FUN4/Lipids Flashcards
a fatty acid is a _____ _____ chain with a terminal ____ group
hydrophobic, hydrocarbon, carboxyl
2 types of fatty acids
unsaturated and saturated
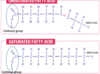
A __________ means that the two hydrogen atoms adjacent to the double bond stick out on the same side of the chain.
cis configuration

eicosanoids are poly__________ FAs with ____ carbons
unsaturated, 20
prostaglandins (PG) are synthesized from _____ acid via _____
arachidonic, cyclooxygenase(COX)
PG’s are _____, but have a short half life,
potent/strong
half life of PGs
seconds
what are the roles of PGs
inflammatory, platelet homeostasis
PG’s are _______ FAs
signalling
Leukotrienes are _____ FAs
signalling
leukotrienes are part of the _____ family
eicosanoid
Leukotrienes are synthesized from ______ acid via ______
arachidonic, lipoxygenase (LOX)
leukotrienes have a (longer/shorter) half life than prostaglandins
longer
half life of leukotrienes
4 hours
what are the roles of leukotrienes
inflammatory, neutrophil adhesion
4 classifications of lipids
FAs and their derivatives, lipids with glycerol, lipids without glycerol, lipoproteins and lipopolysaccharides
2 types of fatty acids
prostaglandins and leukotrienes
what are the lipids containing glycerol

what are lipids that dont contain glycerol
steroids and sphingolipids
3 main functions of lipids
energy, strucutre, cellular signaling
which lipids are involved in cellular signaling events
steroids, prostaglandins, leukotrienes
triglycerides are the ____ in our bodies
fats
a triglyceride is made up of ______
a glycerol and 3 fatty acids
what type of tissue are triglycerides stored in
adipose tissue
triglycerides are also called
triacylglycerols (TAG)
Diacylglycerols function as _____ and _______
cell signaling within the cell, mobilization of calcium
__________ is a breakdown product of TAG in fat digestion
monoacylglycerol
describe the structure of a phospholips from top to bottom
choline, phosphate, glycerol, FAs

a sphingolipid is a _____ + _____ + ______
sphingosine, FA, R group

fill in the chart


fill in the chart


fill in the chart


fill in the chart


FAs attached to certain ______ to enhance the ability of those _____ to associate with membranes
proteins/proteins
FA’s are _______ of the hormone-like prostaglandins
precursors
_______ fatty acids, the form of TAGs stored in ______adipose tissue, serve as a major storage of energy in body
esterified, white
changes in FA metabolism are associated with ___ and _____
obesity, diabetes
FAs can exist freely in the body in 2 ways…. what are they?
unesterified, fatty acyl esters
fatty acyl esters can be found in more complex molecules like ____
triacylglycerols (TAGs)
Plasma free fatty acids (FFA’s) are transported on ______
serum albumin
lipopolysaccs are found in the outer membrane of gram-_______ bacteria
negative
cholesterol is broken down to make ___, ___, and ______
vitamin d, bile acids, steroid hormones
steroids have a ___ or ___ on carbon 3
hydroxyl or keto
number of carbons for cholesterol, bile acids, progesterone/adrenocorticals, androgens, estrogens respectively
27, 24, 21, 19, 18

lipoproteins are particles that _____ lipids
transport
the core of lipoproteins is hydro______ and they are full of ____ and _____
hydrophobic, triacylglycerides, cholesteryl esters

LPS act as ______
endotoxins
LPSs help with a strong ______ response in humans
immune
terpenes are also called
isoprenoids
there are about ________ compounds of terpenes
50,000
terpenes are organic compounds that are composed of ___ hydrocarbon units
2
terpenes are very common in the ______ kingdom
plant
terpenes function as _______ (3)
pigments, molecular signals, and defensive agents
terpenes are used in ____
perfumes!!
essential fatty acids (EFAs) are nutrionally essential but we cannot _______ them
synthesize
what are the 2 types of EFAs?
linoleic acid (omega 6) and alpha-linoleic acid (omega-3)
are EFA deficiencies rare or common
rare
what are the 2 types of EFA deficiencys called
scaly dermatitis/ichthyosis, visual and neurologic problems
know this chart

label 1-5


energy is produced in the ___ and ____ states
fed, fasting
deviating lipid metabolism is called _______
ketoacidosis
ketoacidosis can cause diseases such as ________
diabetes mellitus, esp type 1
medium chain acyl CoA dehydrogenase (MCAD) is involved in ___________
mitochondrial fatty acid Beta oxidation
MCAD fuels _________
hepatic ketogenesis
what is hepatic ketogenisis?
once hepatic glycogen storage depeltes, this acts as a source of energy during long fasts or peroids of high energy demand
MCAD deficiency is autosomal _______
recessive
MCAD deficiency is a condition that prevents the body from converting certain ______ to ____
fats to energy
what are the main clinical signs of an MCAD deficiency
cant fast for a long time, hypoglycemia, impaired ketogenesis, reccurent episodes of hypoglycaemic coma
how to manage an MCAD deficiency
avoid fasting, glucose supplements


