk higher than calculated:
30% risk of severe abnormality/death
50% chance of MR or severe abnormality
What is the risk of disease in child of 2nd degree relatives?
1/16 of genome IBD (6%)
What does SURF1 cause/do?
Most common genetic cause of leigh syndrome
- Complex IV assembly
- Upper arms and lower leg (humeroperoneal) weakness
- achilles, elbow, and spine contractures
Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy
STA - XL
LMNA - AD
What are the 3 most common genes causing long QT syndrome?
KCNQ1, KCNH2 -> LOF
SCN5A -> GOF
- AD: romano-ward
AR: Jervell and Lange-Nielsen (+ Hearing loss)
Which disorders are caused by SCN5A mutations?
GOF (AD)-> Romano ward (long QT)
GOF (AR)-> Jervell and Lange Nielsen (Long QT + hearing loss)
LOF (AD) - Brugada -> multiple arrhythmias (incomplete RBBB and ST elevation)
What are differences between marfan and LDS?
LDS does not have ectopia lentis
LDS has arterial tortuosity, bifid uvula, hypertelorism
Crumpled ears, neonatal contractures, scoliosis
Beal syndrome (congenital contractural arachnodactyly)
FBN2
Prominent eyes, decreased adipose tissue below eyes, thin “pinched” nose, thin lips, hollow cheeks
Thin translucent skin
EDS type IV
Vascular EDS
- COL3A1
+ organ rupture, no hypermobility

vitreous gel anomaly, cleft palate, SNHL, arachnodactyly
Stickler
COL2, 9, 11
Lens dyslocation, thrombophilia, learning disability, cataracts
Homocystinuria
Cystathione beta synthase deficiency
What are the most common presenting features of MELAS?
tRNAleu - A3243G
Mito encephalopathy w/ lactic acidosis and strokes
- Most common: Diabetes and hearing loss
tRNAlys - A8344G
MERRF
- Myoclonic epilepsy, RRF
+ ataxia, dementia, deafness
mt T8992G, T8993C
NARP
Neurogenic weakness, ataxia, RP
-subset of leigh syndrome
What is pearson syndrome?
transfusion dependent sideroblastic anemia/pancytopenia
+ malabsorption (exocrine pancreas failure)
- Mostly mtDNA deletions
Homoplasmic mt A1555G, A7445G
Deafness when exposed to aminoglycosides
Prolonged PR, wide QRS, diabetes, cataracts, long face w/ smooth forehead, pilomatrixoma, distal weakness
Myotonic dystrophy type I
3’UTR CTG expansion in DMPK
>1000 - congenital
100-1000 - classic
50-100 - mild
- 35-50 premutation
<35 - normal
Alpha Thal + ID
ATRX (XL)
- Chromatin remodeling that controls a-globin expression in trans
- also interacts with MECP2 (Rett)
In Hemophilia, which lab is abnormal?
PTT abnormal
(PT normal)
Hyper IgE, eczema, fractures, rough facial skin, coarse facies, denal abnormalities (retain baby teeth)
Jobs syndrome
STAT3, DOCK8
- Severe resp/skin infections
When does neural tube closure occur?
primary neurulation -> 18-26 days post fertilization
2 teratogens that cause Neural Tube defects
Valproic acid and maternal diabetes
Name the 7 NF1 criteria
1) CAL spots: 6+ (0.5cm before puberty, 1.5cm after puberty)
2) neurofibromas: 2+ regular or 1 plexiform
3) Freckling
4) Optic glioma
5) Lisch nodules (2+)
6) Bone: sphenoid dysplasia or thinning of long bone cortex
7) Family history (1st degree relative)
CAL spots, intertriginous freckling, lipoma, macrocephaly, learning disability
Legious syndrome
SPRED1
- NF mimicker, but no neurofromas or tumors
What finding is common in NF2 but rare in NF1?
Deafness
What do you need to look for in NF1 patient w/ HTN?
Increased risk for renal artery stenosis or pheochromocytoma
Low set/posteriorly rotated ears, blue irises, hypertelorism, downslanting palpebral fissures, ptosis, pulmonic stenosis, DD, short stature
Noonan: Ras-opathies
Most common: PTPN11 (50%), SOS1 (10%)
Rarer: RAF1, RIT1, KRAS, NRAS,BRAF, MAP2K1

