Final; Intraoral Radiographic Anatomy Flashcards
This is located palatal to incisors, pear-shaped opening; nasopalatine nerves and vessels

incisive foramen

incisive foramen
This leads to the incisive foramen; radioopaque margins, radiolucent center

incisive canal
This is a palatal radiolucent line between two processes running posteriorly from alveolar crest

median palatine suture

median palatine suture
This is a “V” shaped projection present in midline apical and central incisors; radiopaque

anterior nasal spine

anterior nasal spine
nasal cavities

alar cartilage
This appears more radiolucent than surrounding bone; adjacent to border of nasal bone

canine fossa
This is an air-containing cavity in maxilla, margins are made by a thin layer of dense bone

maxillary sinus
The anterior border of the maxillary sinus often intersects a line formed by what
floor of nasal fossa
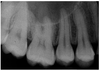
maxillary sinus involving roots of maxillary premolars and molars
This cheek bone extends laterally from maxilla over the roots of maxillary posterior tooth
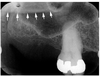
zygomatic arch

zygomatic bone
This is an important landmark in determining the posterior boundary of upper denture; marks the posterior limit for molar periapical image receptor placement

maxillary tuberosity
This is a hook-like process arising from the inferior tip of the medial pterygoid plate
pterygoid hamulus
This is the insertion point for temporalis and masseter muscles, form anterior boundary of mandibular or sigmoid notch; often overlaps maxillary tuberosity; area appears radiopaque

coronoid process of mandible


coronoid process

inferior border of the mandible

lower lip line

soft tissue of chin; depression from lower lip to superior chin
radiolucent area overlying mandibular incisors
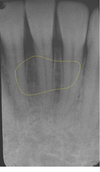
labial depression
This allows for passage of arteries branching from sublingual artery

lingual foramen