Full blood count Flashcards
abnormal results
- Outside the normal range
normal range only includes
- 95% of healthy population
- 2.5% normal values above the range
- 2.5% normal values below the range

results just outside the range may be
normal for that person
Significant fall in value
e.g. 160g/L to 115g/l (both in normal ranges- but still worrying)
nromal rnage changes with
- Age
- Sex
- Ethnicity
- Co-morbidities
If you receive an a result you are not expecting….
repeat test and consider contacting haematologist
interpret abnormal haematology results in light of
clnical context and previous FBC
e.g. to spot acute/chronic change
sources of error
- speciment collection error
- delivery of speicimens to laboratory
- specimen analysis and result reporting
- responsive action
1) Specimen collection error
- Specimen mixed up
- Wrong blood in tube
- Wrong bottle
- Pooling samples
- Adding blood from another tube to fill one up to the line
- Poor technique- may activate (haemolytic) sample
2) Delivery of specimens to laboratory
- Specimen delayed/not delivered
- Wrong delivery method
- Some need to be sent in the dark, on ice, body temp
3) Specimen analysis and result reporting
- Specimen mix up
- Incorrect clinical details
- Wrong test requested/performed
- Inherent test variability
- Technical error
4) Responsive action
- Results not reviewed
- Reflex tests not carried out
- Right result applied to wrong patient
how is the full blood count carried out
Measured using an automated test with a very high level of accuracy that uses an analysing machine that can process thousands of samples every day.
essential parameters of the FBC
-
Red blood cells
- Indices
- RCC
- haemoglobin
- Platelet count
-
White blood cells
- Count
- Full differential
FBC ANALYSER TECHNIQUE
uses Flow cytometry
- hydrodynamic focusing
- single file line of cells
- pass through light beam
- impedance counting
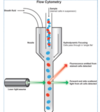
forward scatter=
size
the more scatter= the bigger the cell

Spectrophotometry
*
- Amount of light absorbed by the sample proportional to amount of absorbent compound within it e.g. haemoglobin
- Hypotonic solution to lyse cells
- Use light of appropriate wavelengths
- Use calibration curve to determine sample conc
Flow cytometry differential
- Forward scatter= size
-
Side scatter
-
Mono/polymorphonuclear
- A type of immune cell that has granules (small particles ) with enzymes that are released during infections, allergic reactions, and asthma
-
Intracellular complexity
- Granules
- Myeloperoxidase activity
-
Mono/polymorphonuclear

what are WBC
also known as leukocytes, WBC are cells of the immune system that are responsible for protecting the body againsdt infections or foreign bodies
how are WBCs counted
RBC in a sample of blood are lysed and the majority of remaining cells are WBC.
These are counted automatically as they interrupt a beam of light/ elecrcial current whilst going through a narrow tube in a straight line
what causes an increase in WBC
infection, smoking, leucocytosis, immune system disorders
what causes a decrease in WBC
damaged bone marrow, antibiotics, chemothrrapy drugs
Red blood cells contain
haemoglobin, which gives blood its red colour. The primary role is to transport oxygen and carbon dioxide to and from tissue
how are RBCs measured
measured in the same way as WBC Clight beam) but withou the lysis step.
In comparision to BRC there are very few WBC so it does not affect the RBC count signif



