Biochem Flashcards
Common GBA mutations
AJew: N409S (formerly N370S)
Europe: L483P (formerly L444P)
- Original nomenclature not include first 39AAs
increased aminoadipic acid semialdehyde (AASA), increased pipecolic acid
Pyridoxine Dependent Epilepsy (aminoadipic acid semialdehyde dehydrogenase)
ALDH7A1 (antiquitin)
- High P6C complexes with pyridoxal 5 phosphate (B6)
Tx: B6, folinic acid, lysine restriction, arginine supplement
DDx; PNPO deficiency

Neuroimaging for GA1
Subarachnoid collections, Sylvian fissure enlargement, BG strokes
GA1 treatment
Limit substrate: Lysine free, reduced tryptophan; carnitine (glutaryl carnitine can be excreted), ?add arginine (compete with transporter)
ACP: C5DC
Low carnitine
UOA: 3-OH glutaric acid, glutaric acid
GA1
Clinical: Macrocephaly, encephalopathy, strokes (up to age 6, natural flux of transporter decreased as brain matures)
Gene: Glutaryl-CoA dehydrogenase (GCDH)
UOA: glutaric acid, 3-OH Glutaric acid (co-elutes with 2OH-GA) Decreased carnitine
ACP: glutarylcarnitine = C5DC LOW EXCRETERS EXIST
DDx for elevated glutaric acid in urine
gut bacteria overgrowth
ketosis
SCHAD (breaks down 3OH-glutaryl-CoA),
mitochondrial,
2OH-GA in GA2,
benign GA3 (NO C5DC),
renal disease,
maternal GA1
DDx for high glycine
NKH
VPA treatment
Ketotic (PA, MMA, IVA, B-ketothiolase deficiency)
PNPO deficiency
HIE (BBB breakdown)
prolonged fasting
Lipoic acid dependent pathways
BCKDH, PDH, 2-KGDH, 2-OADH, GCS (glycine cleavage system)
AA (CSF and Plasma) : Glycine elevated, Glycine CSF/Plasma ratio > .08
NKH
Genes: glycine decarboxylase/dehydrogenase (GLDC), aminomethyltransferase (AMT), Modified lipoic acid/dihydrolipoyl dehydrogenase (GCSH)
Elevated lactate in variant forms (lipoic acid/iron-sulfur cluster disorders)
NKH treatment
Na-Benzoate - conjugate with glycine to form hippurate which can be excreted;
dextromethrophan/ketamine for NMDA antagonism; folinic acid
Cherry Red Spots
NP-A (HSM)
GM1 gangliosidossis (HSM)
GM2 gangliosidosis (no HSM)
Sialidosis
Krabbe
Farber
Metachromatic leukodystrophy
Gaucher therapies
ERT: Imiglucerase, velaglucerase, taliglucerase
SRT: miglustat, eliglustat
Fabry therapies
ERT: agalsidase-beta, agalsidase-alpha
Chaperone: migalastat
Angiokeratomas
Fabry (a-Gal) - + renal/cardiac/stroke
Fucosidosis (a-fucosidase) - FUCA - + MPS features
B-Manosidosis (ID) - MANBA - + ID/neuropathy
Schilder (NAGA - aka a-GAL-B) - +neurodegeneration
Extensive mongolian spots
MPSI, MPSII, GM1
Heparan sulfate
Heparan = Head
MPS I, II, III, VII (Brain involvement)
Dermatan sulfate
Dermatan = bone + systemic
MPS I, II, VI, VII (Bone)
Keratan sulfate
MPS VI (Bone)
A-L-Iduronidase deficiency Treatment
MPS1 Hurler
HSCT before age 2
ERT: Iaronidase
Distinguishing features of MPSII vs MPSI
X linked
No corneal clouding
Dermal pebbling
Iduronidase 2- sulfatase
Iduronidase Sulfatase def. treatment
MPS II - Hunter
ERT: Idursulfase
MPSIII diagnosis
Urine: Heparan sulfate
Gene/enzyme:
Heparan N-Sulfatase (SGSH)
Alpha-N-acetyl-glucosaminidase (NAGLU)
aceyl-coa-glucosaminide acetyltransferase (HGSNAT)
N-acetylglucosamine-6-sulfatase (GNS)
MPS IV diagnosis
Morquio
Urine: Keratan sulfate
Normal intellect
Enzyme:
N-acetylgalactosamine-6-sulfatase (GALNS)
Beta-galactosidase (GLB1, Same enzyme as GM1 gangliosidosis)
Morquio treatment
ERT: Elosulfase Alpha for type IV A
arylsulfatase B
MPS VI - Maroteaux Lamy
Enzyme: ARSB
Clinical: Normal intellect, macrocephaly, bone involvement
ERT: Galsufase
Beta glucuronidase
MPS VII (GUSB) - Sly
Hurler like
a-mannosidosis
Gene: MAN2B1 (manosidase alpha)
Clinical: MPS like
Dx: urine oligosaccharides, GAGs NORMAL
Tx: HSCT

Neuraminic acid in urine, cherry red spot
Sialidosis
Enzyme/Gene: Acid sialidase (a-neuroaminidase NEU1) - sialic acid is BOUND to other sugars since this cleaves SA
Type 1: Cherry red spot, myoclonus, decreased vision
Type 2: progressive psychomotorsymptoms, kyphosis, dysmorphic, ataxia, deafness neonatal: congenital hydrops
Dx: urine neuraminic acid, oligosaccharides

Angiokeratoma, ID, neuropathy
B mannosidosis
MANBA gened (beta mannosidase)
Dx: urine oligosaccharides

Neurodegeneration, HSM, dysostosis, angiokeratomas
Fucosidosis
FUCA1 gene (Fucosidase)
Dx: Urine oligosaccharides

Schindler disease
a-N-acetylgalactosaminidase/a-galactosidase B (NAGA)
Clin: neurodegenration, myoclonic epilepsy
Dx: Urine oligosaccharides
HSM, neurodegeneration, connective tissue changes
Aspartylglucosaminuria Aspartylglucosaminase (AGA)
Oligosaccharidosis
Dx: Urine oligos, enzyme testing

UPDGlcNAc 1-P-transferase deficiency
Mucolipidosis II and III diagnosis (I cell disease/Pseudo Hurler)
- Unable to phosphorylate mannose -> cannot get enzymes into lysosomes
- MPS like + gingival hyperplasia
Dx: Elevated urine GAGs
Normal WBC (lysosomal) enzyme activity with elevated plasma enzyme activity due to improper targeting (mannose 6 P)

Salla disease
Sialic Acid Storage
Gene: SLC7A5 (#7) in picture
Biochem: Sialin deficiency -> deficient sialic acid (N-actylneuraminic) transport out of lysosome
Clin: Hypotonia, neurodevelopmental, ataxia, spasticity, epilepsy
Dx: Free sialic acid in urine (also seen in GNE)

Sialiduria
Gene: GNE (UDP Acetylglucosamine 2 epimerase)
Myopathy OR ID, HSM, seizures
Dx: Urine sialic acid
Cystinosis
Gene: CTNS (Cystinosin)
Biochem: Lysosomal cystin transportin
Clin: FTT, HSM, myopathy, corneal crystals, thyroid, pancreas, testes, renal fanconi, renal failure
Dx: cystine in leukocytes
Tx: Cysteamine and cysteamine eye drops
Fabry urine biomarket
GL3
Acid B-galactosidase deficiency
GM1
Morquio type B
galactosialidosis
GM1 clinical subtypes
Infantile: Hydrops, neurodevelopmental arrest, HSM, dysostosis multiplex, cherry red spot, vision loss, death by 2
Juvenile: ataxia, HSP
Adult: ataxia, dystonia
Foamy histiocytes, Vacuolated lymphocytes
Low B-galactosidase activity
+ cherry red spot, spasticity, HSM
NORMAL neuraminidase assay
GM1 gangiosidosis
GLB1
- Hypotonia, DD, coarse facies, dysostosis multiplex, cherry red spot, HSM, spasticity
- Need to do neuraminidase assay when B-Galactosidase is abnormal to rule out galactosialidosis
Biochem types of GM2
Tay Sachs - Hex A
Sandhoff - Hex B (elevated urine oligos, varuolated lymph)
GM2 activator protein (both Hex A and B levels normal)
What are the 3 clinical subtypes of GM2 gangliosidosis?
Infantile: Macrocephaly, cherry red macula, neuro issues, vision loss
Juvenile: ataxia, cognitive, vision loss, seizures, weakness
Adult: ataxia, neuromuscular, neuropsych
Sphingomyelinase deficiency (SMPD)
Niemann Pick A and B
A: HSM, cherry red manula, neurological, interstitial lung disease
B: MIlder, + hyperlipidemia, normal intellect
Dx: Foam cells in bone marrow
Sea blue histiocytes, abnormal cholestane-3β-5α-6β-triol, 7-ketocholesterol (oxysterols), filipin positive
NPC
NPC1 and NPC2 (intracellular cholesterol transporter)-> cholesterol storage
- Neontal: Hydrops, cholestasis, liver failure, HSM, thrombocytopenia,
- Juvenile: neurodegeneration w/ movement do, vertical supranuclear gaze palsy, cherry rest spot (50%), epilepsy, cataplexy, dystonia
NPC clinical symptoms
Supranuclear gaze palsy, HSM, cherry red spots, neuro
NPC treatment
SRT: Miglustat
HSCT
B-galactocerebrosidase disease
Krabbe
GLAC
Clinical: WM disease, extreme irritability
Adult form: vision loss, neuropsych
Dx: CSF protein up
Tx: HSCT before 1 month?
Metachromatic leukodystrophy
ARSA (Arylsulfatase A)
Clinical: CNS, peripheral neuropathy
Dx: urine sulphatides, CSF protein
Beware Pseudo Deficiency
Pompe associations
Cardiomyopathy
Short PR
Myopathy
Pompe treatment
ERT: Aglucosidase alpha
Immune modulation if CRIM negative
Pompe diagnosis
GAA (a-glucosidase)
Urine HEX4
oligosaccharides
Vacuolated lymphocytes
NCL symptoms
Seizure
vision loss
neurodegenerative
extrapyramidal
Buffy Coat EM for ceroid storage, vacuolated lymphocytes
NCL fibroblast findings
LSD with Adrenal calcifications
Wolman Disease
Gene: LIPA (lysosomal acid lipase)
Biochem: storage of cholesterol esters and TG
Clin: Adrenal calcifications, diarrhea, steatorrhea, HSM, anemia
Dx: Elevated cholesterol
Tx: Statins, ERT - sebelipase alpha
SRTs for Gaucher, Fabry, NPC
Gaucher - eliglustat, miglustat
Fabry - migalastat
NPC - miglustat
Features of peroxisomal disorders
Dysmorphic: large fontanelle, high forehead, shallow supraorbital ridge, epicanthal folds, micrognathia
Ears: ear anomalies, hearing loss
Eyes: Retinal dystrophy, cataracts
Liver: Cholestasis/Cirrhosis
Dx of Zellweger Spectrum
VLCFA up
Plasmalogen nl or low
Phytanic acid/pristanic acid/bile acids nl or high (phytanic from diet so normal in newborns)
Pipecolic acid high
MRi findings in ZSD
Zellweger: pachypolymicorgyria neonatal
ALD: WMS
Isolated Plasmalogen low
RCDP
PEX7 (phytanic acid high, pristanic acid low)
Alkylglycerone-phosphate synthase (AGPS)
Glyceronephosphate O-acyltransferase (GNPAT)
RCDP + Hypoplasia of distal phalanges
XL RCDP - males
Gene: ARSE
Hypoplasia of distal phalanges
XL RCDP - females
Conradi Hunermann
Gene: EBP - Sterol delta-8 isomerase (male lethal)
Dx: 8-dehydrocholestrol, 8(9)-cholesterol
- Assymetric
DDx for chondrodysplasia punctata
RCDP
XL RCDP (male and female forms)
Warfarin embryopathy
Maternal SLE
Most common peroxisomal disorder
XALD
Forms of XALD
ALD, ANM, Addison’s
- all boys with adrenal insufficiency should be checked because this can precede neurological sx
XALD Diagnosis
ABCD1 gene
ATP binding cassette transporter for saturated VLCFAs into peroxisome
Disorder of Beta-Oxidation
Biochem: elevated VLCFA (C26:0)

XALD treatment
Early HCST - will take 6-9 months for new glial to be functional -> need to transplant at neurological changes
HSC gene therapy
Lorenzo’s oil (glyceryl trioleate and trierucate 4:1)
Hormone replacement - steroids
XALD in females
20% develope late onset neurological changes, adrenal problems rare
XALD brain MRI
occipital/parietal leukodystrophy
Which peroxisomal disorder has normal VLCFA
RCDP
High phytanic acid, low pristanic acid
Adult Refsum Disease
PHYH (Phytanyl CoA hydroxylase)
Clin: RP, neuropathy, ataxia, deafness, ithchyosis, skeletal, cardiac , NORMAL intellect
Dx: high phytanic acid, low pristanic acid, high CSF protein
Tx: Phytanic acid restriction, PLEX
- can be misdiagnosed as Usher

Dx: Elevated bile acids, high pristanic acid
a-methyl-acyl-CoA racemase deficiency
AMACR (isomerase that converst pristanic acid and bile acids to form needed for B-oxidation)
Adult neuropathy, encephalopathy, neonatal hepatopathy
Tx: bile acid substitution
Joint contracture, Skin nodules, Hoarse voice, neurodegeneration
- Allelic with SMA-PME
Farber disease - acid-ceramidase deficiency
ASAH
Clin: joint, skin nodules, hoarseness, neuro
Tx: HSCT