Low set/posteriorly rotated ears, blue irises, hypertelorism, downslanting palpebral fissures, ptosis, pulmonic stenosis, DD, short stature, Lentigines, SNHL
Noonan with multiple lentigines
PTPN11

Low set/posteriorly rotated ears, blue irises, hypertelorism, downslanting palpebral fissures, ptosis, pulmonic stenosis, DD, short stature sparse hair, red with keratosis pilaris, rough skin
Cardiofaciocutaneous Syndrome
Noonan + ectoderm
MEK1/2, BRAF, KRAS

Low set/posteriorly rotated ears, blue irises, hypertelorism, downslanting palpebral fissures, ptosis, pulmonic stenosis, DD, short stature, papillomas around nose and mouth
Costello Syndrome
HRAS

Most common gene for parkinsonism before age 40
Parkin (PARK2)
When can males be affected by MECP2?
MECP2 is X linked
- Males can be affected in Xq28 duplication, mosiacism, or klinefelters
Rett syndrome + early epilepsy, marked hypotonia
CDKL5 (XL)
- MECP2 patients usually normal for 12-18 months, then regress
Rett syndrome + microcephaly, congenital onset
FOXG1 (AD)
- MECP2 patients usually normal up to 12-18 months, then regress
What is the significance of pseudocholinesterase (CHE1) variants?
Affect ability to breakd down succinylcholine -> prolonged sensitivity to anesthesia -> paralyzed for days rather than 30 min after surgery
What 2 genes cause 70% of malignant hyperthermia?
RYR1 and CACNA1S
RYR1 can also cause central core and minicore myopathy
What accounts for >90% of pathogenic variants in SMN1?
Deletion of exon 7
What is the difference between SMN1 and SMN2?
Both in chromosome 5
- SMN2 has a C->T change in exon 7 that leads to decreased splicing efficiency -> 85% transcripts has no exon 7
Flat midface with depressed nasal bridge, micrognathia
Midline cleft palate, retinal detachment, hypermobility, SNHL
Stickler syndrome
COL2 (AD), 9 (AR), or 11 (AD)
- Also vitreious anomaly and myopia
myopia, cleft palate, SNHL, platyspondyly, ovoid/pear-shaped vertebral bodies, odontoid hypoplasia, flattening and fragmented epiphysis
Spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia
COL2A1
- stickler with more severe skeletal findings
What are the common genetic causes of hypercoagulability (thrombophylia?)
- Factor V leiden
- Prothrombin mutation (factor II leiden)
- Antithrombin 3 deficiency
- Protein C or S deficiency
- Homocysteinuria

R506Q FV
Factor V leiden
- most common thrombophilia - 20% of all idiopathic thrombosis and 60% in pregnancy
- R506Q -> resistance to activated protein C cleavage

FII 20210A mutation
Factor II Leiden (Prothombin mutation)

What does protein C and S do?
Protein C destroys factors V and VIII -> inactivates clotting
Protein S is Vit K dependent cofactor for protein C

What is the workup for inheritled thrombophilia?
- Genetic testing for Factor V leiden (R506Q) and prothombin mutation (20210A)
- Functional testing for Protein C, S, and antithrombin III (genetically heterogeneous)
- Homocystein level

How do you manage pregnant patients with factor V leiden?
Factor V leiden is AD w/ incomplete penetrance
- Heterozygotes at 2-3x risk -> monitor closely
- Homozygotes (and prothrombin mutations patients) should get VTE prophylaxis during pregnancy
What is the pathophys for TSC?
Hamartin (TSC1) and Tuberin (TSC2) are tumor suppressor genes that form heterodimer -> regulates PI3K signaling and inhibits mTOR -> Regulates cell growth/proligeration
- 2 hit hypothesis for individual neoplasms

