foot Flashcards
where is dorsalis pedis artery palpated
between the tendons of the hallucis logus and extensor digitorium longus to the second toe
what is dorsalis pedis a continuation of
anterior tibial artery
what is structure is more deppeis from the ovelrying skin of the popliteal fossa
poplieal artery is the deepest thing in the popliteal fossa
whats superfical in the popliteal fossa (more superfical to the popliteal artery
the polital vein, tibila and common peroneal nerves and short saphernous vein
what muscle prevents against this

vastus medialis
what are the bones of the foot
tarsal bones = 7 irregualr shaped bones proximal aspect of the foot
meta tarsals = 5 metatarsals one for each toe connect the phalanges to the tarsal bones
phalanges
bones of the toe, 2/3 (proximla, middle and distal) except big toe wc onl has 2
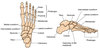


what are the regionsof the foot
hindfoot = talus and calcaneus
midfoot = navicaular , cuboid and cunieforms
forefoot = metatarsals and phlanges
describe the talus
- the most superior bone of the foot and has 3 articualtions
- superiorly = ankle jonint between teh alus tbia and fibula
- inferiorly subtalar joint bw it and the calcaneus
- anteriorly talonavicular joint bw it nd the navlaular
- F = transmit forces rfi the tibia to the calcanoeus (eheel bone)
- the trochlear portion of the talus is the region wc articualtes with the tibia and fibula
- wider anteriorly compared with posterioly and this shape provides addition stability to the dorsiflexed ankle
*
- wider anteriorly compared with posterioly and this shape provides addition stability to the dorsiflexed ankle
what is attathced to the talus?
no muscles just ligaments
this ameans that theres a hgih chage of avascualr necrosis that can occur if taus is fracturesd sicne the b. suply is aslo retrograde just like the scaphoid boen fo the hand
describe the calcaneus
infeior to the talus and is part of the subtlr join
aka heel bone
anteriorly articulaiton = calcaneocuboid joint bt it and cuboid
funtion is take the full weightof the body and thats why is protrudes posteriorly whe the heel touches the ground . this is the calcaneus tuberosity and is whete the Achillies tendon attaches
proximal row of the tarsal bones
tlaus and calcaneus
intermediate row of the tarsal bones
navcualr ( taonavilcaur joint
cuboid (calcaneocuboid joint)
navicular bone
wc artiualtes with the with talus bine in the talonavilaur joint but it also articualte with the cuneiform bones anterirly wc then articualte with the metaatarsal there are
it also articualtes wit the cunodial bone laterlly
ot as a tuberoisty wc is the insrtion of th etibialis posterioe tendon

describe the distal row of tarsals
cuneiforms and the cuboidal
cuboidal articualtes with teh calcanueus posteriorly and medialy with tehlateral cuneiorm and anteoroly with the 45metatarsal
it has a groove fro the tendon of penoneus (fibularis ) lngus
whats special about the cunieforms
tibialis psoterior and peroneus (fibularis) longus and tibilais anteior all insert into the medial cuneiform
joint betwent the met and tarsal? and tarsals and adjascent meta ta and meta tar and proximal phal
phalanx = mtatarsophlangea;
adjacent =intermetarsal
tar and met = tarsometatarsal
describe the ankle joint
hungje joint allowing for dorsiflexion and plantar felxion
tibular and fibular held ogether bu the tijiofibuilar ligaments at distal tiiofiilar joint , together they form a mortise, a breacket sahped socket wehre the trochlea of the talus fits into

what movements are permitted bu the ankklejoint and what movements are strogner and why
dosriflexion andplantarfelxion
the anterior trochlaerof the tlaus is broader than the posterior
so disoriflexion the antior aspect is held well in teh mortise and so more stable but opppste in teh plantflexion becaue tht eposteior trahoclar is more narrow =less tbale
what muscles contribute to dorsiflexion
anterior compartment of the leg
tibilais anteirr, extensor halluics longus, extensor digitorium lingus and pectoneus tertius
what limitesdisriflexion
the mucles fo the posterior compartment
describe the anterior compartemen of the leg
tiilais anterior, extensor digitorium lognus , extensor hallucis lgus , peroneus tertius
f = dorsiflexionand invert the footat ankle joint
but the extensors an also extend the toes
IN = deep peroneal nerve
B = anterior tiial artery

tibilalis anterior
strongest in dorsiflexion adn to test ask patiet to stand on their heels with the forefoot raised offthe ground
O= lateral surface of the tibia
I= medial cuneiform ad base of 1st meta
F = dorsiflexion and inversion of foot
IN = deep peroneal nerve
B = anteiror tibial artery
extensor digitorium longus
lateral to adn deep to the tibilais anteriorm but you can palpate the tendon on the dorsum of the foot
O = lateral condyle of the tibia and medial surface of the fibuka,the fibres then converge into 1 tendon wc passes deeo to the extensor retinacula of the ankle, wc splits into tendons on dorsum of the foot
I = middle and distal phalanges of the 2-5th toe
F = dorsiflexion adnd extension of the toes
IN =deep fibular nerve
b+ anteiror tibial artery