Saposin Disorders
PSAP gene (Protein cleaved into 4 small molecules required for sphingolipid hydrolysis)
A: variant Krabbe (galactosylceramidase)
B: Variant MLD (arylsulfatase A)
C: Variant Gaucher (B-glucosidase)
Combined: severe neuro/HSM
Wolf Parkinson White + pompe like LSD
Danon Disease LAMP2 (X linked) - membrane protein
Pompe-like (liver, heart, muscle) + WPW sndrome
Gaucher Buzzwords
HSM
horizontal saccades (horizonal supranuclear gaze palsy)
tissue paper macrophages
erlenmeyer flask
Hepatic/hypoglycemia GSDs
0, 1

Muscle GSDs
V, VII

Mixed GSDs
III, IV, VI, IX

GSD1 Dx
Gene: G6PC (G6Phosphatase), SLC37A4 (G6P Transporter)
- Last step of gluconeogenesis
Labs: high lactate, TG, uric acid, low glucose
glucose challenge -> fall in lactate

GSD1 features
Doll-like facies, big belly, thin extremities
Type 1B also has neutropenia/infections
Monitor: hepatic adenoma, IBD, renal function, osteopenia, anemia
GSD3 features
Cori/Forbes
Muscle and liver involvement
Milder than type 1 (debranching enzyme, so can process some glycogen)
+ Cardiomyopathy
Hepatic GSD
PAA: low ala, leu, ile, val
GSD3 - Cori
AGL (debranching enzyme)
Gluconeogenesis is funcitonal -> can use proteins for energy
Elevated LFTs, TG, lactate
Tx: same as GSD1, but add alanine (alanine -> pyruvate), fructose, and galactose
Polyglucosan accumulation, FTT, cirrhosis, fetal akinesia
Adult neurodegeneration
Andersen, GSD IV
GBE1 (branching enzyme)
- Polyglucosan = unbranched glycogen -> can accumulate in CNS too
TFF, Hepatomegaly, cirrhosis, neuromuscular, HCM
Dx: enzyme assay
Tx: Transplant
Hepatic GSDs that resolved in puberty
GSD6: Hers Disease, PYGL (Liver phosphorylase)
GSD9: Phosphorylase Kinase subunits: PHKA (X LINKED); PHKB, PHKG2 (AR)
Clinical: Hepatic GSD, mild, hepatomegaly decreases with age
Dx: Low glu, high lactate, LFTs; glucose challenge -> Rise in lactate
Tx: maintain normoglycemia
GSD0
Glycogen synthase Clin: FTT, hypoglycemia, NORMAL liver size (cannot make glycogen)
Muscle GSDs
Type 5, Mcardles: PYGM (Phosphorylase)
Type 7, Tauri: PFKM (PFK)
X linked: PHKA1 (phosphylase kinase)
Fanconi-Bickel Disease
GSD XI
GLUT2 (SLC2A2 - glucose transporter)
Clin: FTT, renal fanconi, rickets, aminoaciduria, phosphaturia, glucosuria, malabsorption, large liver AND kidneys
Most common CDG
PMM2 (CDG1a)
PMM2-CDG features
cherubic face
inverted nipple
fat pads
oringe peel skin
neuropsych
RP
dysostosis multiple
Where are N linked glycans attached
Nitrogen of Asn in part of Asn-X-Ser consensus sequence
N linked glycosylation functions
Protein stability
complex formation
leukocyte targeting/inflammation
cell-cell recognition
O linked glycosylation functions
ABO groups
antibacterial
sperm binding
cell adhesion/migration
Causes of abnormal isoelectric focusing
CDG
Transferrin polymorphisms
HFI/Galactosemia
EtOH use
Liver Disease
O linked CDG features
Muscle-eye-brain disease
GPI anchor disorders cause…
Seizures, ID
CDG1b (MPI) symptoms
protein losing enteropathy
Which CDG do you treat with mannose
CDG1b, phosphomannose isomerase (MPI)
Which CDG uses fructose, xylose, and mannose
O-linked
Hex4 can be seen in
Pompe
CDG-MOGS (hypotonia, dysmorphic)
Dolichol CDG features
bone, skin, growth issues (cholesterol pathway)
CDG treated with heart transplant
DOLK1 CDG
Wilson-like CDG without KF-rings
MPI, TMEM199, ATP6AP1 Treat with transplant
Electron movement in ETC complexes
I - NADH -> CoQ
II - FADH2 -> CoQ
III - CoQ -> Cytochrome C
IV - Cytochrome C -> O2 (pump H+)
V - Proton flow back for ATPase

A3243G, tRNA-leuUUR
MELAS mutation
high ornithine, normal ammonia, vision loss
OAT (ornithine aminotransferase deficiency)
biochem: High ornithine, low creatinine (Orn is product of AGAT, first step of creatine synthesis)
Gyrate atrophy of retina (peripheral vision loss) + cataracts
Tx: Pyridoxine, arginine restriction (after neonatal period)

PAA: high proline
UOA: high proline, OH proline, normal P5C
Hyperprolinemia type 1
PRODH (proline oxidase)
Asymptomatic, risk for schizophrenia
Heterozygotes also have high proline

PAA: high proline
UOA: high proline, OH proline, P5C
Hypreprolinemia type 2
ALDH4A1 (P5C dehydrogenase)
Epilepsy, ID, pyridoxine deficiency (P5C binds pyridoxine)
Tx: may respond to pyridoxine

High OH proline + XLE
hydroxyprolinuria
OHproline oxidase deficiency (takes place in extracellular matrix)
non-disease, but false positive for MSUD because it looks the same as Leu, Ile, and AlloIle on Mass Spec
ID, Ulcers, infections
Prolidase Deficiency
PEPD (peptidase- degrade dipeptides with N terminal Prolines)
Dx: UAA - iminodipeptides elevated
PAA: low proline, ornithine, arginine, citrulline
Hypoprolinemia
P5CS (P5C synthase deficiency)
Cataract, ID, joint laxity, hyperammonemia

P5C reductase deficiency
PYCR1 and 2
1: cutix laxa, osteopenia
2: leukodystrophy
PAA and CSF: Low Serine
PGDH, PSAT, PSPH (dehydrogenase, aminotransferase, and phosphotase)
Biochem: Serine synthesized from 3-P-glycerate (glycolysis)
May have low glycine and CSF MTHF

Clinical features of serine deficiency
Clinical:
Neu-Laxova syndrome (IUGR, severe dysmorphic features and malformations including CNS)
Infantile form: CNS/cataracts, ichthyosis
Tx: Serine supplementation
Low ASN
Asparagine synthase deficiency (ASNS)
Biochem: converts ASP -> ASN
Clinical: severe CNS, hyperekplexia

Isolated CSF Serine deficiency
SLC1A4 – ASCT1 neutral amino acid transporter
CNS Serine transporter
Hypomyelination, atrophy, spasticity
Low glutamine, normal glutamate
Glutamine synthetase deficiency (GLUL)
Hyperammonemia Severe CNS, limb defects
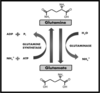
High glutamine, normal glutamate
Glutaminase deficiency (GLS)
Can be caused by 5’UTR expansion
DD, spasticity, seizures, cerebellar atrophy

Low glutamine, high glutamate (UAA, MRS)
Glutaminase hyperactivity (GLS)
NORMAL Glu/Gln in plasma and CSF
DD, regression, cataracts, subcutaneous nodules

Low GAA (Guanidinoacetic acid), Creatine, Creatinine; decreased Creatine/Cr
AGAT (Arginine-Glycine amidinotransferase)
GATM gene
Biochem: Arg + Glycine -> Ornithine + GAA
Clinical: ID
Tx: Creatine supplement

High GAA, low Creatine, decreased Creatine/Cr
GAMT (Guanidinoacetate methyltransferase)
Biochem: GAA + SAM -> Creatine
Clinical: ID, epilepsy, movement do
Tx. Creatine, arginine, ornithine supplement, Na Benzoate

High Creatine/Cr ratio; low Creatine in MRS
Creatine transporter
SLC6A8
X linked
ID (up to 2% of all boys with ID), epilepsy

Urine: 3-methylcrotonylglycine, 3-OH-IVA
ACP: C5OH
3MCC
Gene: MCCA, MCCB
Likely aysmptomatic, may decompensate + secondary carnitine deficiency

Homogentisic acid in urine
Alkaptonuria
HGD gene
Arthritis, ochronosis, dark coloration of urine with exposure, thyroid dysfunction, aortic stenosis, prostate stone
CAVA
Carbonic anhydrase
Biochem: water + CO2 -> bicarb (needed for CPS1, TCA cycle)
Clinical: hyperammonemia + hypoglycemia
Lab: high ammonia, lactate, ketone, glutamine, maybe carboxylate metabolites
Tx: Like UCD (carbaglu)

Urine: Elevated Cystine + Arg, Lys, Orn + nitroprusside test
Cystinuria
SLC3A1 (AR), SLC7A9 (AD)
Nephrolithiasis, may be part of deletion syndrome on 2p
Tx: hydration, urine alkinization with K-Citrate, diet, Thiols/captopril to reduce cystine in to cysteine
Treatment of Pterin defects
L-Dopa
5Oh Tryptophan (serotonin precursor)
Kuvan (tetrahydroBiopterin)
Pterin pathway
GTP -(GTPCH)-> (PTPS) -> (SR) -> BH4 -(PCD) -> BH2 -(DHPR)-> BH4

Normal Phe, Low Neopterin, Low Biopterin
GTPCH (GTP Cyclohydrolase)
GCH1 gene
Dopa Responsive Dystonia
- Homozygotes can have high phe

Normal Phe, Normal Neopterin, High Sepiapterin
SR (Sepiapterin Reductase)
SPR gene
Dopa Responsive Dystonia
- CSF neopterin can be high or normal

High Phe, High Neopterin, Low Biopterin
PTPS (6-pyruvyl tetrahydropterin syntase)
PTS gene
DD, hypotonia, epilepsy, dystonia

High Phe, High Neopterin, Low/Normal Biopterin, Primapterin (Urine)
PCD (Pterin Carbanoamine Dehydratase)
PCBD1 gene
Motor symptoms Allelic with hypomag and MODY

High Phe, normal neopterin, high biopterin
DHPR (Quinoid dihydropteridine reductase)
QDPR gene
severe CNS
Tx: Dopa, 5OH-Try, Folinic acid (secondary cerebral deficiency)
Do NOT give Kuvan (tetrahydrobiopterin)

Clinical subtypes of porphyria
Hepatic/neurovisceral
Cutaneous Blistering (normal urine PBG)
Cutaneous non-blistering (High protoporphyrin)
Hepatic Porphyria: High urine aminolevulinic acid, normal porphobilinogen
ALAD (PGB synthase)
AR - Aminolevulinic acid dehydratase prophyria
Hepatic
DDX for high ALA: tyrosinemia, lead poisoning

Hepatic Porphyria: High porphobilinogen,; no fecal findings
Acute intermittent prophyria (HMBS)
AD
Hepatic

Treatment of hepatic/neurovisceral porphyrias
1) Hemin (feedback inhibition)
2) carb load (inhibit ALAS - first step)
3) Givosiran (siRNA for ALAS)
Hepatic Porphyria: High PGB, High fecal coproporphyrin
Heriditary coprophorphyria (CPOX)
AD
Biochem -> coprophorphyrin oxidase
Hepatic and blistering

Hepatic porphyria: High PGB, high fecal copro and proto porphyrin
Porphyria Variegata (PPOX)
AD
Biochem: protoporphyrin oxidase
Hepatic and blistering

Cutaneous Blistering: high PGB, fecal coproporphyrin
Coproporphyrinogen oxidase
CPOX
Hepatic and blistering porphyria

Cutaneous Blistering: high PGB, fecal copro and protoporphyrin
propoporphyrinogen oxiddase
PPOX
Hepatic and blistering porphyria

Porphyria Cutanea Tarda Tx
Hydroxychloroquine and phlebotomy
Biomarker for porphyrias
Hepatic: ALA high during episodes, high urine PBG (except for ALAD)
Blistering: normal uring PBG
Non blistering: RBC protoporphyrin
Cutaneous Blistering: normal PGB, coproporphyrin > uro/carboxylated porphyrins
Congenital erythorpoietic porphyria (UROS)
URO synthetase
Severe skin + corneal ulceration + teeth discoloration + red urine + hemolytic anemia

Cutaneous Blistering: normal PGB, uro/carboxylated porphyrins > coproporphyrin
Porphyria Cutanea Tarda (AD)
(UROD) - dehydrogenase
Adult onset, most common porphyria (can be secondary)
Hepatoerythropoetic porphyria (AR) - Homozygotes have severe infantile presentation of skin, teeth + hemolytic anemia just like UROS (previous enzyme in pathway)

Non-blistering porphyria: high protoporphyrin (RBC, fecal), RBC zinc < 15%
erythropoetic protoporphyria FECH (ferrochelolase)

Non-blistering porphyria: high protoporphyrin (RBC, fecal), RBC zine 15-50%
X-linked protoporphyria ALAS (ALA synthase) hyperactivity
- Deficiency - X linked siderloblastic anemia

Haem Metabolism pathway
Glycine + succinyl CoA -(ALAS)-> :Non-blistering
ALA -(ALAD)-> :Hepatic
Porphobilinogen -(HMBS)-> :Hepatic
Hydroxymethylbilane -(UROS)-> :Blistering + hemolytic
Urophyrinogen -(UROD)-> :Blistering
Coproporphyrinogen -(CPOX)-> :Hepatic/Blistering
Protoporphyrinogen -(PPOX)-> :Hepatic/Blistering
Protoporphyrin -(FECH) -> :Non-blistering Haem

