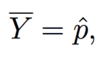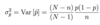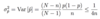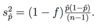Finite Population Sampling Flashcards
(33 cards)
Give two reasons why people choose to sample.
- Cheaper and faster than full census (could be impossible)
- May be more accurate (when census’s get too large quality control is harder)
What does N stand for?
Number of inidividuals in the population
What does xi stand for?
The value of x for individul i
What does θ stand for?
Population parameter, function of the population values.
Name four population parameters.
- Population average
- Population total
- Population variance
- Population standard deviation
What is the equation for population average?
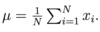
What is the equation for population total?
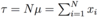
What is the equation for population variance?
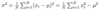
What is the difference between N and n?
- N - Population size
- n - Sample size
What is the number of possible samples, when using a simple random sample without replacement?

Define a statistic.
A statistic is any function of the sample observations.
Define a sampling distribution.
The sampling distribution of a statistic is:
- the set of possible values that the statistic can take
- the probability that the statistic takes each values
Are samples with smaller or larger variacnes more reliable?
Smaller
What is the difference between Ȳn and 𝜇?
- Ȳn is the sample average
- 𝜇 is the population average
Prove 𝔼(Ȳn) = 𝜇.

What does 𝔼(Ȳn) = 𝜇 show?
The sample mean is an unbiased estimator for the population mean.
Define bias and therfore unbiased.
If statistic S estimates population parameter θ, then the bias of S is
b(S, θ) = 𝔼(S) - θ
If the bias is zero, then S is called unbiased.
What does σȲn stand for?
Standard error of estimator Ȳn.
Prove
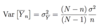
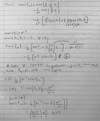
When N >> n what can you say about this inequality?


For large N what does var(Ȳn) approximately equal?
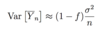
What does f stand for in this equation?
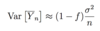
f is the sampling fraciton, n/N
What is the equation for sample variance?

What does sȲ stand for?
Estimated standard error of Ȳ