Final... Flashcards
(106 cards)
1
Q
Exponential Attenuation
A
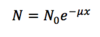
2
Q
Types of Attenuation Coefficients
A

3
Q
Energy Transferred
A
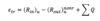
4
Q
Net Energy Transferred
A
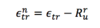
5
Q
Energy Imparted
A
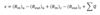
6
Q
Kerma
A
Units: Gy or J/kg
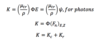
7
Q
Collision Kerma
A
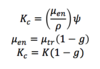
8
Q
Absorbed dose (D)
A
Units: Gy or J/kg

9
Q
Exposure (X)
A
Units: C/kg or R
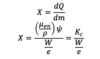
10
Q
Dose Equivalent (H)
A
Units: Sv or rem
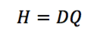
11
Q
Effective Dose Equivalent
A

12
Q
Number of Photon Interactions (n)
A
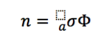
13
Q
Mean Free Path or Relaxation Length
A
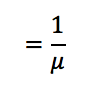
14
Q
Buildup Factor (B)
A

15
Q
Conditions required for Radiation Equilibrium (RE)
A
- The atomic composition of the medium is homogeneous
- The density of the medium is homogeneous
- The radioactive source is uniformly distributed
- There are no electric or magnetic fields present to perturb the charged-particle paths, except the fields associated with the randomly oriented individual atoms
16
Q
Conditions required for Charged Particle Equilibrium (CPE)
A
- The atomic composition of the medium is homogeneous
- The density of the medium is homogeneous
- There exists a uniform field of indirectly ionizing radiation (the rays must be only negligibly attenuated by passage through the medium)
- No homogenous magnetic or electric fields are present
17
Q
CPE
A
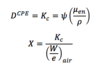
18
Q
Causes for CPE failure
A
- Inhomogeneity of atomic composition within volume V
- Inhomogeneity of density within volume V
- Non-uniformity of indirectly ionizing radiation within volume V
- Presence of a non-homogenous electric or magnetic field in V
19
Q
Transient Charged Particle Equilibrium (TCPE)
A

20
Q
Interactions of Photons with Matter
A

21
Q
Photoelectric
A
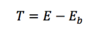
22
Q
Compton
A
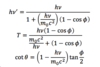
23
Q
Pair and Triplet Production
A

24
Q
Photonuclear
A
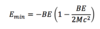
25
Flourescence yield
The fluorescence quantum yield gives the efficiency of the fluorescence process. It is defined as the ratio of the number of photons emitted to the number of photons absorbed.
26
Q\_max equation
Know Derivation!
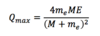
27
Q\_max for different particles

28
Ratio of Radiative to Collisional Stopping Power
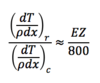
29
Critical Energy
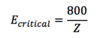
30
Radiation Yield
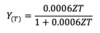
31
Range Straggling
for statistical reasons, particles in the same medium have varying path lengths between the same initial and final energies.
32
CSDA Range
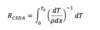
33
Assumptions made in Dose Calculation

34
Light Charged Particle definitions for Dose

35
Energy Absorbed in Thin Slab (Light Charged Particles)
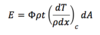
36
Dose due to Light Charged Particles (thin slab)
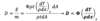
37
Dose due to Light Charged Particles with Energy Spectrum (thin slab)
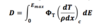
38
Radiation Length (thin slab)
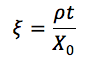
39
Dose due to Heavy Charged Particles (thin slab)
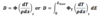
40
Light Charged Particle in thick slab energies
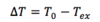
41
Radiation Yield

42
Energy spent in collisions (thick slab)

43
Light Charged Particles in Thick Slab energies corrected

44
Dose in thick foil due to light charged particle

45
Energy imparted to thick foil by light charged particles

46
Heavy Charged Particle Thick Slab Residual R\_CSDA

47
Heavy Charged Particle Energy left over thick slab

48
Heavy Charged Particle Dose in Thick Foil

49
Electron Backscatter
* When incident to a material, electrons backscatter due to nuclear elastic interactions which reduces dose near the surface. This effect is large for materials with high Z, low T0 and thick slabs.
* We need to correct for this in thick foils, but not in thin foils.
* Infinitely Thickness, ∞ - the maximum thickness, that an electron can backscatter; For electrons, this thickness is half of the maximum penetrating depth, tmax/2
50
Electron Energy Backscattering Coefficient

51
Backscattering electron number

52
Maximum Scatter angle of Bremmstrahlung
53
Bremsstrahlung Production
Proportional to Z^2 and inversly proportional to A
54
Energy Transfer Derivation

55
Relativistic Case Energy Transfer

56
Linear Stopping Power
The rate of energy loss per unit path length by a charged particle in a medium

57
Mass Stopping Power
Dividing the Linear Stopping Power by the density of the medium

58
Two Types of Stopping Powers

59
Radiative Stopping Power

60
Bethe Mass Collision Stopping Power Approximation

61
Mean Ionization Potential of the Medium

62
Relationships to Bethe Formula

63
Corrections to Bethe's Expression

64
Bethe Corrected Equation

65
Range vs Projected Range

66
Range for Particles

67
Stopping Time

68
Bragg Curve

69
Ionization Constant

70
Dose in the gas

71
Assumptions in Cavity Theory
* The cavity is thin so that its presence does not perturb the charged particle field.
* Charged particles originating in the cavity don’t contribute to the absorbed dose in the cavity.
72
Bragg-Gray Cavity Theory Assumptions
* The scattering properties do not change for heavy particles and electrons
* Charged particles that enter the cavity were generated elsewhere
* Charged particles could originate in the wall from indirectly ionizing radiation
* Charged particles do not stop in the cavity
* The density of gas is very low compared to the solid
73
Bragg-Gray Cavity Theory can be applied for
* Charged particles entering from outside the vicinity (high energy charged particles)
* Charged particles generated inside the wall from gamma rays or neutrons
74
General Equation for Dose in a medium

75
Derivation of Cavity Theory Pt. 1

76
Derivation of Cavity Theory Pt. 2

77
Derivation of Cavity Theory Pt. 3

78
Conclusions and Comments on B-G Cavity Theory

79
First Corollary of B-G relation

80
Second Corollary of B-G relation

81
Cavity Theory Example

82
Spencer Derivation Assumptions
* N identical particles emitted per gram, each with kinetic energy T0
* CPE exists at cavity
* Bremsstrahlung radiation is neglected
83
Dose and Flux in Spencer Derivation

84
Spencer Derivation Pt. 1

85
Spencer Derivation Pt. 2

86
Spencer Derivation Pt. 3

87
Spencer with Bremsstrahlung

88
Averaging of Stopping Powers

89
Estimating the mass collision stopping power

90
Why use Spencer?

91
Size Parameter Delta

92
Equilibrium spectrum including delta rays

93
finding R(T,T0)

94
Spencer using R(T,T0)

95
Contrast between Spencer and B-G

96
Ultracold Neutrons

97
Very Cold Neutrons

98
Cold Neutrons

99
Thermal Neutrons

100
Epithermal Neutrons

101
Fast Neutrons

102
High Energy Neutrons

103
Energy Transferred to a nucleus from neutron

104
Energy Transferred in Neutron Units

105
Neutron Energy after collision

106
Neutron Spallation
Spallation occurs when a fast neutron n penetrates the nucleus and adds sufficient energy to the nucleus so that is disintegrates into many small residual components such as alphas and protons