What are the protoporphyrias
non-blistering cutaneous porphyrias (Sun -> Pain)
ALAS hyperactivity (first step of pathway)
FECH (Ferrochetolase - Last step of haem synthesis)
Name the 2 ALA - synthase diseases
X linked protoporhyria (Hyperactivity)
X linked sideroblasatic anemia (deficiency)
Which porphyrias are both hepatic and blistering
Hereditary Coproporphyria (CPOX) and Variegate porphyria (PPOX)
- Both caused by oxidase deficiencies
- Final 2 steps of pathway before ferrochetolase

What are the main products of Trytophan degradation?
Niacin (B3), Melatonin, Serotonin
UAA: High Ala, Ser, Thr, His
PAA: Low Ala, Ser, Thr, His
Hartnup SLC6A19 (B0AT1 protein)
Neutral AA transporter
Dermatitis, Diarrhea, Dementia (Pellagra like) + Cerebellar Most asymptomatic (dietary niacin?)
How to tell apart Hartnup from Fanconi or generalized aminoaciduria on UAA?
Gly, proline, Met are normal in Hartnup
high in Fanconi/aminoaciduria
Trp transporter defect
Blue diaper syndrome
Bacterial convert trp to indole –> blue eye
UOA: Xanthurenic acid
Kynureninase and HAAO deficiency
Biochem: Trp -X-> niacin VACTERL-like,
hyperphalangism (extra bone in prox. middle phalanges)

Hypertryptophanemia
Tryptophan Dioxygenase Deficiency (TDO)
non-disease
Tx: nicotinic acid (niacin) supplement

Nicotinamide nucleotide adenylyltransferase 1 (NMNAT1) deficiency
Leber congenital amaurosis
Congenital coloboma, optic atrophy NAD biosynthesis defect
ACP: Elevated C10:2
Dienoyl-Coa reductase (DECR)
NADK2
Defect in NAD phosphorylation to NADH
CNS: Movement do, seizure, hypotonia, optic atrophy
PAA: high lysine
Hydrated NAD (NADHX) repair defects
NAXD (dehydrogenase) and NAXE (epimerase)
Febrile triggered - neurodegeneration, blistering skin lesions, cardiac
2 causes of elevated Histidine
Histidinemia - HAL gene, imidazolepyruvic acid in urine
Urocanic aciduria (UROC1 gene)
Both non-disease

What 3 AA make up glutathione
Glutamate, Cysteine, Glycine
AKA: gamma-glytamylcysteinylglycine
Low glutathione, hyperaminoaciduria, normal 5-oxoproline
Gamma-glutamylcysteine synthetase deficiency
Part of glutathione synthesis
Hemolytic anemia + ?neurodegeneration
Tx: Avoid triggers (like G6PD), Vit C + E

High urine and plasma glutathione
gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase deficiency (First step of glutathione degradation)
GGT1 gene
ID, psychosis

High cystinylglycine
Dipeptidase deficiency
Biochem: Glutathione breakdown pathway
Glutathione levels normal
CNS, neuropathy, deafness

Low glutathione, high 5-oxoproline
Glutathione synthetase deficiency
GSS gene Hemolytic anemia + neurodegeneration
Tx: Vit E, N-acetylcystine, avoid G6PD triggers

DDx for high 5-oxoproline
Glutathione synthetase deficiency (Hemolysis + CNS)
5-oxoprolinase deficiency (OPAH gene, non disease?)
Acute metabolic decompensation (mito, PA, urea cycle)
SJS
medications
prematurity
Nutritional
Rotting fish odor
Trimethylaminuria (FMO3 or DMGDH)
Biochem: Choline degradation pathway
Dx: Choline loading protocol (measure TMA and TMA-oxide in urine before and after)
Tx; Dietary restriction (milk, choline, lecithin, seafood)

DDx Elevated sarcosine (PAA)
Sarcosinemia (SARDH) -> causes false elevation in Creatinine measurements -> false positive for renal failure (BUN normal)
GA2
Folate deficiency

Choline breakdown products
1) Choline -> Betaine -> Dimethylglycine -> Sarcosine -> Glycine
2) Choline -> Trimethylamine -> TMA-oxiide

Treatment for GSD 1
Glycosade (modifined cornstarch) or uncooked cornstarch Liver/kidney transplant
GSD V vs GSD VII distinguishing characteristic
GSD V -> second wind
GSD VII -> Out of wind (F6P inhibition of FAO), golyglucosan storage (high G6P activates glycogen synthase, mild erythrocytosis and hemolysis (gluconeogenesis defect affecting RBCs)
5 Coenzymes for PDH complex
1 - Thiamine (TPP)
2 - Flavin (FAD)
3 - Lipoic acid
4 - CoA
5 - Nicotinamide (niacin)
3 steps of pyrimidine catabolism
Uracil/Thymine —> B-alanine/B-aminoisobutyric acid
1) dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase
2) dihydropyrimidase
3) B-ureidopropionase

Hight urine thiamine and uracil
Dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase deficiency
Gene: DPYD
- asymptomatic vs seizures and ID
- 5FU toxicity

UOA: high dihydrouracil/dihydrothymine, uracil, thymine
dihydropyrimidinase deficiency
Gene: DPYS
- asymptomatic vs seizures and DD -
5FU toxicity

high ureidopropionate, B-alanine, and ureidoisobutyrate (normal-high dihydrouracil, dihydrothymine, uracil, thymine)
B-ureidopropinase deficiency (B-alanine synthase deficiency)
gene: UPB1
- Asymptomatic vs dystonia
- 5FU toxicity

CSF AA: high GABA, B-alanine, homocarnosine
GABA transaminase Deficiency gene ABAT
Biochem: GABA -> succinate semialdehyde
Clin: epileptic encephalopathy, macrosomia; increased growth
Avoid vigabatrin

UOA: 4-hydroxybutyric acid (Gamma hydroxy-butyrate)
Succinic Semialdehyde Dehydrogenase
SSADH gene: ALDH5A1
Clin: Slowly progressive neuropsych, movement do, seizures
MRI: BG/WM disease
- Avoid VPA

High carnosine
Carnosinase deficiency - incidental finding - ?homocarnosinosis
Creatine synthesis pathway
Arg + Glycine - (AGAT) -> ornithine + Guanadinoacetate - (GAMT) -> creatine -(SLC6A8 transporter)-> creatinine

CSF: High 3OMD, low 5-HIAA, low HVA, low MHPG, low VMA
AADC
DDC gene
biochem -> converts 5-OHT and DOPA into serotonin and Dopamine
- urine profile may be opposite of CSF

Treatment for AADC
Pyridoxine (B6),
MAOi, agonists
- Do NOT give DOPA or 5-OHT

CSF: Low HVA, low MHPD, low VMA, low 3OMD; normal 5-HIAA
Tyrosine hydroxylase (TH)
Biochem: tyrosine -> DOPA
- Movement DO, encephalopathy
- Dopa responsive

CSF: Low MHPG, low VMA
Dopamine B- hydroxylase (DBH)
Biochem: Dopamine -> Norepi
- Dysautonomia
Tx - droxidopa

CSF: Low MHPG, VMA, 5HIAA, and HVA; normal 3OMD
MAO deficiency
MAOA (X linked), MAOB
Clin: Serotonin + carcinoid features; atonic episodes,
Dx - Elevated urine/CSF neurotransmitters (serotonin, tyramine, normetanephrine, etc)
Tx: Diet

What neurotransmitter produces the following metabolites? 1) HVA 2) 5HIAA 3) MHPG 4) VMA 5) 3OMD
1) Dopamine
2) Serotonin
3) Norepi
4) Epinephrine
5) L DOPA
CSF: High HVA (isolated)
Dopamine Transporter (presynaptic uptake defect) SLC6A3
Clinical: Movement do
HVA/5HIAA ratio >5
CSF: normal
Urine: high HVA and 5HIAA, low dopamine and norepinephrine
VMAT2 (SLC18A2)
Biochem: defective vesicular loading
Clin: Movement do
Tx: Dopamine receptor agonist (pramipexole) -
WORSE with L DOPA (dopamine does not make it into vesicle)
GSDs by ascending number
0 - Glycogen synthase (Hepatic, No HSM)
I - G6P Phosphotase (Hepatic)
II - Acid Maltase (Muscle) - cardiac involvement
III - Debranching (Mixed) - cardiac involvement
IV - Branching (Mixed) - cardiac involvement
V - Myophosphorylase (Muscle) - 2nd wind
VI - Liver Phosphorylase (Mixed) - mild
VII - Muscle PFT (Muscle) - no wind
IX - Liver Phosphorylase Kinase (Mixed) - mild

Hurler-like MPS and their enzymes
“-Ronidase”
MPS I - a L iduronidase
MPS II - Idurotnate sulfatase (X linked)
MPS VII - B-Glucoronidase
Primary CNS MPS + enzymes
“Heparan and -glucosaminde”
MPS III
A: Hepran sulfatase (SGSH)
B: N acetylglucosamidase (NAGLU)
C: acetyl-Coa glucosaminide acyltransferase (HGSNAT)
D: N-acetylglucosamine 6 sulfafase (GNS)
Primary Bone MSP and enzymes
“galacto-“
MPS IV and VI
IV A - galactose - 6- sulfatase (GALNS)
IV B - B- Galactosidase
VI - N-acetylgalactosamine 4 sulfatase (arylsulfatase B)
PAA: Low cit, high gln
Urine: low orotic acid
CPS1 or NAGS
CPS1 = rate limiting step
Severe neonatal UCD
N gets funneled into glutamine synthesis
- NAGS can be replaced by carbamylglutamate (Carboglu)

PAA: High Gln, Low Cit/Arg
Urine: Orotic acid high
OTC
X linked - 2/3 inherited, 1/3 de novo
Zinc-required for function

PAA: High gln, High cit, low Arg
Urine: high orotic acid
Citrullinemia type I
ASS
Arginosuccinate synthase
Milder UCD

PAA: High Arginosuccinic acid, high Cit, low Arg
Urine: high orotic acid, high arginosuccinic acid
Arginosuccinic aciduria
ASL (Lyase)
+ Trichorexis Nodosa
Urine arginosuccinic acid is more sensitive than plasma

PAA: high Arg
Urine: high orotic acid
Arginase Deficiency
ARG1 gene
Mild hyperammonemia, chronic sx
High Arg -> high GAA (creatine synthesis) -> ID, seizures, neuropathy in 2nd decade
- May be ornithine deficient

PAA: High Citrulline, may be high Thr/ Met/ Tyr
Citrin Deficiency (Citrullinemia type 2)
Aspartate transporter (SLC25A13)
Neonate: cholestatis, hepatomegaly
Juvenile/Adult: hyperammonemia, dyslipidemia, FTT
Tx: REPLACE ASP with high protein/high fat/low carb diet

PAA: High ornithine, normal Cit/Arg, high glutamine (ammonia)
UOA: high ornitine, homocitrulline
HHH (Hyperammonemia, Hyperornithinemia, Homocitrulline)
SLC25A15 - ornithine transporter
Ammonia > Gln levels
- Can cause coagulopathy
Tx: ammonia scavengers, cit supplement, protein restriction

DDx for hyperornithine
OAT (gyrate atrophy/eye changes) - treat with pyridoxine, arginine restriction after infancy
HHH (Ornithine transporter) - treat with citrulline supplement, protein restriction, ammonia scavengers

How are UCDs IDed on NBS
Not all identifiable
High Cit, Arg, or Arginosuccinic acid
What are ammonia scavengers
Na Benzoate (Conjugates with Gly)
Phenylacetate (conjugates with Gln)

UOA: Succinylacetone
Tyrosinemia type 1
FAH (Fumarylacetoacetase)
PAA: n-high Tyr
SUAC inibits ALAD -> ALA, porphyrins up
Clin: Hepatorenal, hypoglycemia, neuropathy
Tx NTBC, diet
Monitor: Hepatcellular Carcinoma w/ AFPs

PAA: Very high Tyr, Phe
UOA: 4OH phenylpyruvate/lactate/acetate
Tyrosinemia type II
Tyrosine aminotransferase (TAT)
Clinical: cornea lesions, hyperkeratosis
Tx: diet

PAA: High Tyr
Tyrosinemia type III
4OHpyruvate dioxigenase deficiency (HPD)
? neuro involvement
Diet
Heterozygotes = hawkinsonuria (?FTT, acidosis)

UOA: homogentisic acid
Alkaptonuria
Homogentisate dioxygenase (HGD)
Clin: dark urine when alkalinized, arthritis, cardiac valve disease, skin discoloration (onchronosis)
Tx: Diet, NTBC?