Hypomelanotic macules, raised leathery patches, angiofibromas, retinal hamartomas, SEGA, renal angiomyoplipomas, lymphanioleiomyomatosis
TSC
Tuberin and Hamartin (AD)
Hypomelanotic macule = ash leaf spot
thickened, leathery “orange peel” like skin = shagreen patch
- Renal angiomyolipomas common
- Get chest CT for Lymphangioleiomyomatosis
What are ages of onset for XALD and XANM?
ALD - 3-10 years
ANM - 20-40 years
What dose ABCD1 gene cause?
XALD
- VLCFA elevated (C26:0 lysophosphatidylcholine)
- Carriers also have VLCFA elevation
- Tx: BMT, HSCT early, Lorenzo’s oil (Oleic and erucic acid)
What are oleic and erucic acid?
Lorenzo’s oil -> improve VLCFAs in XALD; may slow disease progression, clinical utility unclear
Marfanoid + mucosal neuromas
MEN2B
Rett
Drugs to void in mitochondrial disease
VPA
Aminoglycosides
Metformin
Barbiturates
Tetracycline
Zidovudine
DMPK expansion is more likely in to occur in which patient?
Maternal
How long do you need to take folic acid to prevent NTD during pregnancy?
Until 12 weeks
occipital encephalocele, bilateral large kidneys w/ multicystic dysplasia, polydactyly
Meckel syndrome
ciliopathy
MKS1, MKS2,
Which Rasopathy often has hearing loss?
Noonan w/ multiple lentigines
PTPN11
Phenotype for homozygotes w/ PMS2, MLH1, MSH2, MSH6
NF-like syndrome
Homozygotes for Lynch
- CALS, Freckling, multiple GI cancers
hypomelanocytic macules, raised leathery patch, angiofibromas, ungual fibromas
TSC
Prenatal finding in TSC
Cardiac Rhabdomyoma
Most common tumor in TSC
angiomyolipoma
What genes are associate with increased risk for triple negative breast ca?
BRCA1, BRCA2, PALB2
What is the significance of serous papillary cystadenocarcinoma?
Ovarian tumor seen in BRCA1 and BRCA2
What is the definition of high risk for breast cancer?
Lifetime risk >40% from age 20
Moderate is lifetime risk >20% from age 20
What screening should be offered to women w/ increased risk for breast cancer?
Always - breast awareness
Age 30 - MRI (20 for tp53)
Age 40- mammo (avoid in tp53)
- U/S if MRI/mammo should be done but not suitable/tolerated
AR condition that is on DDx for multiple polyposis
MUTYH associated polyposis
Check if APC/STK11 are negative
Macrocephaly, GI polyps, Autism, lipoma, trichilemmoma, oral papilloma, AVM, hemangiomas
Cowden
PTEN
Cerebellar dysplastic gangliocytoma, trichilemmoma, breast cancer
Cowden
PTEN
What are the major tumors in PTEN syndromes?
Breast, Thyroid, and Uterine - benign or malignant
- Colon (polyps), Renal cell
>100 polyps, desmoid tumor, osteoma, supernumery teeth
FAP
APC gene - null/nonsense/frameshift variants
- screen for polyps at age 10
What do missense variants in APC cause?
benign unless splicing is affected
- FAP mutations are null/nonsense/frameshift
What is the significance of MUTYH?
Phenocopy of FAP that is AR
- >9 colon adenomas with no AD family history
- DNA oxidation damage repair
Surveillance for FAP
- Colon screening at 10
- Consider colectomy before 20
What gene is associated with linitis plastica and lobular breast cancer?
CDH1 (E-cadherin)
Hereditary Diffuse Gastric Cancer
- Gastric and lobular breast ca
Palmar/Plantar pits, cerebral falx calcifications, odontogenic keratocyst/polyostic bone cyst, BCC
Gorlin Syndrome
PTCH1 (AD), SUFU (AD)
+ macrocephaly, clefting, polydactyly, ovarian fibroma, medulloblastoma, cataracts
>5 juvenile polyps in colon/rectum
- Juvenile polyps in intesting/upper GI tract
Juvenile polyposis
- BMPR1A (TGFB pathway) - isolated
- SMAD4 (TGFB pathway) - w/ HHT
- PTEN - w/ Cowden
- PTCH - w/ Gorlin
Juvenile polyposis + HHT
SMAD4
Juvenile polyps + macrcephaly, trichilemmoma, freckling
PTEN
Juvenile polyps + BCC
Gorlin
PTCH1
What gene accounts for non-syndromic juvenile polyposis?
BMPR1A
Screening for juvenile polyposis
Colonoscopy at 15
EGD at 25
What type of variants in APC result in FAP?
Null/nonsense/frameshift
- Missense only if splicing
What does BRAF presence in colon cancer cells mean?
Most likely sporadic (not common in lynch syndrome)
Surveillance for Cowden
Thyroid at 16
Breast MRI at 30
Colonoscopy at 35
Renal US at 40
desmoid tumors, papillary thyroid, supernumerary teeth, adrenal gland adenomas, osteomas, medulloblastoma
Extra-colonic features of FAP