Maternal PKU treatment goal
< 360umol/l (<6mg/dL)
PKU treatment options
Diet - treat if >600; do NOT treat if <360
Tyr supplement
Kuvan (sapropterin) if not null alleles
Palinziq (enzyme replacement) if > age 18 and for less strict diet
Goal <360 in pregnancy (ID and CHD)
PAA: Low Lys, Arg, Orn
UAA: High Lys, Arg, Orn
Lyrinuria Protein Intolerance
Dibasic AA transporter -> reabsorption defect
High Lys, Arg, Orn in urine
Citrulline may be low
Clinical: FTT, diarrhea, osteoporosis, renal failure, hemolysis, hyperammonemia, HLH (high LDH, ferritin)
Tx: Protein restriction, citrulline replacement
Clinical differences between PA and MMA
PA: cardiomyopathy, long QT, autism
MMA: renal disease, metabolic strokes
UOA: 3OH Propionic acid, methylcitric acid, propionylglycine, tiglylglycine
ACP: high propionylcarnitine (C3)
PAA: high Gly, Ala
Propinonic aciduria
Propionyl-CoA carboxylase (PCCA, PCCB)
Biotin dependent enzyme
Clin: ID, movement do, osteoporosis, pancreatitis, cardiac
- PA inhibits urea cycle, krebs cycle -> hyperammonemia and hypoglycemia

What is C-VOMIT
Propiongenic substances:
Cholesterol
Valine
Odd Chain FA (other: thymine, uracil)
Methionine
Isoleucine
Threonin
Treatment of PA
Tx: Diet (limit C-VOMIT - threonine, methionine, valine, isoleucine), Carnitine, Abx to decreased GI bacteria
UOA: methylmalonic acid, 3OH propionic acid, methylcitric acid
ACP: C3, C4DC
MMA
Methylmalonyl-CoA mutase (mut)
- residual function = B12 responsive, nonresponsive = mut0
PAA - high glycine, alanine
Tx: hydroxocolbalamin, carnitine, limited C-VOMIT

3 colbalamin pathways
Adenocbl (MMA) -> A, B, D-MMA
MethylCbl (homocysteine) - E, G, D-HC
Common - C, F, J

High MMA, high Homocysteine, low cobalamin
Colbalamin Absorption defect
Intrinsic factor, intestinal receptors (cubilin CUBN, amnionless AMN), transcobolamin I or II
Neuro + megaloblastic anemia + FTT
Tx: Hydroxocolbalamin

High MMA, high Hcy, normal cobalamin levels
Cbc C (MMACHC), Cbl F (LMBRD1), CblJ (ABCD4)
Tx: OH colbalamin, betaine, folate
FTT, neuro, anemia,

High MMA, normal Hcy, normal Cbl
Cbl A (MMAA), Cbl B (MMAB), Cbl D-mma (MMADHC)
Phenocopy of MMA
Tx: Hydroxocolbalamin, diet, carnitine

High HCy, normal MMA, normal cbl
Cbl E, Cbl G, Cbl D-HC
Tx: Hydroxocolbalamin, Betaine
FTT, neuro, anemia
- DDx also include MTHFR, Folate deficiency, Homocystinuria

High MMA, High Hcy
Bulls eye maculopathy, Hemolytic uremic syndrome
CblC
Tx: Hydroxocobalamin and betaine
- Do NOT restrict protein (need methionine)
high MMA, high malonic acid
Combined malonic acid and methylmalonic aciduria
ACSF3 (MMA-coa and MA-coa synthetase)
Asymptomatic - neuropsych, FTT
CMAMMA: MMA > MA
(in Malonyl-Coa Dehydrogenase deficiency MA> MMA)
Causes of isolated MMA elevation
MMA (mut)
Cbl A, B, D
Transcbl receptor - benign
MM Epimerase (MCEE) - acidosis, neuro
CMAMMA (ACSF3) - asympatomatic - neuropsych
Mito encephalopathy w/ MMA (SUCLA2, SUCLG1) - encephalopathy w/ mtDNA depletion

UOA: Isovalerylglycine, 3OH-IVA
ACP: Isovalerylcarnitine
Isovaleric aciduria
Isovaleryl-CoA dehydrogenase (IVD)
FAD dependent
Clinical: similar to PA/MMA
Tx: Diet, carnitine, glycine supplement

Sweaty feet/cheesy odor, C5 carnitine
Isovaleric Aciduria
UOA: Isovalerylglycine, 3OH IVA
ACP: isovalerylcarnitine (C5)
Tx: carnitine, glycine, diet

UOA: 2 methylbutyric acid
SBCAD
(ABCADSB) - 2 methylbutryl-coa dehydrogenase
- C5 on NBS
- Hmong population
non-disease

UOA: 3-methylglutaconic acid, 3OH isovaleric acid
3-methylglutaconyl-CoA Hydratase deficiency
AUG gene
- Leukoencephalopathy in adults

Ddx for 3-methylglutaconic aciduria
3 methylglutaconyl-coA hydratase (+3OH-isovaleric acid)
Mitocondrial Membrane Lipid disorders - also involve cardiac manifestations, neurological problems, +/- lactic acidosis:
Barth syndrome (X linked, Taz)
SERAC1 (MEGDHEL)
AGK (Senger)
Costeff (OPA3)
DCMA syndrome (DNAJC19)
TMEM70

UOA: 3 methrylcrotonylglycine, 3OH-Isovaleric acid
3-methylcrotonyluria
3-methylcrotonyl-CoA Carboxylase (MCCC1)
Non disease
- Carnitine may be low

UOA: 2,3-dihydroxy-2 methylbutyrate
Crotonase Deficiency (Short chain enoyl-CoA Hydratase)
ECHS1 gene
Leigh like disease

UOA: 2 methyl-3 hydroxybutyric acid, tiglylglycine
ACP: normal
HSD10 disease (X linked)
2-methyl-3 hydroxybutyryl-Coa Dehydrogenase
Neurodegenerative in males only
cardiomyopathy

UOA: isobutyrylglycine
ACP: C4
Isobutyryl-CoA Dehydrogenase deficiency
ACAD8
Mostly asymptomatic, some DD/hypotonia

ACP: C4OH
3-hydroxyisobutyryl-CoA Hydrolyse (AKA deacylase)
HIBCH
C4OH - 3OH isobutyryl-carnitine
Leigh like, FTT

UOA: 2-oxoisocaproic acid
(2-oxo or 3 keto acids)
MSUD
BCKDH (E1), could also be E2, or E3
PAA: High Leu, Ile, Val (normally Ile>Leu>Val) + Alloisoleucine
Should have ketones in acute state (alpha-keto acids elevated)
Clin: Chronic and acute encephalopathy; opisthotonus
Tx Diet

Normal branch chain ratio
Lle: Leu: Val
1:2:3
XLE on NBS
MSDU (alloisoleucine)
Hydroxyprolinuria (benign)
PAA: high methionine
Mudd’s Disease
Methionine S-adenosyltransferase (MATI/MATIII)
Half benign (most common cause of high Met)
Half dystonia + demyelination (met > 800umol/L)
Cabbage-like breath
Carriers can have high Met with no symptoms

Treatment for Mudd’s disease
MATI/III def
Met restricted diet if met > 800umol/L -> goal 500-600
Supplement SAM if symptomatic on treatment

PAA: high Met, high S-adenosylMet (SAM), low S-adenosylHomocy (SAH)
Glycine N-methyltransferase Def
GNMT (MT in picture)
Benign

High Met, High S-adenosylMet (SAM), high S-AdenosylHcy (SAH)
S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase (SAHH) deficiency
AHCY gene
Myopathy (high CK), demyelination, ID
Tx: Met restriction

High homocysteine, low methionine
Methionine Synthase (MS/CblG)
Megaloblastic anemia + neurological
MTR gene
DDx: CblE, MTHFR

High Met, High SAM, high SAH,
+high adenosine
Adenosine Kinase Deficiency
ADK
Neurological like SAHH + frontal bossing

High Met, high homocysteine (high SAM, high SAH)
Low cysteine
Homocystinuria
Cystathinone Beta Synthase deficiency
- common in Qatar
Marfanoid (cysteine residues in fibrillin)
ID
lens dislocation
myopia
thromboembolism

Treatment for homocystinuria
Goal homocysteine <30umol/L
FIrst: asses B6 (pyridoxine) responsiveness
- must be given with folate
- If <50umol/L = responsive
- if >20% reduction = partial response
If NON-responsive:
- met restricted diet
- betaine
- hydroxocolbalamin

Cystathione in urine
Cystathioninuria
Cystathion gamma lyase (CGL)
benign
DDX: liver disease, mito disease, anything that elevated homocysteine

High taurine, high sulfocysteine, low Cys, low Homocys
Urine sulfite
Sulphite oxidase deficiency
SUOX
Cystic brain changes + epilepsy + Lens dyslocation

High sulfocysteine, sulfite +, high xanthine, high hypoxanthine
low Uric acid
Molybdenum Cofactor Deficiency
MOCS1 and MOC2
Cystic brain changes + Epilepsy + Lens dyslocation
Cofactor for SUOX and Xanthine breakdown (purine breakdown pathway)
Tx: Cyclic Pyranopterin Monophosphate (cPMP) - Fosdenopterin for MOCS1

Urine: high hypoxanthine, high xanthine
low uric acid
Xanthinuria
Xanthine oxidase def
May be benign vs renal failure + stones, arthropathy, myopathy
Tx: Purine restricted diet
ACP: C4, C5
UOA: ethylmalonic acid, methylsuccinic acid
Lactic acidosis
Ethylmalonic encephalopathy
Mitochondrial sulfur dioxygenase deficiency
Clin: Neurodevelopmental, motor signs, Petechiae, Acrocyanosis, diarrhea
Tx: Metronidazole, N-acetylcysteine (neutralized H2S), transplant

Acrocyanosis, petichiae, diarrhea, encephalopathy
Ethylmalonic encephalopathy
ETHE (Sulfur Dioxygenase)
Tx: N-acetylcysteine, metronidazole, transplant

DDx for ethylmalonic acid
Ethylmalonic encephalopathy (ETHE)
Jamaican Vomiting sickness (unripe ackee fruit)
Lychee encephalopathy
SCAD (high butrylcarnitine and butyrlglycine) - benign
MADD (GA2 + glutaric acid)
List the enzymes for:
Fabry
GM1-gangiosidosis
Krabbe
Gaucher
Pompe
Fabry: Alpha-galactosidase
GM1: Beta-galactosidase
Krabbe: Galactocerebrosidase
Gaucher: Glucocerebrosidase
Pompe: Alpha-Glucosidase

What are the 3 functions of trifunctional protein
1) Hydratase (Add water -> hydroxy acyl)
2) OH-acylt coA Dehydrogenase (remove OH -> keto-acyl)
3) ketoThiolase (remove acetyl-CoA -> shorten chain)

FAOD with Hyperinsulinism
HADH (3 Hydroxyl CoA- Dehydrogenase)
Equivalent of SCHAD (LCHAT for short chains)
Also hypoglycemia/liver disfunction

FAOD with retinopathy and neuropathy
LCHAD and TFP
Pregnant female with fatty liver of pregnancy and HELLP syndrome
Carrier for LCHAD/MTP
ACP: C14, C14:1, C14:2, C16, C:18
VLCAD
ACADVL gene
Variable presentation
Hypoglycemia, hepatopathy, rhabdo, myopathy, cardiomyopathy

ACP: C16OH, C16:1OH, C18OH
LCHAD
Hypoglycemia, Liver, muscle, cardiomyopathy
+ Retinopathy, neuropathy
+ Maternal fatty liver/HELLP syndrome

Urine hexanoylglycine
MCAD
ACADM gene
- Hypoglycemia (No muscle involvement)
- Reye like severe liver failure
ACP: C8
ACP: C4
Urine: Ethylmalonic acid
SCAD
ACADS gene
Non-disease
DDX for ethylmalonic encephalopathy
ACP: C4OH
SCHAD
Hyperinsulinism (lack of GDH inhibition in pancreatic islet cells)

Ichthyosis + spastic tetraplegia + short stature
+ Leukotriene B4 in urine
Sjogren Larsson Syndrome
ALDH3A2 (fatty alcohol dehydrogenase)
+ hyperkeratosis
+ “Glistening dots” in retina
+ ID/epilepsy
Skin, CNS, Bone, Eye
Tx: LTB4 antagonist
Metabolic disease with Renal cysts (3)
GA2
Zellweger
CDG-PMM2
What is the electron acceptor for acyl-coa dehydrogenases?
Electron Transfer Flavoprotein (GA2)
ACP - Elevations in all chain lengths
MADD (GA2)
UOA: Lactate, ethalmalonic acid, 2OH glutaric acid
Clinical: Myopathy, cardiomyopathy, renal cysts, CNS, acidosis, hypoglycemia

UOA: Ethylmalonic acid, adipid acid, 2OH glutaric acid
GA2
- Cystic kidneys, hypoglycemia, acidosis, CNS, myopathy
ACP: multiple chain length elevations
Low F/T carnitines
ACP: all carnitines low
Carnitine transporter/uptake deficiency
SLC22A5
Clin: Weakness, Cardiomyopathy, hypoglycemia/hepatic
Tx: EKG, carnitine supplement

How to tell apart CACT from CPTII
CACT: renal malformations, always severe
CPTII: most commonly adult myopathic form
ACP: Low C16, C18, C18:1
High C0
CPT1 def
- Inuits (alaska)
Liver, RTA, cardiomyopathy, hypoglycemia

Low free and total carnitine
ACP: high C16, C18, C18:1
C18/C2 ratio high
+ Renal malformation
CACT (Carnitine translocase/SLC25A20)
- bound to long chain but cannot get into mito
- Cardiac, Liver, hypoglycemia, weakness
- Most die by 3 months

Low free and total carnitine
ACP: high C16, C18, C18:1
C18/C2 ratio high
Adult w/ weakness
CPTII
- Cannot releast long chain - carnitine
Most common form = adult w/ myopathy

Low free and total carnitine
ACP: high C16, C18, C18:1
C18/C2 ratio high
CPTII or CACT (translocase)
carnitine stuck on long chains
CACT has renal malformations, always severe presentation
CPTII can be severe, but usuall late onset myopathy