Protein-losing enteropathy, macrocephaly, juvenile polyposis, hypotonia
10q23 deletion
- Includes PTEN and BMPR1A
Breast ca, leiomyosarcoma, adrenocortical tumor, wilms tumor, phyllodes tumor
Li Frameni
TP53
- Adrenocortical and phyllodes highest absolute risk increase
How does EPCAM cause Lynch Syndrome?
EPCAM is next to MSH2, large deletion canl ead to epigenetic silencing of MSH2 -> colorectal cancer
What is Muir-Torre Syndrome?
Any interal cancer (colon usually) + sebacious skin tumor (epithelioma, ednoma, carcnioma)
- most commonly due to Lynch, but not always
What is turcot syndrome?
Polyposis + primary brain tumor
- Usually APC or Lynch gene
How do you interpret microsatellite instability from a somatic tumor sample?
- MSI is common in sporadic colon cancers -> low PPV for Lynch, but high NPV
- MSI is rare in extra-colonic cancers -> high PPV for lynch in ovarian, endometria, gastric cancers
What drug reduces risk of colon cancer in lynch syndrome?
Aspirin
What is the pathophys of MEN1 and MEN2?
MEN1 - Menin - tumor suppressor gene
MEN2 - Ret - GOF in proto-oncogene
Blue nevi and lentigenes, schwannoma, atrial myxoma, pitruitary tumor, thyroid cancer
Carney Complex
PRKAR1A
Surveillance for MEN1
- clinical for endocrine issues
- Annual calcium and prolactin starting at age 5
When is thyroidectomy recommended in MEN2?
MEN2A - 5yo
MEN2B -early as possible -> metastasis can happen by age 2
Meningioma, glioma, posterior subcapsular lenticular opacities, cerebral calcifications, schwannomas
NF2
- Merlin - tumor suppressor gene
Criteria:
- bilateral vestibular schwanomma
- 1st degree relative w/ NF2 + Unilateral schwanomma + other tumors
- Unilateral schwanomma + 2 other tumors
- multiple meningiomas + other tumors
What genes account for the majority of genetic ovarian cancer?
BRCA1, BRCA2, Lynch account for majority
- BRIP1, RAD51C, and RAD51D also associated
GI intussusception, perioral freckling
Peutz-Jeghers
STK11
- Polyps tend to be large and pedunculated -> often lead to intusscuception
- Get baseline EGD and colonoscopy at 8yo
+ Stomach, breast, colon, pancrease, ovarian cancer
Name 3 genes associated with pheochromocytoma
VHL (+ hemangioblastoma)
SDHB, SDHD (+ paraganglioma)
RET (+ medullary thyroid carcinoma)
Pheochromocytoma + marfanoid body habitus
MEN2B
+ medullary thyroid
RCC + fibrofolliculoma, pneumothorax
Birt-Hogg-Dube
FLCN - folliculin
+ pulmonary cysts
RCC + hemangioblastoma
VHL
+ pheo
RCC + paraganglioma
SDH
+ pheo
RCC + fibroids
Fumarase deficiency
- Fibroids = leiomyomatosis
What is the most common second hit in RB?
Loss of heterozygosity
What is “Trilateral RB”?
Bilateral RB + pinealblastoma (common in RB as part of primary cancer)
What are the major secondary cancers in RB?
Osteosarcoma, soft tissue sarcome, melanoma, brain tumors
What clinical test should be offered to parents of children affected by RB?
Eye exam to look for spontaneously regressed retinoblastoma
Surveillance for RB1
Eye exam under anesthesia from 3 weeks to 3 years
What are the most common manifestation of VHL?
Retinal angiomatosis > cerebellar hemangioblastoma > RCC > pheo
When should you start surveillance in VHL?
Eye exam at 5
Pheo at 11 (Urine VMA or plasma metanephrines)
MRI brain + body at 15
11p13 deletion
WAGR
- Wilms, aniridia, GU, retardation
WT1 and PAX6 included
Wilms tumor, GU anomaly, renal impairment (Mesangial sclerosis)
Denys-Drash
- WT1
Wilms tumor, gonadoblastoma, renal impairment (FSGS)
Frasier syndrome
WT1 mutations intron 9 -> splicing isoform change
How do you screen for wilm’s tumor in at risk individuals?
Abdominal US every 3-4 months until age 7-8
What testing needs to be checked after diagnosing 22q deletion?
Endo: Calcium, TSH, PTH
Immunology: T cells (do not give live vaccine until T cells are normalized), platelets
Cards: TTE, ECG
Other: Eye exam, audiology
Phenotype for 47, XXX
tall stature, slightly lower IQ (avg 10-15 points lower)
Azoospermia, undescented testes, hypergonatotrophic hypogonadism w/ low testosterone, gynecomastia, language delay
Klinefelter 47 XXY
what is the most common mechanism for 47 XYY?
non-dysjunction in paternal meiosis II
How much autosomal imbalance can a fetus tolerate in most cases?
2% monosomy (~60Mb) or 4% trisomy (!120Mb)