Trimethyllysine high in urine and plasma
Trimethyllysine dioxygenase
gene: TMLHE (hydratase-epsilon)
X linked
Carnitine synthesis pathway
Trimethyllysine elevated in urine/plasma
- Autism risk gene that can be treated w/ carnitine supplement
normal GGT
Diarrhea, jaundice, hepatopathy, rickets
Bile acid synthesis disorders
3Bhydroxysterol dehydrogenase (HSD3B7)
3oxysterol 5B reductase (AKR1D1)
Oxysterol 7a hydroxylase (CYP7B1)
- low cholesterol, high bili
Tx: Bile acid replacement
High Cholestanol
cataracts, diarrhea, xanthoma, ataxia
Cerebrotendinous Xanthomatosis
Sterol 27-hydroxylase def
CYP27A1
Tx: statins + Chenodeoxycholic acid (Chenodal)
Why is there high ammonia in PA and MMA
Secondary inhibition of NAG synthase
High Hydroxybutyrate even when fed
High urine ketones
Normal ACP
SuccinylCoA-3-oxoacid CoA Tranferase (SCOT) deficiency
- Episodic acidosis (ketoacids), tachypnea, hypotonia, encephalopathy

High hydroxybutyrate
ACP: tiglycarnitine, 2-methyl-3OH butrylcarnitine
UOA: tiglyglycine, 2-methyl-3OH butryic acid, 2 methyl-acetylacetic acid
Beta-ketothiolase (3-oxothiolase)
Both Ketolysis and ILE breakdown
- nauses + emesis -> encephalopathy
- hypoglycemia (cannot use ketones for energy), metabolic acidosis, hypoerammonemia (NAGS inhibition)

Fasting: 4 hydroxy - 6- methyl- 2 pyrone (related to acetylacetone)
Hypoketotic hypoglycemia
HMG-CoA Synthase
Presents like FAOD
UOA: high dicarboxylic acids (adipic, malonic, glutraic, succinic acid)
Tx: avoid fasting

UOA: 3-hydroxy-3 methylglutaconic acid, 3 Oh isovaleric acid, 3 methylglutaric acid, 3 methylglutaconic acid
ACP: C5OH, C6DC
HMG-CoA Lyase deficiancy
- FAOD and organic aciduria (final step in Leu breakdown and ketone breakdown)
Hypoketotic hypoglycemia (severe)
Hyperammonemia (secondary NAGS inhibition)
Acidosis
Tx: Carbohydrates, carnitine

Name the Valine breakdown intermediates
Isobutyryl-CoA -> Dehydration (IBD)
Metharylyl-Coa -> Hydration (Crotonase/ short chain enyol-CoA hydratase)
3OH Isobutyryl-CoA -> Dehydration (HIBCH/deacylase)
3OH Isobutyrate
MMA Semialdehyde -> Thiolysis (MMSDH)
PA
MMA
SuccinylCoA

Name the ILE breakdown Intermediates
2 methylbutyryl CoA -> Dehydration (2MB Dehydrogenase)
Tiglyl-CoA -> Hydration (Crotonase/Short chain enyol-CoA hydratase)
2 Methyl-2OH Butyryl CoA -> dehydration (HSD10, MHBD)
2 methylaceoacetyl CoA -> thiolysis (Beta ketothiolase)
PA + Acetyl CoA
MMA
Succinyl CoA

Name the Leu Breakdown intermediates
Isovaleryl CoA -> Dehydration (IVD)
3 MethylCrotonyl CoA (3MCC)
3 methylglutaconyl CoA -> Hydration (hydratase)
3Oh 3 mehtylgluarylCoA -> Thiolysis (HMG-CoA Lyase)
AcetylCoA + Acetoacetate

Name the main intermediates and products in Leu, Ile, and Val metabolism
Leu: Isovaleric, Methylcortonyl, Methylglutaryl -> Acetyl CoA + acetylacetate
ILE: Methylbutyryl, Tiglyl -> PA + acetyl CoA
Val: Isobutyryl -> MMA semialdehyde -> PA

What AA is the precursor to endogenous Carnitine synthesis?
Lysine (Trimethyllysine)
Sleeping through night -> hypoglycemia + high LFTs
MCAD or GSD1 (elevated TG, uric acid)
Rhabodomyolysis with CK > 10,000 at baseline. Most common cause of rhabdo in children after FAODs (10%)
LPIN1 deficiency
Phosphatidic acid phosphohydrolase (PAP)
BIochem: PA -> Diacylglycerol
- Role in PPAR activation and regulation of ETC expression
LPIN2 deficiency -> inflammatory signlating -> recurrent osteo

Jordan’s anomaly (empty vacuoles in PMN cells that stain red), myopathy
Neutral lipid storage disorder
Biochem: inability to break down TG in lipid droplet (Jordan’s anomaly = lipids in macrophages)
AGTL (adipocyte TG lipase deficiency)
CGI 58 (chanarin Dorfman) + ichthyosis

Disorders of triglyceride synthesis that cause lipodystrophy
AGPAT, Seipin/BSCL2 (s), HSL, PLIN-1

3-methylglutaconic acid, positive filipin stain
SNHL, Hepatopathy, encephalopathy, dystonia
MEGDHEL
SERAC1 deficiency (mito membrane lipid remodeling)
3-MethylGlutaconic Acid
Deafness
Hepaopathy
Encephlopathy
Leigh syndrome

3 methylglutaconic acid; high LysoCL:CL ratio
Dilated cardiomyopathy, Neutropenia
Barth syndrome
TAZ (XL)
Dilated CM, neutropenia, lactic acidosis, GI, growth, developmental issues
Tx: Elamipretide (stabalize cardiolipin)

Neuropathy, hearing loss, ataxia, RP, Cataracts
Normal phytanic acid
PHARC syndrome
(ABDH12)
Polyneuropathy, Hearing loss, Ataxia, RP, Cataracts
Resembles refsum disaese, but NORMAL phytanic acid

Dense congenital cataracts, Hypotonia, ID, renal fanconi (RTA 4)
Lowe syndrome (Oculocerebrorenal syndrome)
OCRL XL
Phosphoinositide phosphorylase
Eye: catracts, glaucoma
Cerebro: ID, hypotonia
Renal: tubular dysfunction
X linked metabolic conditions
OTC
Glycerokinase
XALD
Fabry
G6PD
Lysch Nyhan
Creatine Transporter
Menkes
Pseudotriglyceridemia
Glycerol Kinase deficiency
Biochem: Gllycerol + ATP -> glycerol-3-phosphate + ADP
Standard TG assay cleaves Acyl groups from TG and measures glycerol levels… Plasma will be clear instead of cloudy (no lipemia)
- Also F-1,6-bisphosphatase deficiency (secondary buildup of glycerol)

Ketotic hypoglycemia, DD, emesis, high TG
Glycerol Kinase Deficiency
XL
- high urine glycerol, pseudotriglyceride
- can be part of deletion syndrome with adrenal hypoplasia congenita and duchennes muscular dystrophy
- false positive TG (since glycerol backbone is elevated) with normal lipid levels
Tx: Fat restricted diet
- Daiper cream also can cause false glycerol elevation

What is the first cyclic molecule in cholesterol synthesis pathway?
Lanosterol
(oxidosqualine cyclase = lanosterol synthase)

UOA: high mevalonic acid, high mevalonoacetone, high IgD
Mevalonic aciduria, or hyper IgD (mild)
Mevalonic kinase
Inflammatory syndrome: Fever, rash, HSM, diarrhea, may have neuro + retinal findings
Mild form = hyper igD
Tx: Steroids, IL1 receptor antagonist (anakinra), replace uniquinone

MVK, PMVK, MVD, FDPS
Porkeratosis
Mevalonate kinase, phophomevalonate kinase, dehydrogenase, famesyl-diphosphate synthase
AD diosrders of keratinization -> raised hyperkeratotis plaques with evident borders
Pre-squalene cholesterol disorders

High desmosterol
Desmosterolosis
3OH oxysterol/Desmosterol reductase (DHCR24)
- Ambiguous genetalia (sex hormones = sterols)
- Dysmorphic, Short limbs, CNS abnormalities, arthrogryposis, ID

High lanosterol, dihydrolanosterol
Antley Bixler
POR (Cyp450 oxidoreductase)
Craniosynostosis, limb defects, ambiguous genetalia, dysmorphic

Cholesta-8,14-dien-3B-ol
Skeletal dysplasia
Greenberg dysplasia
3-hydroxysterol Delta-14 reductase (right below antley-bixler in pathway)
LBR gene
+ Pelger Huet anomaly

Microcephaly, congenital cataracts, psoriaform dermatitis
SC4MOL
Sterol-C4-methyl oxidase
High 4-methylsterols

Female: Unilateral ichthyosis with sharp demarcation and stippled epiphysis
Males: ID, pachygyria, dysmorphic
3 hydroxysterol -4 demeythylase
NDSHL (XL)
Females: CHILD syndrome (Congenital Hemidysplasia with Ichthyosiform nevus and Limb Defects)
Males: Syndromic ID
- High 4-methylsterols
Tx: Cholestrol Supplementation

Assymetric RCDP + ichthyosis, alopecia, cataracts
Conradi-Hunermann
X-linked CDP
Sterol-7,8-isomerase (EBP) - Male lethal
Lab: high 8 dehydrocholestrol, 8(9)cholestrol

High lathosterol
Lathosterolosis
Sterol-delta5-deatruase
SLOS-like: ID, microcephaly, catarats, micrognathia, polydactyly, liver disease

Low maternal estriol
High 7 dehydrocholesterol and 8 dehydrocholestrol
SLOS
Sterol-7-reductase (DHCR7)
2/3 toe syndactyly, FTT
Dysmorphic: ptosis, anteverted nares, low set ears
- AV canal defects (like DS)
- GU abnormalities (cannot synthesize hormones)

Name the syndrome for following sterol pathway enzymes:
1) sterol-14-desaturase
2) sterol 8,7 isomerase
3) sterol 5 desaturase
4) Sterol 24 reducatase
5) sterol 7 reductase
1) sterol-14-desaturase - Greenberg dysplasia
2) sterol 8,7 isomerase - XL-RCDP
3) sterol 5 desaturase - Lathosterolosis (SLO like)
4) Sterol 24 reducatase - desmosterolosis (CNS + other malformations)
5) sterol 7 reductase (SLOS)
2 disorders with high 4-methylsterols
Sterol-C4-methyloxidase - SC4MOL- psoriaform dermatitis, cataracts, microcephaly
Sterol-4-demethylase - CHILD syndrome - hemiichthyosis + assymetric rhizomelic condrodysplasia
- Cholesterol supplement may help with skin findings

Most common genes for Zellwegere spectrum
PEX1 (60%)
PEX6 (15%)
Others rare
Stippling of epiphysis -> Flaring epiphysis, irregular metaphysis, cataracts, rhizomelia, ID
RCPD
PEX7, GNPAT, AGPS
DDx: ARSE, sterol8,9isomerase, warfarin embryopathy, maternal SLE
What is the NBS marker for XALD?
C26:0 lyso phosphotidylcholine
Ddx for high phytanic acid
Alpha-oxidation pathway
- Refsum disease (pristanic low)
- Zellweger spectrum (pristanic low, VLCFA high)
- RCPD 1 (pristanic low)
- a-methyl-ethyl-coa Racemase (pristanic high)

Main pathways that require riboflavin
FAD - electron carrier, helps with dehydrogenases
BCAA - IVD, SBCAD, IBD
FAD: SCAD, MCAD, LCAD, VLCAD, ACAD
- Choline metabolism
ETC - complex II, GA2 like presentation when deficient -> myopathy, neuro phenotypes

Presentation and biochemical profile of riboflavin transport/metabolism defects
SLC52A1/A2/A3, FLAD1 (synthase), SLC25A32 (mito transporter)
- FAD needed for FAO dehydrogenases, BCAA dehydrogases, and ETC (complex II)
Clinical: weakness, hypotonia, neuropathy, myopathy
BIochem: GA2 like -> multiple acyl-carnitine elevations, organic acid elevations

What are the NBS analytes for MSUD
Ratio Leu or Ile to Ala or Phe
What is the standard lab technique for UOA, ACP?
UOA: GC/MS
ACP: MS/MS
NBS: C5OH, healthy baby
Most likely 3MCC or maternal 3MCC
What AA coelutes with homocitrulline in urine?
Methionine
(false elevation in Met on OAA in HHH)
What molecule does carbamoyl phosphate and lysine form?
homocitrulline
Hyperammonemia, high met on UAA
HHH
(homocitrulline co-elutes with methionine in urine)

High tyrosine and methionine
Tyroseinemia type I
Methionine is sign of liver injury

High methylmalonic acid, high malonic acid
ACP: C3DC
Malonic aciduria
MLYCD (Malonyl-Coa Decarboxylase)
MA > MMA (Opposiite in CMAMMA)
ID, emesis, epilepsy
Tx: High carb diet, carnitine

Hypoglycemia, High free fatty acids, low ketones
FAOD
FFA high = Acitve liposis
if ketones are normal or low, then you have a disorder of FAO
Hypoglycemia, low Free fatty acids, low ketones
Hyperinsulinism - lipolysis is being inhibited
hyperglycemia with high ketones
Disorders of ketolysis
GSD 0 (glycogen synthase) - no stored glycogen -> more FAO
GSD 3 (Debranching) - glycogen unavailable -> more FAO
Organic acidurias
hypoglycemia + high lactate + hepatomegaly
GSDs, gluconeogenesis disorders
Hypoglycemia + Hepatopathy
HFI, tyrosinemia type I, FAOD (longer chain), mitochondrial
Hearing loss, weakness (upper limb > lower limb), neuropathy, few facial symptoms, responsive to riboflavin
Brown-Vialetto-Van Laere syndrome
SLC52A2 - CNS riboflavin transporter
- GA2 like metabolic profile