t(11:22)(q23;q11)
Most common recurrent non-robertsonian translocation
- Can lead to 3:1 segregation -> duplication of 22q10 and 11q23 -> emmanual syndrome (FTT, microcephaly, hypotonia, DD, renal issues)
3/4 finger syndactyly + clinodactyly, 2/3 toe syndactyly + bulbous toes
Body assymetry, ID, streaky skin hyper/hypopigmentation
Mosaic diploidy/triploidy
Large forehead, high hairline with sparse hair over temples
Large mouth and full philtrum
Pallister Killian
Mosaic tetrasomy 12p
Deep longitudinal creases on soles of feet
Absent/hypoplasic patella
Finger contractures
Mosaic trisomy 8
- also look for heme malignancies
Preauricular tags, ear malformations, CHD, renal atresia, radial ray defects
Mosaic trisomy 22
Name the 7 chromosomes that cause imprinting syndromes
6, 7, 11, 14, 15, 16, 20
Most common terminal deletion syndrome
1p36 del
- DD, seizures, hypotonia, deep set eyes, straight eyebrows, delayed fontanelle closure, clefts
Iris coloboma, sagging everted eyelids, short nose, very short phlitrum, seizures
Wolf Hirschorn
4p del
5p terminal deletion syndrome
Cri Du Chat
- cat like cry, DD
4p terminal deletion syndrome
Wolf-Hirschhorn
- Greek warrior helmet face, coloboma, seizures, FTT
16p terminal deletion syndrome
ATR
- HbH (1/4 alpha thal) + mental retardation
17p terminal deletion syndrome
Miller Dieker
- LIS1 + microcephaly, MR, dysmorphic
Xp terminal deletion
SHOX, KAL
- Short stature + syndromic
What is the major factor in increased mortality in infancy for patients with down syndrome?
Congential heart defects
What is the risk of having a liveborn child with down syndrome when a parent has (14:21) robertsonian translocation?
1% if paternal
10-15% if maternal
100% if either parent is t(21:21)
Short sternum, IUGR, prominent occiput, simple ears, overriding fingers, nail hypoplasia, rocker bottom feet, pale fundi
Edwards syndrome
Trisomy 18
+ polyvalvular dysplasia
What factors increase the chances of abnormal offspring for parents with paricentric inversion?
large inversions -> most likely to recombine, recombination results in smaller areas of del/dup -> more likely viable
scaphocephaly (dolichocephaly), digital contractures, hemiertebrae, renal anomalies, deep plantar creases
Mosiac trisomy 8
- Male > female
- Cell line disappears in lymphocytes -> check fibroblasts
What is the most common trisomy in abortuses?
Trisomy 16
What is the most common issue in management of patau syndrome?
GERD
- Aspriation -> cardiopulmonary arrest common COD
What is the ring chromosome phenotype?
Phenotype from all ring chromosomes due to mitotic instability (dyanamic mosaicism) in addition to specific imbalance issues
- FTT, microcephaly, ID, dysmoprhic features
What does Ringed X cause?
If large -> XIST present -> mosaic turner
If small -> XIST absent -> X disomy -> severe ID
- Need to do FISH to look for XIST
What are the common robertsonian translocation?
13;14 and 14:21
What are the main phenotypes assocaited with robertsonian translocation?
Trisomy 21
Trisomy 13
UPD 15 (PWS, AS)
UPD 14 -
Mat: Temple Syndrome - hypotona, FTT, DD, macrocephaly, small hands/feet
Pat: Kagami-Ogata Syndrome - coat hanger ribs, bell shaped thorax, hairy forehead
What does idic(15) cause?
isodicentric chromosome 15
- normal if PW/AS region (q11-13) is not involved
- most commonly DD and epilepsy
What does idic(22) cause?
Isodicentric 22
Cat eye syndrome
- Coloboma, ear tags/pits, anal anomalies, TOF/TAPVD, renal atresia, DD
If a supernumery marker chromosome is detect prenatally, what features make it more likely to cause abnormality in fetus?
- de novo
- large
- contains euchromatin (seen on array)
- ring
- may cause UPD in 15
How do you screen for breast ca in Li frameni
MRI at age 20
Avoid mammograms (radiation increases risk)
Which Lynch genes have less severe phenotypes
PMS2, MSH6
MLH1 and MSH2 = classic
What does MLH1 promoter methylation tell you?
More likely for tumor to be sporadic (vs Lynch)
Treatment for schwannomas in NF2
VEGF inhibitor
Bevecizumab
NF2 surveillance
Hearing and Eye - childhood
MRI in early teens and adulthood
What kind of ovarian cancer is seen in BRCA1/2?
Serous ovarian
- Non serous is seen in Lynch
What is olaparib
PARP (poly ADP ribose polymerase) inhibitors
- Targeted therapy for BRCA1/2 related breast, ovarian, pancreatic cancer
Surveillance for Peutz Jeghers syndrome
- Baseline EGD/colonoscopy at 8 (prevent intussiception) -> If no polyps screen every 3 years at 18
- Breast MRI at 25
What is significance of HOXB12 gene?
Causes isolated prostate cancer
What is the mechanism of triploidy?
Digynic: 2nd polar body incorporated into fertilized oocyte
Diandric: 2 sperm, 1 egg -> big placenta
- Big placenta = high B HCG (chart is wrong)

Where is beta HCG secreted from?
Placenta
What is the health risk associated with partial or complete hydatiform mole?
Malignant transformation into choriocarcinoma
what is 45,X/46,X,r(X) mean?
Mosaic ringed X
If XIST present -> Mosaic turner
If XIST absent -> severe MR due to X disomy
2 most common features of Turner Syndrome
Short stature and gonadal dysgenesis
What phenotype(s) are unbalanced X-Autosome translocations associated with?
- abnormal X selectively inactivated
- Males infertile
- Females sometimes infertile
- Increased risk for hypomelanosis of ito
omphalocele, polyhydramnios, macroglossia
Beckwidth Weidemann Syndrome

Telephone receiver femurs, short limbs
Thanatophoric dysplasia
FGFR3
Prenatal US: undermineralization of skull
Infantile hypophosphatasia or OI
Prenatal US: bowed limbs
- Maternal virizliation
Antley bixler
POR
Congenital diaphragmatic hernia, cutis aplasia
Trisomy 13
Congenital diaphragmatic hernia, overlapping digits
Trisomy 18
Congenital Diaphragmatic hernia, prominent philtrum, rhizomelia
Pallister Killian
Mosaic isochromosome 12p
Congenital diaphragmatic hernia, limb reduction defects, microbrachycephay, depressed nasal bridge with anteverted nares, long smooth philtrum, micrognathia
CDLS
NIPBL
Congenital Diaphragmatic hernia, short distal phalanges, cleft L/P, genital malformation
Fryns Syndrome
Congenital diaphgramatic hernia, heart defect, polydacylty, overgrowth
Simpon Gloabi Behmel
GPC3 (XL)
What does fetal fluconazole exposure cause?
Antley Bixler phenocopy
- Fluconazole inhibits CYP450 oxoreductase (POR)
short palpebral fissures, flat midface, long/flat philtrum, thin vermilion of upper lip
Fetal Alcohol Syndrome
- low birthweight, microcephaly, DD
which antiepileptic exposure in utero can lead to hypoplastic nails?
Carbamazepine
Which antiepileptic in lead to NTD when exposed in utero?
VPA
3 most likely outcomes after fetal US showing echogenic bowel
1) normal
2) Trisomy 21 (3rd if screening is negative)
3) Cystic fibrosis
Most common cause of low maternal estriol
Steroid Sulfatase Deficiency
STS gene - 90% deletions
X-linked ichthyosis
- DDX: SLOS (DHCR7), Antley Bixler (POR)
What are the teratogenic effects of phenylalanine?
Microcephaly, ID
CHD: TOF, aortic coarct
Dysmorphic (similar to fetal alcohol) - long/smooth philtrum w/ thin upper lip, micrognathia, maxillary hypoplasia, flattened nasal ridge, epicanthal folds
Goal: <360umol/L
What percent of miscarriages have a chromosomal abnormality?
50%
What is the first line treatment for homocystinuria?
Pyridoxine (B6) -> some are responsive