What tissue does not have mitochondria? What does it use for ATP
RBC, penthose phosphate pathway
Which polymerase replicates the mitochonidral genome?
Gamma -> PolG
Which complex in ETC is completely encoded for by nuclear genes?
Complex II (it is part of the TCA cycle)
Which amino acid reflects long-term lactate elevation?
alanine

What is the treatment for MELAS?
IV arginine for acute stroke like episodes
PO citrulline (Arg precursor) or taurine (modifies mtLeu tRNA) may also help
high plasma/urine levels of Thymidine and deoxyuridine
+ Psuedo obstruction
MNGIE (mito-neuro-gastro-intestinal encephalopathy)
Thymidine phosphorylase deficiency
- Disruptions DNA replication system by limiting availability of T -> accumulation of mutations
+neuropathy, myopathy, ophthalmoplegia, leukoencephalopathy
Mitochondrial encephalopathy with cortex > BG involvement
+ Liver dysfunction
Alpers syndrome
POLG, C10ORF2
What are 3 markers for mitochondrial disease in blood?
Lactate
Alanine
GDF15
- TCA intermediates in urine
Normal complex II activity but decreased complexes I, III, and IV
Mitochondrial depletion syndrome
- reflced abnormal mito DNA replication -> complex II is fully nuclear encoded
- SUCLA2 (Leigh like + deafness) - high MMA and C3/C4DC on NBS

mt3243A>G
MELAS
tRNA Leu
Mt1, 4, and 6 - homoplasmic mutations
Occurs in males > females
LHON
Progressive external ophthalmoplegia, Retinitis pigmentosa, onset <20 + ataxia/conduction block/CSF protein elevation
Kearns-Sayre
Large mDNA deletions/duplications
Mt 8344G>A
Epilepsy, multiple symmetric lipomatosis
MERRF
tRNA Lys
Cataract, cardiomyopathy, myopathy, lactic acidosis
Sengers syndrome
AGK

Long philtrum, thin vermillion, upturned nose
Leigh-like, neuropathy
+ high lactate, alanine, and pyruvate
low-nl Lactate/pyruvate ratio
Pyruvate dehydrogenase deficiency
Most common PDHA1 (XL, females can be affected)
Converts pyruvate to acetyl-CoA
- Brain malformation: ventriculomegaly, agenesis of CC
- Fetal alcohol like facial features (EtOh -> acetaldehyde -> inhibits PDH)
Tx: Ketogenic diet (generates acetyl-CoA), thiamine

High lactate, alanine, and pyruvate, low-nl Lactate/pyruvate ratio
Elevated Leu, Ile, Val
high a-keto-glutarate
E3 (Dihydrolipoamide Dehydrogenase deficiency)
- Shared by a-KG dehydrogenase, pyruvate dehydrogenase, and Branched chain alpha-ketoacid dehydrogenase
Leigh syndrome + liver failure
In the ETC how many ATPs are generated per each NADH and FADH?
NADH: 3
FADH: 2
*really closer to 2.5 and 1.5 due to leakiness of inner membrane
PAA: High Cit, Thr, Met, Tyr
Cholestasis, fatty liver, hypoglycemia
Citrin deficiency
SLC25A13 - Asp, Glu carrier
Common in Japan
- Liver disease in neonates
- encephalopathy in adults + aversion to carbs
Tx: Galactose free diet, Ammonia scavengers, Arginine, Liver Transplant

UOA: high D-2-hydroxyglutaric acid
Hypotonia, DD, cardiomyopathy
D-2-hydroxyglutaric acidruia type 2
(IDH2 Gain of function)
Type 1 is due to D2HG Dehydrogenase (no cardiomyopathy, lower extretion ~1000 instead of 2000)

UOA: High a-ketoglutaric acid
E3 deficiency (a-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase + high BCAA, lactate) -leigh syndrome + liver failure
TPK - leigh syndrome
SLC19A2 (thiamine transporter) - Biotin responsive BG Disease
SLC25A19 (thiamine transporter) - Amign lethal microcephaly

Leigh syndrome + deafness
UOA: MMA elevation
Succinyl-CoA synthetase (ligase)
SUCLG1, SUCLA2
- C3 and C4DC on NBS

Which TCA disorder presents as an Oxphos phenotype?
Succniate dehydrogenase
- Part of complex II
- Succinate + FAD -> FADH2 (used by complex II for oxphos) + fumarate
High lactate, pyruvate, and TCA intermediates (Fumarate, malate)
- Parents at risk for malignancy (paraganglioma + pheo)
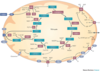
AD: paragangliomas and pheochromocytomas
Succinate Dehydrogenase deficiency B-D subunits
SDHB, C, D
- HIF regulation -> angiogenesis and inhibition of apoptosis

ISCU (Iron-sulfur cluster protein)
Combined SDH and aconitase deficiency
(both enzymes need Fe-S clusters)
Swedish type mitochondrial myopathy

Hereditary leiomyomatosis and renal cell carcinoma
HLRCC
Fumarase - FH heterozygotes (AD)
- Cutaneous and uterine leiomyomas
- Renal cell carcinoma

UOA: high fumarate
Polymicrogyria, atrophy, open opernacula
Hypotonia, DD, seizures
Frontal bossing, hypertelorism, depressed nasal bridge
Fumarase deficiency
“Polygamist Down Syndrome” - common in polygamous towns in Colorado City, AZ and HIldate, Utah

UOA: high D-2-hydroxyglutaric acid
D-2 hydroxyglutaric aciduria
Both: DD, hypotonia, seizures
Type 1: D2HG Dehydrogenase deficiency (no cardiomyopathy) - D2HG -> aKG
Type 2: IDH2 GOF (also has cardiomyopathy) - Isocitrate -> [aKG] -> D2HG
UOA: high L-2-hydroxyglutaric acid
CSF AA - high lysine
L-2-Hydroxyglutaric aciduria
L2HG Dehydrogenase
Converst L2HG -> aKG
DD, epilepsy, leukodystrophy + brain tumor predisposition
Mito Glutamate Carrier
SLC25A22
neonatal myoclonic epilepsy
Mito ADP/ATP carrier
SLC25A4
AD progressive external opthalmoplegia + exercise intolerance
Mito Phosphate Carrier
SLC25A3
Hypotonia, cardiomyopathy, lactate acidosis
Steroid resistant nephrotic syndrome, hearing loss, myopathy, encephalopathy/ataxia
Lactic acidosis
CoQ10 biosynthesis defect
CoQ2, CoQ9, PDSS1, PDSS2, ADCK3
Complex I, II, or III activity in isolation = normal
Complex I+III or Complex II+III activity = decreased
Tx; ubiquinol

What food should patients with multiple carboxylase deficiency avoid?
Avoid raw eggs (Avidin binds biotin and sequesters it)
MCD = Holocarboxylase or biotinidase
Neurological symptoms, Hair loss, eczema, metabolic acidosis
C5OH on NBS
Multiple carboxylase deficiency
biotinidase or holocarboxylase
Neuro + derm + acidosis
UOA: 3MCC (3OH-IVA, 3-methylcrotonylglycine) + PCC (Methylcitrate, 3OH propionate, tiglylglycine, propionylglycine, + PC (lactate)

PAA - high alanine
ACP - low carnitine
UOA: 3OH IVA, methylcrononylglycine, methylcitric acid, tiglylglycine
Multiple Carboxylase deficiency
Biotinidase or holocarboxylase (distinguish with biotinidase or holocarboxylase synthatase enzyme assay)
NBS: C5OH
Neuro + derm + acidosis
elevations due to affected 3MCC (3OH IVA, methylcrotonylglycine); PCC (methylcitrate, 3Oh propionate, propionylglycine, tiglylglycine)
PC; (lactate, alanine)

Neurological regression with high succinate on MRS
Succinate dehydrogenase deficiency
Part of complex II
Succinate + FAD -> FADH2 (used immediately) + fumarate
Urine may excrete succinic acid, fumarate, or malate (TCA intermediates due to oxphos backup)

Which GSD is X linked
GSD9
4 subunites:
PHKA1, PHKA2 are XL
PHKB and pHKG2 are AR
What common factors can interfere with biotinidase assay?
Ampicillin
Hemoglobin (in test tube)
Liver dysfunction (low albumin or high bilirubin)
Prematurity
X linked GSD
GSD 9 (Hers)
PHK - A2, B, G2, A1 (2 are X linked, 2 are AR)
Liver GSD, tends to be milder but can be severe in males
What stain is used for glycogen?
PAS - periodic acid schiff
Less branched glycogen = polygucosan
Hyperuricemia, Lactic acidosis, High alanine, high TG, low BG
GSD I

What are differences between GSD1 and GSD3?
GSD3 more mild and can use proteins (gluconeogenesis NOT affected)
- Thus ala/BCAA low; add alanine for treatment
TFF, fasting hypoglycemia, postprandial hyperglycemia
GSD0
- cannot put glucose into glycogen, thus hyperglycemia after meals.
(Postprandial hyperglycemia also seen in GLUT2 (GSD XI) due to abnormal glucose transporter into and out of liver)
Hypotonia, hepatomegaly, cardiomyopathy + WPW syndrome
Danon disease (LAMP2)
- Pompe like + WPW
X-Linked
GSD V vs GSD VII (tauri)
GSD V (myophosphorylase): Muscle only, Second wind (use glucose from blood or FAO)
GSD VII (Muscle PFK): Muscle and hemolysis with erythrocytosis (RBC use glycolysis for energy, but synthesis upregulated by lack of F1,6BP); out of wind because glycolysis does not work; + polyglucosan (glycogen synthase upregulated, branching enzyme activity does not match)
What are the common clinical features of disorders of glycolysis?
Hemolysis (RBCs do not have mitochondria and need this for energy)
Myopathy (Think GSD VII - PFK)

Myopathy + rhabdo with low LDH
LDH deficiency
- Myopathy/cramps/rhabdo
- Some have rash
+ high CK but LOW LDH

Hemolysis + myopathy + severe neurological disease
Trisephosphate isomerase deficiency
DHAP needs to be converted into G2P, otherwise buildup -> toxic metabolite

X linked glycolysis disorder
Phosphoglycerate Kinase
- Clinically similar to PFK (tauri)
- Anemia, muscle, CNS

Hemolysis with erythrocytosis, out of wind phenomenon,
GSD VII (Tauri)
PFK is glycolysis enzyme -> RBC need this for energy
Decreased product -> upregulate marrow erythrocytosis
+ out of wind phenomenon
+ polyglucosan (high glycogen synthase activity, normal branching enzyme)
What is the mechanism of hemolysis in G6PD?
Decreased NADPH -> cofactor for glutathione reductase -> necessary for ROS removal
X-Linked, first step in pentose phosphate shunt

MRS and urine polyols: high ribitol, D-arabitol
Ribose-5-P isomerase deficiency
(RPIA gene)
Leukoencephalopathy, ataxia, neuropathy

Urine polyol: High ribitol, D-arabitol, erythritol, sedoheptulose
Transaldolase Deficiency
Gene: TALDO1
- Most common pentose phosphate disorder
- Liver disease + HSM, hemolytic anemia, renal failure, cutis laxa, hepatocellular carcinoma

Severe liver disease, CHD, HSM, hemolytic anemia, RTA, cutis laxa
Transaldolase deficieny
TALDO1
+hepatocellular carcinoma
Urine polyols: high Ribitol, D-arabitol, erythritol, sedoheptulose
UOA: L-xylulose, xylose, arabinose
Essential pentosuria
L-xylulose reductise deficiency (DCXR)
- Non disease
Hyperammonemia
high: Cit, Ala, Lys, Pro
Low: Asp, Glutamate
Pyruvate Carboxylase Deficiency
- Defect in glycolysis and gluconeogenesis
Lactic acidosis, Neurological, liver failure, cystic periventricular leukomalacia
Low OAA -> Low aspartate -> ASS cannot work; thus secondary UCD with high Cit;
Lys requires aKG to degrate
Proline oxidase inhibited by lactate
- high L/P ratio; Low 3OH-butyrate/acetoacetate ratio
- ketones
- Low TCA intermediates (2oxoglutarate/aKG, Malate, fumarate, etc)

high L/P ratio; Low 3OH-butyrate/acetoacetate ratio
Pyruvate Carboxylase Deficiency
Defect in glycolysis and gluconeogenesis
Lactic acidosis, Neurological, liver failure, cystic periventricular leukomalacia
- Low asparatate -> Malate/Asp shuttle cannot transfer NADH from cytoplasm into mitochondria -> high NADH in cytoplasm (L/P) and low NADH in mitochondiral (HB/Acetoacetate)
- Postprandial ketosis (glucose -> Acetoacetate instead of TCA)
- Low TCA intermediates (low OAA)
- Hyperammonemia (secondary ASS deficiency since Asp + Cit = Arginosuccinate
- High Lys, Pro, Cit

Postprandial ketosis, liver failure, encephalopathy, lactic acidosis
Pyruvate Carboxylase Deficiency
Defect in glycolysis and gluconeogenesis
glucose -> Acetoacetate -> ketones instead of TCA
high L/P ratio; Low 3OH-butyrate/acetoacetate ratio (Low asparatate -> Malate/Asp shuttle cannot transfer NADH from cytoplasm into mitochondria -> high NADH in cytoplasm (L/P) and low NADH in mitochondiral (HB/Acetoacetate))
- Low TCA intermediates (low OAA)
- Hyperammonemia (secondary ASS deficiency since Asp + Cit = Arginosuccinate
- High Lys, Proline, Cit

Lactate acidosis, liver failure, hypoglycemia
- High TCA intermediates
Phosphoenolpyruvate Carboxykinase Deficiency
PEPCK
- OAA is high -> high TCA intermediates
- Impaired gluconeogenesis