what are the most common causes of increased fetal nuchal translucency?
1) Cardiac malformation - get fetal echo
2) Chromosomal (Turner, Down syndrome)
3) Hemoglobinopathies
What are the main components of Potter synquence?
Oligohydramnios -> micrognathia, pulmonary hypoplasia, postural anomalies (talipes)
micrognathia, pulmonary hypoplasia, talipes, renal cysts
ARPKD
renal cysts + potter sequence
micrognathia, pulmonary hypoplasia, talipes, occipital encephalocele, enlarged kidneys, liver fibrosis
Meckel syndrome
MKS1, TMEM67, CEP290, RPGRIP1L -> ciliopathy
- Potter sequence + encephalocele + renal/liver disease
micrognathia, pulmonary hypoplasia, talipes, branchial fistula, ear anomalies
Brachial-oto-renal syndrome
EYA1 (AD)
Potter sequence = renal disease
micrognathia, pulmonary hypoplasia, talipes, cryptophthalmos, laryngeal stenosis, syndactyly
Fraser Syndrome
FRAS1, GRIP1, FREM1/2
potter sequence (renal) + cryptophthalmos + laryngeal stenosis
What GALT variant is most likely to lead to premature ovarian failure?
Classic: Q188R/Q188R
What does congneital rubella look like?
Exposure in utero from 2-10 wks
- IUGR
- Microcephaly
- RP
- SNHL
- PDA, pulmonary artery stenosis
What does congenital CMV look like?
IUGR
Microcephaly, abnormal CT (Calcifications)
Jaundice, HSM, elevated ALT
Petechiae, purpora, thrombocytpenia, anemia
Which syndromes can have bilateral radial ray defects?
Fanconi anemia and trisomy 18
Short femur on prenatal US + low maternal estriol
SLOS