CSF/Blood glucose ratio <0.45, low lactate/alanine
GLUT1
SLC2A1 (AD)
CNS glucose transporter
EIEE, epilepsy, exercise induced movement disorder
Tx- Ketogenic diet

Fasting hypoglycemia, postprandial hyperglycemia, hepatomegaly, nephropathy
NBS positive for galactosemia
UAA: multiple amino acids (including gly, met, pro) elevated
Fanconi Beckle (GSD IX)
GLUT2 - SLC2A2 gene
Renal/liver glucose transporter
- Abnormal glucose import into liver -> postprandial hyperglycemia
- Abnormal glucose export -> glucogen buildup
- Abnormal glucose reabsorption -> renal fanconi: animoaciduria, phosphaturia, glucosuria, rickets
- abnormal enterocyte absorption = glucose/galactose intolerance w/ diarrhea

Amish
Diarrhea, glucosuria
Glucose-Galactose malabsoprption
SGLT1 deficiency (SLC5A1)
glucose/galactose transporter
- abnormal absoprtion -> diarrhea
- abnormal renal reabsoprtion -> glucosuria
Tx: Fructose based diet
Hereditary Renal Glucosuria
SGLT2 (SLC5A2)
Glucose transporter
- abnormal renal reabsoprtion -> glucosuria
Benign (SGLT1 can do most of the work)
High Galactose, High Gal-1-P, high galactitol, urine reducing substances
Galactosemia (GALT) or Epimerase (GALE)
- Distinsuish with GALT activity assay
What are the short and long term symptoms of galactosemia?
Early: Liver failure, Infection “E.Coli sepsis”, cataracts, encephalopathy
Late: Primary ovarian insufficiency, ID

High Galactose, High Gal-1-P, normal GALT activity
GALE (epimerase)
Presents similar to classic galactosemia
- MIlder biochemical variants exist
- High galactitol, + reducing substances
Tx: Low lactose/Galactose diet

High Galactose, low Gal-1-P
Galactokinase deficiency (GALK)
- Cataracts
- May have hgh calactitol and glucose (Urine)

GALT N314D
Duarte Galactosemia
~50% activity (25% when compound het with classic variant)
- Benign
GALT S135L (c.404C>T)
Variant galactosemia
- Common in African Americans
- Same neonatal presentation (Liver faliure +/- encephalopathy, infection)
- Less long term ID/ovarian insufficiency
High urine fructose after meals, no symptoms
Essential fructosuria
Fructokinase (Ketokexokinase) - KHK gene
Fructose -> F-1-P
Benign

Liver failure at 4-6 months + hypoglycemia, renal tubular dysfunction, encephalopathy
Hereditary Fructose intolerance
Aldolase B deficiency
+ Urine reducing substances, Hyperuricemia, Hypermagnesemia
+ Abnormal Transferrin isoelectic focusing and olisosaccharidosis enzymes (AGA, B annosidase) - sugars unavailable to attach
Tx: fructose restricted diet

Abnormal transferring isoelectic focusing + adult with no dental carries
Hereditary Fructose intolerance
Aldolase B deficiency
+ Urine reducing substances, Hyperuricemia, Hypermagnesemia
+ Abnormal Transferrin isoelectic focusing and olisosaccharidosis enzymes (AGA, B annosidase) - sugars unavailable to attach
Tx: fructose restricted diet

Abnormal transferrin isoelectic focusing + liver failure at 6 months
Hereditary Fructose intolerance
Aldolase B deficiency
+ renal tubular dysfunction, fructose aversion
+ Urine reducing substances, Hyperuricemia, Hypermagnesemia
+ Abnormal Transferrin isoelectic focusing and olisosaccharidosis enzymes (AGA, B annosidase) - sugars unavailable to attach
Tx: fructose restricted diet
Ketoacidosis + Lactic acidosis + hepatomegaly
UOA: high glycerol, G-3-P
Plasma TG high
Fructose - 1,6-bisphosphatase deficiency
Gluconeogensis defect
+ hypoglycemia
+ Pseudotriglyceridemia due to glycerol elevation
Can have ketoacidosis without hypoglycemia (ddx for ketolytic disorders)
- acutely responds to treatment with glucose

Ketosis AND lactic acidosis
Think about gluconeogensis defects - unable to turn pyruvate into glycose duirng fasting -> lactate and acetoacetate buildup

Glycogen storage in liver, high triglycerides
Liver GSD OR F1,6BPase deficiency
- F1P, F1,6BP, and G3P intermediates inhibit glycogen phosphorylase -> secondary GSD VI
- Pseudotriglyceridemia (2/2 high glycerol) resolves between acute episodes

What is the prognosis/management for F1,6BPase deficiency
- Some fructose can be tolerated (unlike HFI)
- Glucose infusion during acute epidoes
- improve with age as glycogen stores buildup -> less need for gluconeogenesis
GALT Q188R, K285N
Classic galactosemia variants
Q188R - Caucasian
K285N - Central europe
Hyperphosphatsia with ID
Mabry disease
Feature of GPI (glycosylphosphatidulinositol) anchor disorders

What organ systems are commonly affected in O-glycosylation disorders?
Muscle, eye, brain (congenital muscular dystrophies) and LGMD
- Alpha dystroglycan needs to be glycosylated
Dev Delay, cerebellar hypoplasia, happy disposition, strabismus, inverted nipples, suprapubic/buttock fat pads
PMM2-CDG
- Most common CDG
+ liver failure, can be hyper AND hypocoagulatble, nephrotic syndrome
+ cherubic facies, orange peel skin, esotropia, downslanting palpebral fissures
- Type I pattern on transferring isoelectric focusing
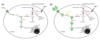
CDG with liver fibrosis, diarrhea, hypoglycemia, coagulopathy, NORMAL intellect
MPI-CDG
- Treat with mannose
Type 1 pattern on transferring isoelectic focusing

Transferrin isoelectic focusing: Elevations in 2 and 0 sialofransferring
Type 1 pattern -> PMM2 or MPI
- represent early steps when coupled sialic acids are added

What is a type 2 pattern in transferring isoelectic focusing?
high 3, 2, 1, and 0 sialotransferrin
- represent defects in processing (later steps)

Nephropathy w/ renal fanconi, short stature (hypophosphatemic rickets), myopathy, conreal crystals
Cystinosis
CTNS (lysosomal cystin transporter)
Tx - cysteamine PO and eye drops

High N-acetylneuraminic acid (Sialic acid) in urine
Finiish, Hypotonia, ataxia, MR, growth retardation, epilepsy
Salla disease
SLC17A5
Lysosomal sialic acid transporter (7 in figure)

High N-acetylneuraminic acid (Sialic acid) in urine
Infant with coarse facial features, HSM, severe dev delay
Infantile free sialic acid storage disease (ISSD)
SLC17A5 (lysosomal sialic acid transporter)
- Severe form of salla disease

High N-acetylneuraminic acid (Sialic acid) in urine
ID, dysostosis multiplex, HSM
Sialiuria
UDP-GlcNac-2-epimerase (GNE) mutation in allosteric side
- Too much sialic acid synthesis due to lack of allosteric inhibition
- Sialic acid builup in cytoplasm instead of lysosome
- # 1 in figure

Decreased muscle N-acetylneuraminic acid (Sialic acid) staining
Myopathy
GNE myopathy
UDP-GlcNac-2-epimerase (GNE) LOF
- Unable to produce enough sialic acid -> terminal o-linked sugar in alpha-dystroglycan
Tx: IVIG contains some sialic acid
Can also give mannose-6-P (Product of GNE)
- # 1 in figure

GBA N448H
Type 3 Gaucher (chronic neuronopathic form) - neurological + systemic (osteoporosis, HSM, cytopenia) w/ Cardiac valve calficiations
Cornea Verticillata, Angiokeratoma, high lysoGB3
Fabry
GLA - alpha galactosidase
- Renal, Cardiac, Stroke
+ Cornea verticillata = whorling
+ hypohydrosis
a-galactosidase B (a-N-acetylgalactosaminidase)
Schindler disease
NAGA gene
- Neurodegeneration, angiokeratoma, neuropathy, myoclonic epilepsy
What is the reproductive complication for men with cystinosis?
Testicle fibrosis -> low testosterone and azoospermia
- Fibrosis also seen in thyroid, pancreas, and other endocrine glands
- Females normal fertility (take off cysteiamine duirng pregnancy -> teratogen in mice)
What is the difference in mechanism between cystinosis and cystinuria
Cystinosis = lysosomal transport defect
Cystinuria = plasma membrane transport defect
What type of Gaucher Disease can ichthyosis be seen in?
Type 2
Which populations are at increased risk for Tay-Sachs?
Ashkenazi Jews (1:3600)
French-Canadians
Cajuns
When working up Gm2 gangliosidosis, when should you not check HexA activity in serum?
- often inconclusive in pregnancy women or women on contraceptives -> Check in leukocytes instead
- When looking for GM2AP deficiency
- In Juvenile forms when B1 variant (R178H) is present it may be fale negative
High TG, High Cholesterol
LIPA deficiency
Vacuolated WBCs, foamy histiocytes in bone marrow
Lysosomal acid lipase deficiency
Infantile: Wolman disease - HSM, FTT, malabsorption, adrenal calcifications
Adult: Cholesterol Ester Storage disease = HSM, cirrhosis, atherosclerosis
Tx: Sebelipase Alfa (ERT), statins, steroids for adrenal dysfunction
Cherry red spot, + oxysterols, elevated lyso-sphigomyelin 509
Acid-sphingomyelinase deficiency
Niemann Pick A - Cherry red spot, FTT, hypotonia, HSM, neurodegeneration
NP- B - splenomegaly, Interstitial lung disease, hypercholesterolemia
What is the difference between Niemann PIck A and Niemann PIck B?
Both have HSM and poor growth
A is severe infantile form w/ neurodegeneration
B is later onset with normal intellect. + Intertitial lung disese
Abnormal EMG, elevated CSF protein, high urine sulfatides
Metachromatic leukodystrophy
ARSA, or Saposin B
- Tigroid leukodystrophy on MRI
INfantile: 1-2yo spasticity, gait changes, regression + optic atrophy/neuropathy -> death by age 6
Juvenile/Adult - childhood cognitive + gait + ataxia
Tx: HSCT for juveile cases
Tigroid leukodystrophy on MRI + Hurler like presentation + ichthyosis
Multiple Sulfatase Deficiency
SUMF1 gene - formylglycine generating enzyme -> neessary in postranslational acivation of sulfatases including ARSA and many MPS enzymes
- Test other sulfatases if cononical genes are negative for these disorders
Extreme irritability, neuropathy, opisthotonis, hyperpyrexia
+ multinucleated macrophages
Krabbe Disease, AKA globoid leukodystrophy
Galactocerebrosidase/Galactosylceramidase (GALC) or saposin A
Multinucleated macrophage = globoid cell
Late onset form = ataxia, HSP, vision loss
Tx: early HSCT
High N-acetylaspartic acid in urine and CNS
Canavan disease
ASPA - N-acetylaspartic aciduria/aspartoacylase deficiency
NAA is normally marker of brain health and LOW in leukodystrophies, NAA is HIGH in canavan
- Macrocephaly, hypotonia + leukodystrophy
- Death by 10
Name disease with MRI pattern:
1) Posterior white matter hyperintensity
2) TIgroid with sparing of u fibers
3) Anterior leukodystrophy that moves posteriorly
1) Posterior white matter hyperintensity - XALD
2) TIgroid with sparing of u fibers - Metachromatic
3) Anterior leukodystrophy that moves posteriorly - Alexander
Heparan-N-Sulfatase
MPSIIIA - Sanfilippo
SGSH
N-acetylglucosaminidase
MPSIIIB - Sanfilippo
NAGLU
Acetyl-CoA Glucosamine N-Acetyltrasnferase
MPS IIIC - Sanfilippo
HGSNAT
N-Acetyl-glucosamine-6-sulfatase
MPSIIID
GNS
N-Acteylgalactosamine-6-sulfate sulfatase
MPS IVA - Morquio A
GALNS
ERT: Elosulfase Alfa
B-Galactosidase
MPSIVB -Morquio B (or GM1)
GLB1
Arylsulfatase B def
MPS VI - Maroteaux-Lamy
ARSB
- Dermatan and Chondrotin sulfate
- Systemic MPS
ERT: Galsulfase
B-Glucuronidase
MPS VII - Sly
GUS
Systemic MPS
Dermatan, Heparan, Chondrotin Sulfate
Tx estronidase Alfa
In which MPS are chondrotin sulfate elevated?
VI (Maroteaux lamy) and VII (Sly)
Name the MPS that goes with each ERT:
Vestronidase
Elosulfase Alfa
Idursulfase Beta
Laronidase
Idursulfase
Galsulfase
Vestronidase - VII - B-glucoronidase
Elosulfase Alfa - IVA - N-acetylgalactosamine-6-Sulfate sulfatase
Idursulfase Beta - II - Iduronte-2-sulfatase
Laronidase - I - A-L-Iduronidase
Idursulfase - II -Iduronte-2-sulfatase
Galsulfase - VI - Arylsulfatase B
Joint hyperlaxity, tilted radial epiphysis, dysostosis multifplex
MPSIV -> morquio
B-galactosidase def or N-acetylgalactosamine-6-sulfate-sulfatase
ERT: elosulfase alfa for MPS4A
Cathepsin A deficiency
Galactosialidosis
- Responsible for stablization of enzyme complex including both neuraminidase AND B-galactosidase
- MPS like disorder