How does congenial toxoplasmosis present?
microcephaly, CNS anomalies, chorioretinitis
Compare locations of cysts in ARPKD vs ADPKD
ARPKD: Multiple small cysts in collecting ducts
ADPKD: Fewer, large cysts, in nephron or collecting duct
How does polycystic kidney disease present on prenatal US?
Large, Hyperechogenic kidneys +/- oligohydramnios
How does fetal varicella present?
Skin, CNS, and limb changes
Agenesis of corpus callosum, hydrocephalus, ID, adducted thumbs, spastic paraplegia
X-linked hydrocephalus
L1CAM
Which phase of prophase 1 is meiosis arrested in for females?
Diplotene
Pachytene is where recombination happens
acute megakaryoblastic leukemia
Cancer seen in down syndrome
What does NOTCH 1, 2, and 3 cause?
NOTCH1 - Adams oliver - cutis aplasia + transerve limb defects
NOTCH2 - Alagille
NOTCH3 - CADASIL
Coat hanger ribs, bell shaped thorax, hairy forehead
Kagami Ogata
Paternal UPD 14
Hypotonia, short stature, macrocephaly, small hands/feet
Temple syndrome
Maternal UPD 14 - paternally expressed genes
What malfromation is young maternal age associated with?
Gastroschisis
What GSDs can present as fetal akinesia?
GSD4 - polyglucosan buildup
GSD7 - muscle
How much folic acid should a pregnant woman take?
0.5mg all comers
5mg if history of NTD or on anticonvulsants
what % of hypoplastic left heart is syndromic?
5%
- 20% will have other findings on ultrasound, but not necessarily syndromic
What heart defect is maternal diabetes associated with?
Hypoplastic left heart
When you can accurately determine fetal sex on U/S
13-14 weeks
- hard to see 12 weeks or before
What is the easliest you can do NIPT?
8 weeks
What chromosomal testing should you do if you find isolated prenatal gastroschisis, unilateral multicystic dysplasic kidneys, or talipes?
None; not associated with chromosomal abnormalities.
When is the right time to do CVS/Amnio?
CVS - 11-13 weeks
Amnio - 15-17 weeks
Failure to progress in labour, prolonged labor, prolonged gestation
- low maternal estriol
Steroid Sulfatase deficiency
STS gene - 90% deletions
XL
which aneuploidies are NOT associated with advanced maternal age?
Triploidy, 45,X ,47XYY
What malformation has highest increased RR in maternal diabetes? What is most common?
Caudal Regression > Laterality disturbance > NTD
Most common: NTD > CHD > CL/P
What is fragment size of fetal DNA at NIPT?
160-340bp
What organ defect should you associate with oligohydramnios? polyhydramnios?
Oligo -> renal (cannot produce urine)
Poly -> GI ( cannot swallow)
Polyhydramnios, macrosomia, maternal glucose intolerance
BWS
what % of women with fragile X prematutation have POF?
20%
post-auricular lymphadenopathy
Congenital Rubella