Elevated Gastrin, Low HCl in gastric fluid, lysosomal inclusions
Mucolipin 1 deficiency (Mupolipidosis IV)
- abnormal trafficking of proteins and lipids into lysosome
- Corneal clouding, retinal dystrophy, pyschomotor delay
High oxalate and glycolate
Kidney stones
Primary Hyperoxaluria type 1
AGTX gene
Arginine-glycosylate aminotransferase deficiency - inability to process glyoxylate in proxisome -> glyoxylate converted into oxalate in cytoplasm -> deposition
+ renal failure
- 1/3rd of cases B6 responsive (co factor for aminotransferase)
- tx = transplant

High oxalate and L-glycerate
kidney stones
Primary Hyperoxaluria type 2
Glyoxalate reductase deficiency
- 20% get renal failure

High oxalate and hydroxyoxoglutarate
renal stones
Primary Hyperoxaluria type 3
Hydroxyoxotluratrate Aldolase 1 deficiency
- hypercalciuria
- renal railure rare

Neuropathy, hearing loss, ID, optic atrophy
Low Uric acid
Undetectable hypoxanthine
Phosphoribosylphyrophosphate synthetase deficiency
PRPS (XL)
First step of purine synthesis

High uric acid (serum and urine), high hypoxanthine
Adults: Uric acid urolithiasis, Gout
Children: SNHL, ataxia, hypotonia
Phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate synthease superactivity
PRPS (XL)
Tx: allopurinol

Psychomotor retardation, seizures, autism, ataxia, growth retardation
High succinyladenosine, high SAICA Riboside
Adenylosuccinate lyase deficiency
ADSL
- Abnormal AMP biosynthesis

Epilepsy, ID, congenital blindness, cutaneous dimples on extensor surfaces
high AICA riboside
5-Amino-4- imidazolecarboxamide Ribosiduria (AICAR-uria)
ATIC gene - AICAR formyltransferase

Myoadenylate deaminase deficiency
AMPD1 gene
- High CK, myopathy
- Normal ammonia in forearm ischemia test (cannot cleave ammonia in muscle)
- part of purine nucleotide cycle that creates fumarate (TCA intermediate) as byproduct
Tx: Ribose

High adenosine, deoxyadenosine, lymphopenia, hypogammaglobulinemia
SCID
Adenosine deaminase deficiency (ADA)
Tx; BMT, ERT, gene therapy

Low uric acid, high inosine, guanosine
ID, spasticity
Purine nucleoside phosphorylate deficiency (NP)
PNP gene
SCID + Neurological symptoms
Tx BMT

Low uric acid, high xanthine and hypoxanthine
Myopathy, arthropathy, nephrolithiasis, renal failure, hematuira
Xanthine Oxidase deficiency
XDH (dehydrogenase and oxidase same complex)
No neurological findings (seen in molybdenum cofactor deficiency)
Tx: purine redtricted diet, fluids
Uromodulin, Rennin
Hyperuricemia, low renal uric acid excretion
Familial juvenile hyperuricemic nephropathy (HNFJ)
Causes gout and renal failure
- Problem with uric acid excretion
High uric acid, hypoxanthine, and xanthine
movement disorder, epilepsy, hypotonia
Lesch Nyhan
Hypoxanthine:guanine phosphoribosyltransferase deficiency (XL)
+ self mutilation, gout, uric acid stones
Tx: allopurinol, purine restriction

High adenine, 2,8-dihydroxyadenine
Adenine phosphoribosyltransferase deficiency
APRT
- Renal stones -> renal failure
Tx: Purine restriction, allopurinol

High orotic acid
Megaloblastic anemia (unresponsive to B12 and folic acid)
Hereditary Orotic aciduria
Uridine-monophosphate synthase deficiency (UMPS)
- Megaloblastic anemia + FTT, ID
Tx: uridine supplementation

Uridine Monophosphate Hydrolase Deficiency
Pyrimidine-5’ nucleotidase deficiency
UMPH enzyme; NT5C gene
- chronic hemolytic anemia w/ basophilic stippling
- Lead toxicity inhibits UMPH

High lactate, glyoxalate
Megaloblastic anemia, Diabetes, hearing loss
Rogers syndrome
Thiamine transporter 1
SLC19A2

high lactate, glyoxalate
Fever -> leigh like illness, basal ganglia lesions
Thiamine/biotin responsive BG disease
Thiamine transporter 2, SLC19A2
- Biotin upregulates transporter expression

Amish
High lacate, glyoxalate, 2-ketoglutarate
Sever microcephaly, progressive neuropathy and BG injury
Mito Thiamine transporter deficiency

High lacatate, glyoxalate, low thiamine pyrophosphate
TPK deficiency
Thiamine pyrophosphokinase
Leigh like duirng illness + neurodegeneration

Epilepsy
High 3OMD, Low NT metabolites
high Ala, Thr, Gly, ornithine
Pyridoxiamine 5’ phophate oxidase (PNPO) deficiency
Pyridoxial phosphate-responsive epilepsy
- idential to B6 responsive epilepsy, but may also have hypotonia, prematurity, liver disease
movement disorder, liver disease, polycythemia
high Manganese levels
SLC30A10
Manganese exporter deficiency
- manganese accumulate within cells, including liver
- Cannot be excreted in bile
Tx: chelation (EDTA)

Movement disorder
High manganese
SLC39A14
Divalent metal transporter (Mn, Zn, Fe, Mag)
- No liver injury (not absorbed by hepatocyte)
Tx: Chelation (EDTA), Fe supplement

hypotonia, ID, cerebllar atrophy
Hutterite founder
Type 2 isoelectric focusing pattern
Low prolidase activity
High urine manganese
SLC39A8 Defciency
Manganese transporter
- Low serum and high urine Manganese
- Decreased reabsoprtion in kidneys
- Mn is cofactor for a glycosylation enzyme and prolidase
Rash in fingertips/toes, FTT, diarrhea at 4-6 months
- Low Zinc, low Alk Phos activity, high ammonia
Acrodermatitis Enteropathica
ZIP4 - SLC39A4
- Zinc transporter -> moves zinc into the cytoplasm
- Zinc is cofactor for OTC and Alk Phos (ddx for UCD and hypophosphatasia)
- presents after weening breastmilk
Tx: Zinc supplement -> monitor Cu levels since Zn chelates copper

Rash in fingertips/toes, diarrhea while on breastmilk
- Low Zinc, low Alk Phos activity, high ammonia
Transient neonatal zinc deficiency
maternal zinc transporter deficiency
- SLC30A2 (ZnT2) -> transports Zn into secretory vesciles in breasts
- Zinc is co factor for OTC and Alk Phos
- No zinc in breastmilk -> Deficient baby -> acrodermatitis enteropathica phenotype while breastfed

Low ceruloplasmin, high urine Cu, high liver Cu
Wilson’s
ATP7B
- Decreased biliary Cu excretion, decreased incorporation of Cu into ceruloplasmin (stable form in blood)
- Blood Cu levels not useful in Dx; usually low
Tx: Chelation (Penacillamin, Trientine, Zinc)

Subdural hematoma, easy bruising, fractures, hair changes, CNS changes
- Low serum copper and ceruloplasmin
Menke’s
ATP7A
- Unable to absorb Cu from enterocytes -> deficiency
- Labs may be normal before 3 months of age
- Adult variant = occipital horn disease and motor neuropathy
- May mimic child abuse (SDH, fractures, bruising)
Tx: Copper-Histidine injection

Low T3 with high T4, high TSH
SNHL, DD, myopathy
Low selenium
Selenocysteine synthesis disorder
SBP2 protein (SECISBP2)
- necessary for itodothyorine deiodeinase (converts T4 to T3)
- Selenocysteine is synthesized from serine (OH changed for SeH on tRNA)

Progressive cerebello-cerebral atrophy
- low selenium
Disorder of selenocysteine synthesis
SEPSECS
- Selenium is coded for by UGA stop codon + downstream secondary structure element

HSM, cirrhosis, hepatocellular carcinoma, arthropathy, cardiomyopathy, hypogonadism, DM, hyperpigmentation
C282Y
Classic HFE
- reculator of cellular iron uptake vis transferrin receptor 1
- May be compound het with H63D
HFE G320V
Severe Iron overload before age 30, cardiomyopathy, abd pain, cirrhosis, hypogonadism, arthropathy
Juvenile hemachromotosis
- May also be HAMP (Hepcidin mutation) or HJV (Hemojuvelin)
High ferritin, normal transferrin
liver fibrosis, microcytic anemia
Hemochromatosis type 4
SLC11A3
- Iron accumulation in liver and spleen due to transporter defect
Tx: Phlebotomy, deferoxamine (same as classic hemochromatosis)
Low ceruloplasmin, Low copper, Low Iron
Diabetes, retina degenration, dementia, parkinsonism
Aceruloplasminemia
CP gene
- Deficient cerupomasmin (ferroxidase)
Tx: IV ceruloplasmin
Which 2 disorders of BH4 metabolism have NORMAL phe
AD GTP Cyclohyrdrolase and Sepiapterin Reductase

Musty Odor
PKU
Liver failure, high AFP, High ferritin, low transferrin in neonate
Neonatal Hemochromatosis
- Autoimmune disease
- May present as hydrops
Hypoglycorrhachia
GLUT1 deficiency
SLC2A1 (AD)
CNS glucose transporter
Hypoglycorrhachia = low CSF glucose
CSF/Blood glucose ratio <0.45, low lactate/alanine
- Seizures/Kinesiogenic movement disorder that respond to ketogenic diet

Sleep disturbance + behavior changes + coarse facies
MPSIII San Filippo
ACSF3
High MMA
CMAMMA
- Acyl-CoA Synthetase
- Deficiency leads inability to conjugate to carnitine -> thus ACP will be normal
What test can help find low excreter GA1?
urine acylcarnitines (C5DC), molecular testing
BCAA Ratio in MSUD and normal
Normal: Val:Leu:Ile 4:2:1
MSUD: Leu:Val:Ile
Which AA synthesis disorders result in:
Cutis Laxa
Neu Laxova
Hyperammonemia with low glutamine
Hyperkeplexia
Cutis Laxa - Proline synthesis
Neu Laxova - Serine synthesis
Hyperammonemia with low glutamine - Glutamine synthesis
Hyperkeplexia - Aspargine synthesis
Acetoacetic acid and 3-OH butyric acid
These are the most common ketones founds in urine
elevation = ketone elevation

When do you need leukocyte sample to test for Tay Sachs
Pregnant women and women on oral contraceptives
- Serum enzyme activity often inconclusive
high cholesterol, high phytosterols, high sitosterols
Sitosterolaemia
Twinnned sterol transporter deficiency (ABCG5, ABCG8)
- Increased absorption/decreased biliary excretion of plant/fish sterols
- Dietary treatment
Triglycerides > 500mg/dl
Familial chylomicronemia
Lipoprotein lipase (LPL) or ApoCII (APOC2) - both AR
Unable to break down chylomicrons/VLDL
- Tx: low fat diet, aphoresis, can supplement ApoC2 in FFP

High TG and cholesterol
Familial dysbetalipoproteinemia
APOE -> deficient IDL/remnant uptake in liver
- treat like metabolic syndrome

Low HDL, low ApoA1, normal TG/cholesterol
Atheroscleoriss, xanthomas, corneal clouding
Apolipoprotein A1 deficiency
APOA1 (AD)
- Risk factor for atherosclerosis

Low HDL, low ApoA1, high TG, normal/low cholesterol
Neuropathy, HSM, corneal clouding, CAD
Tangier disease
ABCA1 - distubed intracellular transpot of cholesterol esters in macrophages
+ Faom cells, orange tonsils

low HDL, low ApoA1, high TG, free/total cholesterol >0.7
nephropathy, anemia, “fish eye disease”
Lecithin Cholesterol acyltransferase deficiency
LCAT (AR)
- Fish eye = isolated corneal clouding

Name 3 disorder with low HDL and ApoA1
Apolipoprotein A1 deficiency - deficient APOA1 - normal TG and cholesterol
Tangier Disease (hypoalphalipoproteinemia) - ABCA1 (intracellular cholesterol ester transporter) - high TG, low cholesterol + Orange Tonsils
Lecithin Cholesterol acyltransferase deficiency - LCAT - high TG, free/total cholesterol <0.7 - nephropathy, anemia, “fish eye”

Low cholesterol and TG, no/low ApoB, acnthocytes
neuropathy, ataxia, retinopathy, myopathy, diarrhea
Familial abetalipoproteinemia
- Microsomal TG transfer protein (MTTP) - AR
- ApoB deficiency (familial hypobetalipoproteinemia) is milder and semidominant
- Deficient TG transporter into ER -> deficient ApoB containing lipoproteint -> cannot transport fat-soluble vitamines/erythrocyte dyfunction
- Fat malabsorption, VitE deficiency (neuropathy, ataxia, retinopathy, myopathy)
- Tx - low fat diet, Vit E supplement

Low cholesterol and TG, low ApoB and ApoA1
Fat droplets in enterocytes
Chylomicron retention disease
SAR1B -> intracellular chylomicron trafficking in enterocytes
- Fat malabsportion, FTT, vitamin deficiency

Name 3 diseases with low TG and cholesterol
FTT, malabsorption, and vitamin deficiency
Famillal abetalipoproteinemia - Micorsomal TG transfer protein (MTTP, AR) -> deficient apoB lipoprotein production -> low apoB, acanthocytosis
Familial hypobetalipoproteinemia - ApoB gene (semi Dominant) -> deficient ApoB production -> low ApoB, acanthocytosis - Milder than MTTP
Chylomicron Retention disease - SAR1B -> intracellular chylomicron trafficking in enterocytes - low apoB and apoA1; fat droplets in enterocytes

sterol 27 hydroxylase
CTX
sterol27 hydroxylase
high cholestanol


